
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Robin Hood, by Joseph Ritson
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
Title: Robin Hood
A collection of all the ancient poems, songs, and ballads,
now extant, relative to that celebrated English outlaw.
To which are prefixed historical anecdotes of his life.
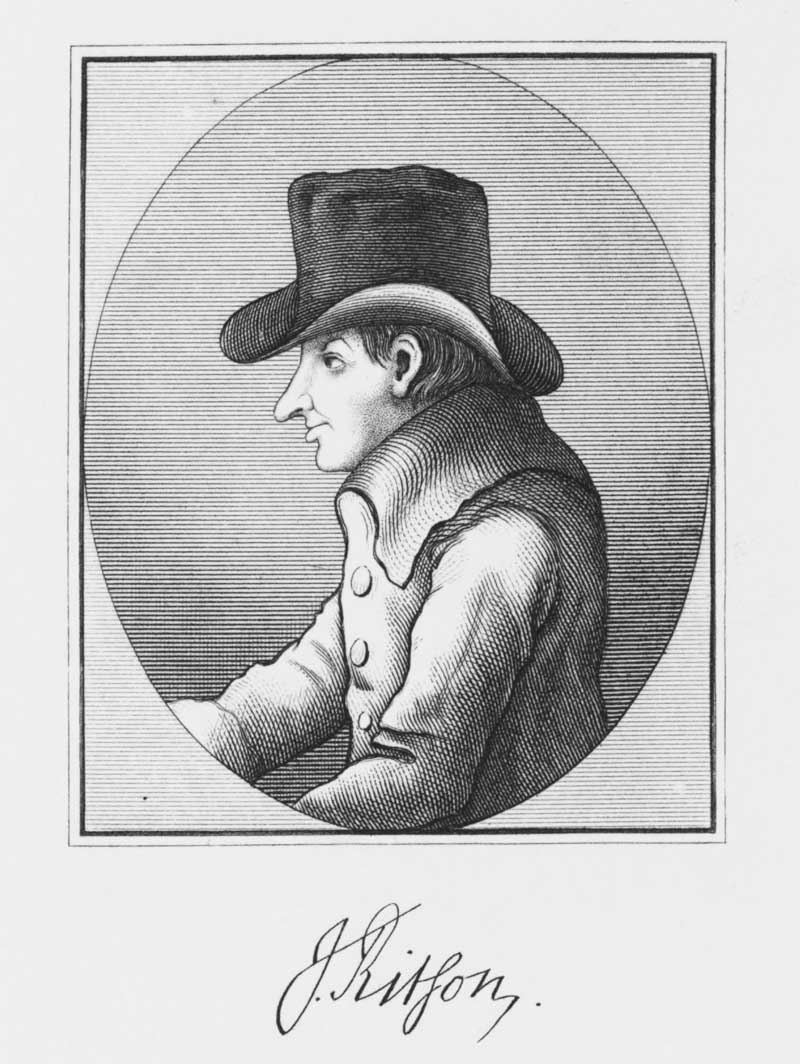
Author: Joseph Ritson
Illustrator: Thomas Bewick
A.H. Tourrier
E. Buckman
Release Date: April 5, 2018 [EBook #56926]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK ROBIN HOOD ***
Produced by MWS, RichardW, and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net. Music transcribed
by Linda Cantoni. (This file was produced from images
generously made available by The Internet Archive.)

Of this fine Large Paper Edition one hundred copies are printed, each being numbered.
The portrait and nine etchings are given in duplicate, one being printed on Whatman paper and the other on Japanese.
No. 61



THIS edition of ROBIN HOOD is printed from that published in 1832, which was carefully edited and printed from Mr. RITSON’S own annotated edition of 1795.
The original wood engravings, by the celebrated THOMAS BEWICK, have been again used; and from being printed on China paper, will be found superior in clearness and beauty to the first impression.
The nine etchings now given have been newly etched from original pictures painted by A. H. TOURRIER and E. BUCKMAN.


 HE
singular circumstance that the
name of an outlawed individual of
the twelfth or thirteenth century
should continue traditionally popular,
be chanted in ballads, and, as one may say,
HE
singular circumstance that the
name of an outlawed individual of
the twelfth or thirteenth century
should continue traditionally popular,
be chanted in ballads, and, as one may say,
at the end of the eighteenth, excited the editor’s curiosity to retrieve all the historical or poetical remains concerning him that could be met with: an object which he has occasionally pursued for many years; and of which pursuit he now publishes the result. He cannot, indeed, pretend that his researches, extensive as they must appear, have been attended with all the success he could have wished; but, at the same time, it ought to be acknowledged that many poetical pieces, of great antiquity and some merit, are deservedly rescued from oblivion.
The materials collected for the “Life” of this celebrated character, which are either preserved at large or carefully referred to in the “Notes and Illustrations,” are not, it must be confessed, in every instance, so important, so ancient, or, perhaps, so authentic, as the subject seems to demand; although the compiler may be permitted to say, in humble second-hand imitation of the poet Martial:
Desirous to omit nothing that he could find upon the subject, he has everywhere faithfully vouched and exhibited his authorities, such as they are: it would, therefore, seem altogether uncandid or unjust to make him responsible for the want of authenticity of such of them as may appear liable to that imputation.

 T
will scarcely be expected that one should
be able to offer an authentic narrative of
the life and transactions of this extraordinary
personage. The times in which he lived, the
mode of life he adopted, and the silence or loss of
contemporary writers, are circumstances sufficiently
favourable, indeed, to romance, but altogether inimical
to historical truth. The reader must, therefore,
be contented with such a detail, however scanty or
imperfect, as a zealous pursuit of the subject enables
one to give; and which, though it may fail to satisfy,
may possibly serve to amuse.
T
will scarcely be expected that one should
be able to offer an authentic narrative of
the life and transactions of this extraordinary
personage. The times in which he lived, the
mode of life he adopted, and the silence or loss of
contemporary writers, are circumstances sufficiently
favourable, indeed, to romance, but altogether inimical
to historical truth. The reader must, therefore,
be contented with such a detail, however scanty or
imperfect, as a zealous pursuit of the subject enables
one to give; and which, though it may fail to satisfy,
may possibly serve to amuse.
No assistance has been derived from the labours of his professed biographers (1);1 and even the {ii} industrious Sir John Hawkins, from whom the public might have expected ample gratification upon the subject, acknowledges that “the history of this popular hero is but little known, and all the scattered fragments concerning him, could they be brought together, would fall far short of satisfying such an inquirer as none but real and authenticated facts will content. We must,” he says, “take his story as we find it.” He accordingly gives us nothing but two or three trite and trivial extracts, with which every one at all curious about the subject was as well acquainted as himself. It is not, at the same time, pretended, that the present attempt promises more than to bring together the scattered fragments to which the learned historian alludes. This, however, has been done, according to the best of the compiler’s information and abilities; and the result is, with a due sense of the deficiency of both, submitted to the reader’s candour.
ROBIN HOOD was born at Locksley, in the county of Nottingham (2), in the reign of King Henry the Second, and about the year of Christ 1160 (3). His extraction was noble, and his true name ROBERT FITZOOTH, which vulgar pronunciation easily corrupted into ROBIN HOOD (4). He is frequently styled, and commonly reputed to have been, EARL OF HUNTINGDON; a title to which, in the latter part of his life, at least, he actually appears to have had some sort of pretension (5). In his youth he {iii} is reported to have been of a wild and extravagant disposition; insomuch that, his inheritance being consumed or forfeited by his excesses, and his person outlawed for debt, either from necessity or choice, he sought an asylum in the woods and forests, with which immense tracts, especially in the northern parts of the kingdom, were at that time covered (6). Of these, he chiefly affected Barnsdale, in Yorkshire, Sherwood, in Nottinghamshire, and, according to some, Plompton Park, in Cumberland (7). Here he either found, or was afterward joined by, a number of persons in similar circumstances—
“Such as the fury of ungovern’d youthThrust from the company of awful men,” (8)
who appear to have considered and obeyed him as their chief or leader, and of whom his principal favourites, or those in whose courage and fidelity he most confided, where Little John (whose surname is said to have been Nailor), William Scadlock (Scathelock or Scarlet), George a Green, pinder (or pound-keeper) of Wakefield, Much, a miller’s son, and a certain monk or frier named Tuck (9). He is likewise said to have been accompanied in his retreat by a female, of whom he was enamoured, and whose real or adopted name was Marian (10).
His company, in process of time, consisted of a hundred archers; men, says Major, most skilful in battle, whom four times that number of the boldest fellows durst not attack (11). His manner of recruiting was somewhat singular; for, in the words of an {iv} old writer, “whersoever he hard of any that were of unusual strength and ‘hardines,’ he would desgyse himselfe, and, rather then fayle, go lyke a begger to become acquaynted with them; and, after he had tryed them with fyghting, never give them over tyl he had used means to drawe [them] to lyve after his fashion” (12): a practice of which numerous instances are recorded in the more common and popular songs, where, indeed, he seldom fails to receive a sound beating. In shooting with the long bow, which they chiefly practised, “they excelled all the men of the land; though, as occasion required, they had also other weapons” (13).
In those forests, and with this company, he for many years reigned like an independent sovereign; at perpetual war, indeed, with the King of England, and all his subjects, with an exception, however, of the poor and needy, and such as were “desolate and oppressed,” or stood in need of his protection. When molested, by a superior force in one place, he retired to another, still defying the power of what was called law and government, and making his enemies pay dearly, as well for their open attacks, as for their clandestine treachery. It is not, at the same time, to be concluded that he must, in this opposition, have been guilty of manifest treason or rebellion; as he most certainly can be justly charged with neither. An outlaw, in those times, being deprived of protection, owed no allegiance: “his hand was against every man, and every man’s hand against him” (14). {v} These forests, in short, were his territories; those who accompanied and adhered to him his subjects:
“The world was not his friend, nor the world’s law:”
and what better title King Richard could pretend to the territory and people of England than Robin Hood had to the dominion of Barnsdale or Sherwood is a question humbly submitted to the consideration of the political philosopher.
The deer with which the royal forests then abounded (every Norman tyrant being, like Nimrod, “a mighty hunter before the Lord”) would afford our hero and his companions an ample supply of food throughout the year; and of fuel, for dressing their vension, or for the other purposes of life, they could evidently be in no want. The rest of their necessaries would be easily procured, partly by taking what they had occasion for from the wealthy passenger who traversed or approached their territories, and partly by commerce with the neighbouring villages or great towns.
It may be readily imagined that such a life, during great part of the year, at least, and while it continued free from the alarms or apprehensions to which our foresters, one would suppose, must have been too frequently subject, might be sufficiently pleasant and desirable, and even deserve the compliment which is paid to it by Shakespeare in his comedy of As you like it (act i. scene 1), where, on Oliver’s asking, “Where will the old duke live?” Charles answers, “They say he is already in the forest of Arden, and {vi} a many merry men with him; and there they live like the OLD ROBIN HOOD OF ENGLAND; . . . and fleet the time carelessly as they did in the golden world.” Their gallant chief, indeed, may be presumed to have frequently exclaimed with the banished Valentine, in another play of the same author:2
“How use doth breed a habit in a man!This shadowy desert, unfrequented woods,I better brook than flourishing peopled towns:Here can I sit alone, unseen of any,And, to the nightingale’s complaining notes,Tune my distresses and record my woes.”
He would doubtless, too, often find occasion to add:
“What hallooing and what stir is this to-day?These are my mates, that make their wills their law,Have some unhappy passenger in chace:They love me well; yet I have much to do,To keep them from uncivil outrages.”
But, on the other hand, it will be at once difficult and painful to conceive,
“When they did hear
The rain and wind beat dark December, how,In that their pinching cave, they could discourseThe freezing hours away!” (15).
Their mode of life, in short, and domestic economy, of which no authentic particulars have been even traditionally preserved, are more easily to be guessed at than described. They have, nevertheless, been elegantly sketched by the animating pencil of an excellent though neglected poet:—
“The merry pranks he play’d, would ask an age to tell,And the adventures strange that Robin Hood befell,When Mansfield many a time for Robin hath been laid,How he hath cousen’d them, that him would have betray’d;How often he hath come to Nottingham disguis’d,And cunningly escap’d, being set to be surpriz’d.In this our spacious isle, I think there is not one,But he hath heard some talk of him and Little John;And to the end of time, the tales shall ne’er be done,Of Scarlock, George a Green, and Much the miller’s son,Of Tuck the merry frier, which many a sermon madeIn praise of Robin Hood, his outlaws, and their trade.An hundred valiant men had this brave Robin Hood,Still ready at his call, that bowmen were right good,All clad in Lincoln green (16), with caps of red and blue,His fellow’s winded horn not one of them but knew,When setting to their lips their little beugles shrill,The warbling ecchos wak’d from every dale and hill.Their bauldricks set with studs, athwart their shoulders cast,To which under their arms their sheafs were buckled fast,A short sword at their belt, a buckler scarce a span,Who struck below the knee, not counted then a man:All made of Spanish yew, their bows were wondrous strong;They not an arrow drew, but was a cloth-yard long.Of archery they had the very perfect craft,With broad-arrow, or but, or prick, or roving shaft,At marks full forty score, they us’d to prick, and rove,Yet higher than the breast, for compass never strove;Yet at the farthest mark a foot could hardly win:At long-outs, short, and hoyles, each one could cleave the pin:Their arrows finely pair’d, for timber, and for feather,With birch and brazil piec’d to fly in any weather;And shot they with the round, the square, or forked pile,The loose gave such a twang, as might be heard a mile.And of these archers brave, there was not any one,But he could kill a deer his swiftest speed upon,Which they did boil and roast, in many a mighty wood,Sharp hunger the fine sauce to their more kingly food. {viii}Then taking them to rest, his merry men and heSlept many a summer’s night under the greenwood tree.From wealthy abbots’ chests, and churls’ abundant store,What oftentimes he took, he shar’d amongst the poor:No lordly bishop came in lusty Robin’s way,To him before he went, but for his pass must pay:The widow in distress he graciously reliev’d,And remedied the wrongs of many a virgin griev’d: (17)He from the husband’s bed no married woman wan,But to his mistress dear, his loved Marian,Was ever constant known, which wheresoe’er she came,Was sovereign of the woods; chief lady of the game:Her clothes tuck’d to the knee, and dainty braided hair,With bow and quiver arm’d, she wander’d here and there,Amongst the forests wild; Diana never knewSuch pleasures, nor such harts as Mariana slew.” 3
That our hero and his companions, while they lived in the woods, had recourse to robbery for their better support is neither to be concealed nor to be denied. Testimonies to this purpose, indeed, would be equally endless and unnecessary. Fordun, in the fourteenth century, calls him “ille famosissimus siccarius,” that most celebrated robber, and Major terms him and Little John “famatissimi latrones.” But it is to be remembered, according to the confession of the latter historian, that, in these exertions of power, he took away the goods of rich men only; never killing any person, unless he was attacked or resisted: that he would not suffer a woman to be maltreated; nor ever took anything from the poor, but charitably fed them with the wealth he drew from the abbots. I disapprove, says he, of the rapine {ix} of the man: but he was the most humane and the prince of all robbers (18). In allusion, no doubt, to this irregular and predatory course of life, he has had the honour to be compared to the illustrious Wallace, the champion and deliverer of his country; and that, it is not a little remarkable, in the latter’s own time (19).
Our hero, indeed, seems to have held bishops, abbots, priests, and monks, in a word, all the clergy, regular or secular, in decided aversion.
“These byshoppes and thyse archebyshoppes,Ye shall them bete and bynde,”
was an injunction carefully impressed upon his followers. The Abbot of Saint Mary’s, in York (20), from some unknown cause, appears to have been distinguished by particular animosity; and the Sheriff of Nottinghamshire (21), who may have been too active and officious in his endeavours to apprehend him, was the unremitted object of his vengeance.
Notwithstanding, however, the aversion in which he appears to have held the clergy of every denomination, he was a man of exemplary piety, according to the notions of that age, and retained a domestic chaplain (Frier Tuck, no doubt) for the diurnal celebration of the divine mysteries. This we learn from an anecdote preserved by Fordun (22), as an instance of those actions which the historian allows to deserve commendation. One day, as he heard mass, which he was most devoutly accustomed to do (nor would {x} he, in whatever necessity, suffer the office to be interrupted,) he was espied by a certain sheriff and officers belonging to the king, who had frequently before molested him in that most secret recess of the wood where he was at mass. Some of his people, who perceived what was going forward, advised him to fly with all speed, which, out of reverence to the sacrament, which he was then most devoutly worshipping, he absolutely refused to do. But the rest of his men having fled for fear of death, Robin, confiding solely in Him whom he reverently worshipped, with a very few, who by chance were present, set upon his enemies, whom he easily vanquished; and, being enriched with their spoils and ransom, he always held the ministers of the Church and masses in greater veneration ever after, mindful of what is vulgarly said:
“Him God does surely hearWho oft to th’ mass gives ear.”
Having, for a long series of years, maintained a sort of independent sovereignty, and set kings, judges, and magistrates at defiance, a proclamation was published (23) offering a considerable reward for bringing him in either dead or alive; which, however, seems to have been productive of no greater success than former attempts for that purpose. At length, the infirmities of old age increasing upon him (24), and desirous to be relieved, in a fit of sickness, by being let blood, he applied for that purpose to the Prioress of Kirkleys nunnery in Yorkshire, his {xi} relation (women, and particularly religious women, being, in those times, somewhat better skilled in surgery than the sex is at present), by whom he was treacherously suffered to bleed to death. This event happened on the 18th of November 1247, being the 31st year of King Henry III. and (if the date assigned to his birth be correct) about the 87th of his age (24). He was interred under some trees, at a short distance from the house; a stone being placed over his grave, with an inscription to his memory (25).
Such was the end of Robin Hood: a man who, in a barbarous age, and under a complicated tyranny, displayed a spirit of freedom and independence which has endeared him to the common people, whose cause he maintained (for all opposition to tyranny is the cause of the people), and, in spite of the malicious endeavours of pitiful monks, by whom history was consecrated to the crimes and follies of titled ruffians and sainted idiots, to suppress all record of his patriotic exertions and virtuous acts, will render his name immortal.
With respect to his personal character: it is sufficiently evident that he was active, brave, prudent, patient; possessed of uncommon bodily strength and considerable military skill; just, generous, benevolent, faithful, and beloved or revered by his followers or adherents for his excellent and amiable qualities. Fordun, a priest, extols his piety, Major (as we have seen) pronounces him the most humane and the prince of all robbers; and Camden, whose testimony is of {xii} some weight, calls him “prædonem mitissimum,” the gentlest of thieves. As proofs of his universal and singular popularity: his story and exploits have been made the subject as well of various dramatic exhibitions (26), as of innumerable poems, rimes, songs and ballads (27): he has given rise to divers proverbs (28); and to swear by him, or some of his companions, appears to have been a usual practice (29): his songs have been chanted on the most solemn occasions (30); his service sometimes preferred to the Word of God (31): he may be regarded as the patron of archery (32); and, though not actually canonised (a situation to which the miracles wrought in his favour, as well in his lifetime as after his death, and the supernatural powers he is, in some parts, supposed to have possessed (33), give him an indisputable claim), he obtained the principal distinction of sainthood, in having a festival allotted to him, and solemn games instituted in honour of his memory, which were celebrated till the latter end of the sixteenth century; not by the populace only, but by kings or princes and grave magistrates; and that as well in Scotland as in England; being considered, in the former country, of the highest political importance, and essential to the civil and religious liberties of the people, the efforts of government to suppress them frequently producing tumult and insurrection (34). His bow, and one of his arrows, his chair, his cap, and one of his slippers, were preserved, with peculiar veneration, till within {xiii} the present century (35); and not only places which afforded him security or amusement, but even the well at which he quenched his thirst, still retain his name (36): a name which, in the middle of the present century, was conferred as a singular distinction upon the prime minister to the king of Madagascar (37).
After his death his company was dispersed (38). History is silent in particulars: all that we can, therefore, learn is, that the honour of Little John’s death and burial is contended for by rival nations (39); that his grave continued long “celebrous for the yielding of excellent whetstones;” and that some of his descendants, of the name of Nailor, which he himself bore, and they from him, were in being so late as the last century (40).

1 For Notes, &c., see p. xiv. et seq.
2 Two Gentlemen of Verona, act v. scene 4.
3 Drayton’s Polyolbion, song xxvi.
(1) “Former biographers,” &c.] Such, that is, as have already appeared in print, since a sort of manuscript life in the Sloane Library will appear to have been of some service. The first of these respectable personages is the author, or rather compiler, of “The noble birth and gallant achievements of that remarkable outlaw Robin Hood; together with a true account of the many merry extravagant exploits he played; in twelve several stories: newly collected by an ingenious antiquary. London, printed by W. O.” [William Onley], 4to, black letter, no date. These “several stories,” in fact, are only so many of the songs in the common Garland transposed; and the “ingenious antiquary,” who strung them together, has known so little of his trade, that he sets out with informing us of his hero’s banishment by King Henry the Eighth. The above is supposed to be the “small merry book” called Robin Hood, mentioned in a list of “books, ballads, and histories, printed for and sold by William Thackeray at the Angel in Duck-lane” (about 1680), preserved in one of the volumes of old ballads (part of Bagford’s collection) in the British Museum.
Another piece of biography, from which much will not be expected, is “The lives and heroick atchievements of the renowned Robin Hood and James Hind, two noted robbers and highwaymen. London, 1752.” 8vo. This, however, is probably nothing more than an extract from Johnson’s “Lives of the Highwaymen,” in which, as a specimen of the authors historical authenticity, we have the life and actions of that noted robber, Sir John Falstaff.


The principal if not sole reason why our hero is never once mentioned by Matthew Paris, Benedictus Abbas, or any other ancient English historian, was most probably his avowed enmity to churchmen; and history, in former times, was written by none but monks. They were unwilling to praise the actions which they durst neither misrepresent nor deny. Fordun and Major, however, being foreigners, have not been deterred by this professional spirit from rendering homage to his virtues.
(2) —“was born at Locksley, in the county of Nottingham.”] “Robin Hood,” says a MS. in the British Museum (Bib. Sloan. 715), written, as it seems, toward the end of the sixteenth century, “was borne at Lockesley in Yorkshyre, or after others in Nottinghamshire.” The writer here labours under manifest ignorance and confusion, but the first row of the rubric will set him right:
“In Locksly town, in merry Nottinghamshire,In merry sweet Locksly town,There bold Robin Hood was born and was bred,Bold Robin of famous renown.” 4
Dr. Fuller (Worthies of England, 1662, p. 320) is doubtful as to the place of his nativity. Speaking of the “Memorable Persons” of Nottinghamshire, “Robert Hood,” says he, “(if not by birth) by his chief abode this country-man.”
The name of such a town as Locksley, or Loxley (for so we sometimes find it spelled), in the county of Nottingham or of York, does not, it must be confessed, occur either in Sir Henry Spelman’s Villare Anglicum. in Adams’s Index Villaris, in Whatley’s England’s Gazetteer,5 in Thoroton’s History of Nottinghamshire, or in the Nomina Villarum Eboracensium (York, 1768, 8vo). The silence of these authorities is not, however, to be regarded as a conclusive proof that such a place never existed. The names of towns and villages, of which no trace is now to be found but in ancient writings, would fill a volume.
(3) —“in the reign of King Henry the Second, and about the year of Christ 1160.”] “Robin Hood,” according to the Sloane MS., “was borne . . . in the dayes of Henry the 2nd, about the yeare 1160.” This was the 6th year of that monarch; at whose death (anno 1189) he would, of course, be about 29 years of age. Those writers are therefore pretty correct who represent him as playing his pranks (Dr. Fuller’s phrase) in the reign of King Richard the First, and, according to the last-named author, “about the year of our Lord 1200.” 6 Thus Mair (who is followed by Stowe, Annales, 1592, p. 227), “Circa hæc tempora [sci. Ricardi I.] ut auguror,” &c. A MS. note in the Museum (Bib. Har. 1233), not, in Mr. Wanley’s opinion, to be relied on, places him in the same period, “Temp. Rich. I.” Nor is Fordun altogether out of his reckoning in bringing him down to the time of Henry III., as we shall hereafter see; and with him agrees Andrew of Wyntowne, in his “Oryginale Cronykil,” written about 1420, which, at the year 1283, has the following lines:
“Lytil Jhon and Robyne HudeWayth-men were commendyd gud:In Yngil-wode and BarnysdaleThai oysyd all this tyme thare trawale.”
A modern writer (History of Whitby, by Lionel Charlton, York, 1779, 4to), though of no authority in this point, has done well enough to speak of him as living “in the days of abbot Richard and Peter his successor;” that is, between the years 1176 and 1211. The author of the two plays upon the story of our hero, of which a particular account will be hereafter given, makes him contemporary with King Richard, who, as well as his brother Prince John, is introduced upon the scene; which is confirmed by another play, quoted in Note 5. Warner, also, in his Albion’s England, 1602, p. 132, refers his existence to “better daies, first Richard’s daies.” This, to be sure, may not be such evidence as would be sufficient to decide the point in a court of justice; but neither judge nor counsel will dispute {xvii} the authority of that oracle of the law Sir Edward Coke, who pronounces that “This Robert Hood lived in the reign of King R. I.” (3 Institute, 197).
We must not therefore regard what is said by such writers as the author of “George a Greene, the pinner of Wakefield,” 1599 (see Note 9), who represents our hero as contemporary with King Edward IV.,7 and the compiler of a foolish book called “The noble birth, &c. of Robin Hood” (see Note 1), who commences it by informing us of his banishment by King Henry VIII. As well, indeed, might we suppose him to have lived before the time of Charlemagne, because Sir John Harington, in his translation of the Orlando Furioso, 1590, p. 391, has made
“Duke ’Ammon in great wrath thus wise to speake:This is a Tale indeed of Robin Hood,Which to beleeve, might show my wits but weake;”
or to imagine his story must have been familiar to Plutarch, because in his Morals, translated by Dr. Philemon Holland, 1603, p. 644, we read the following passage:—“Evenso [i.e. as the crane and fox serve each other in Æsop], when learned men at a table plunge and drowne themselves (as it were), in subtile problemes and questions interlaced with logicke, which the vulgar sort are not able for their lives to comprehend and conceive; whiles they also againe for their part come in with their foolish songs, and vain ballads of Robin-Hood and Little John, telling tales of a tubbe, or of a roasted horse, and such like.” Who, indeed, would be apt to think that his skill in archery was known to Virgil? And yet, as interpreted by our facetious friend Mr. Charles Cotton, he tells us that
“Cupid was a little tyny,Cogging, lying, peevish nynny;But with a bow the shit-breecht elfWould shoot like Robin Hood himself.”
In a word, if we are to credit translators, he must have {xviii} existed before the siege of Troy; for thus, according to one of Homer’s:
“Then came a choice companionOf Robin Hood and Little John,Who many a buck and many a doe,In Sherwood forest, with his bow,Had nabb’d; believe me it is true, sir,The fellow’s Christian name was Teucer.”Iliad, by Bridges, 4to, p. 231.8
This last supposition, indeed, has even the respectable countenance of Dan Geoffrey Chaucer:
“Pandarus answerde, it may be well inough,And held with him of all that ever he saied,But in his hart he thought, and soft lough,And to himselfe full soberly he saied,From hasellwood there Jolly Robin plaied,Shall come all that thou abidest here,Ye, farewell all the snow of ferne yere.”Troilus (B. 5), Speght’s edition, 1602.
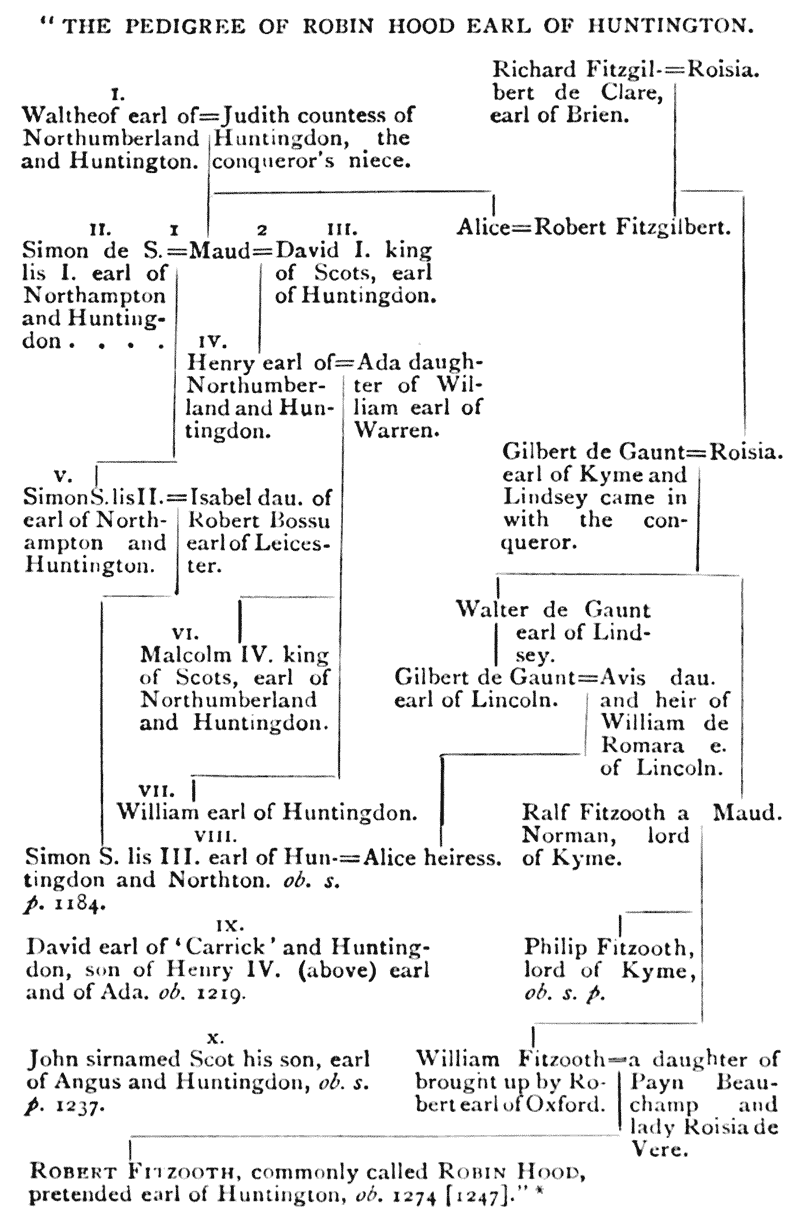
(4) “His extraction was noble, and his true name Robert Fitzooth.”] In “an olde and auncient pamphlet,” which Grafton the chronicler had seen, it was written that “This man discended of a noble parentage.” The Sloane MS. says “He was of . . . . parentage;” and though the material word is illegible, the sense evidently requires noble. So, likewise, the Harleian note: “It is said that he was of noble blood.” Leland also has expressly termed him “nobilis” (Collectanea, i. 54). The following account of his family will be found sufficiently particular. Ralph Fitzothes, or Fitzooth, a Norman, who had come over to England with William Rufus, married Maud or Matilda, daughter of Gilbert de Gaunt, Earl of Kyme and Lindsey, by whom he had two sons: Philip, afterward Earl of Kyme, that earldom being part of his mother’s dowry, and William. Philip the elder died without issue; William was a ward to Robert de Vere, Earl of Oxford, in whose household he received his education, and who, by the king’s express command, gave {xix} him in marriage to his own niece, the youngest of the three daughters of the celebrated Lady Roisia de Vere, daughter of Aubrey de Vere, Earl of Guisnes in Normandy, and lord high chamberlain of England under Henry I., and of Adeliza, daughter to Richard de Clare, Earl of Clarence and Hertford, by Payn de Beauchamp, baron of Bedford, her second husband. The offspring of this marriage was our hero, Robert Fitzooth, commonly called Robin Hood. (See Stukeley’s Palæographia Britannica, No. I. passim.)
A writer in the Gentleman’s Magazine for March 1793, under the signature D. H.,9 pretends that Hood is only a corruption of “o’ th’ wood, q.d. of Sherwood.” This, to be sure, is an absurd conceit; but, if the name were a matter of conjecture, it might be probably enough referred to some particular sort of hood our hero wore by way of distinction or disguise. See Scot’s Discoverie of Witchcraft, 1584, p. 522. In Jonson’s masque of “The king’s entertainment at Welbeck” (Works, 1756, vii. 53), certain characters are introduced “in livery hoods,” of whom Fitz-ale says,
“Six hoods they are, and of the blood,They tell of ancient Robin Hood.”
It may be remembered that Hugh Capet, the first king of France of the third and last race, obtained that surname from a similar circumstance. It is unnecessary to add that Hood is a common surname at this day, as well as a place in Yorkshire, formerly Hode; and that Edward the Third, in the tenth year of his reign, confirmed to Thomas, the son of Robert de Hode, of Hoveden, in tail-general, certain places of moorland, &c. in vasto de Incklesmore, &c. (Ro. Pa. 10 E. 3. m. 31).
(5) “He is frequently styled . . . Earl of Huntingdon, a title to which, for the latter part of his life at least, he actually appears to have had some sort of pretension.”] In Grafton’s “olde and auncient pamphlet,” though the author had, as already noticed, said “this man discended of a NOBLE PARENTAGE,” he adds, “or rather beyng of a base stocke {xx} and linage, was for his manhood and chivalry advaunced to the noble dignitie of an ERLE.”
In the MS. note (Bib. Har. 1233) is the following passage: “It is said that he was of noble blood no lesse then an earle.” Warner, in his Albion’s England, already cited, calls him “a county.” The titles of Mundy’s two plays are: “The downfall” and “The death of Robert earle of Huntington.” He is likewise introduced in that character in the same author’s Metropolis Coronata, hereafter cited. In his epitaph we shall find him expressly styled “Robert, Earl of Huntingtun.”
In “A pleasant commodie called Looke about you,” printed in 1600, our hero is introduced, and performs a principal part. He is represented as the young Earl of Huntington, and in ward to Prince Richard, though his brother Henry, the young king, complains of his having “had wrong about his wardship.” He is described as
“A gallant youth, a proper gentleman;”
and is sometimes called “pretty earle” and “little wag.” One of the characters thus addresses him:
“But welcome, welcome, and young Huntington,Sweet Robyn Hude, honor’s best flowing bloome,”
and calls him
“an honourable youth,
Vertuous and modest, Huntington’s right heyre.”
It is also said that
“His father Gilbert was the smoothst fac’t lordThat ere bare armes in England or in Fraunce.”
In one scene, “Enter Richard and Robert with coronets.”
“Rich. Richard the Prince of England, with his ward,The noble Robert Hood, earle Huntington,Present their service to your majestie.”
Dr. Percy’s objection, that the most ancient poems make no mention of this earldom,10 but only call him a yeoman, will be considered in another place. How he founded his pretensions to this title will be seen in his pedigree. Here it is. {xxi}
(6) “In his youth he is reported to have been of a wild and extravagant disposition,” &c.] Grafton’s pamphlet, after supposing him to have been “advaunced to the noble dignitie of an erle,” continued thus: “But afterwardes he so prodigally exceeded in charges and expences, that he fell into great debt, by reason whereof, so many actions and sutes were commenced against him whereunto he answered not, that by {xxiii} order of lawe he was outlawed.” 12 Leland must undoubtedly have had good authority for calling him “nobilis ille exlex.” 13 Fordun supposes him in the number of those deprived of their estates by King Henry III. “Hoc intempore,” says he, “de exheredatis surrexit & caput erexit ille famosissimus siccarius Robertus Hode & littill Johanne cum eorum complicibus” (p. 774). The Sloane MS. says he was “so ryotous that he lost or sould his patrimony & for debt became an outlawe;” and the Harleian note mentions his “having wasted his estate in riotous courses.” The former authority, however, gives a different, though, it may be, less credible, account of his being obliged to abscond. It is as follows: “One of his first exployts was the going abrode into a forrest & bearing with him a bowe of exceeding great strength, he fell into company with certayne rangers or woodmen, who fell to quarrel with him, as making showe to use such a bowe as no man was able to shoote withall. Whereto Robin replyed that he had two better then that at Lockesley, only he bare that with him nowe as a byrding bowe. At length the ‘contention’ grewe so hote that there was a wager layd about the kyllyng of a deere a greate distance of, for performance whereof Robin offered to lay his head to a certayne some of money, the advantage of which rash speach the others presently tooke. So the marke being found out, one of them, both to make his hart faynt and hand unsteady, as he was about to shoote urged him with the losse of head if he myst the marke. Notwithstanding Robyn kyld the deare, and gave every man his {xxiv} money agayne, save to him which at the poynt of shooting so upbraided him with danger to loose his hed for that wager; & he sayd they would drinke togeyther: whereupon the others stomached the matter and from quarelling they grewe to fighting with him. But Robin, getting him somewhat of, with shooting dispatch them, and so fled away; and then betaking himselfe to lyve in the woods,” &c.14
That he lurked or infested the woods is agreed by all. “Circa hæc tempora,” says Major, “Robertus Hudus Anglus & parvus Joannes, latrones famatissimi, in nemoribus latuerunt.”
Dr. Stukeley says that “Robin Hood took to this wild way of life in imitation of his grandfather Geoffrey de Mandeville, who being a favorer of Maud empress, King Stephen took him prisoner at S. Albans, and made him give up the tower of London, Walden, Plessis, &c., upon which he lived on plunder” (MS. note in his copy of Robin Hood’s Garland).
(7) “Of these, he chiefly affected Barnsdale,” &c.] “Along on the lift hond,” says Leland, “a iii. miles of betwixt Milburne and Feribridge I saw the wooddi and famose forrest of Barnesdale, wher thay say that Robyn Hudde lyvid like an outlaw” (Itinerary, v. 101).
“They haunted about Barnsdale forrest, Compton [r. Plompton] parke,15 and such other places” (MS. Sloane).
“His principal residence,” says Fuller, “was in Shirewood forrest in this county [Notts], though he had another haunt (he is no fox that hath but one hole) near the sea in the North Riding in Yorkshire, where Robin Hood’s Bay still retaineth his name: not that he was any pirat, but a land-thief, who retreated to those unsuspected parts for his security” (Worthies of England, p. 320). {xxv}
In Thoroton’s Nottinghamshire, p. 505, is some account of the ancient and present state of Sherwood forest; but one looks in vain through that dry detail of land-owners for any particulars relating to our hero. “In anno domini 1194, King Richard the First, being a hunting in the forrest of Sherwood, did chase a hart out of the forrest of Sherwood into Barnesdale in Yorkshire, and because he could not there recover him, he made proclamation at Tickill in Yorkshire, and at divers other places there, that no person should kill, hurt, or chase the said hart, but that he might safely retorne into forrest againe, which hart was afterwards called a hart-royall proclaimed” (Manwood’s Forest Laws, 1598, p. 25, from “an auncient recorde” found by him in the tower of Nottingham Castle).16
(8) “Here he either found,” &c.] After being outlawed, Grafton tells us, “for a lewde shift, as his last refuge, [he] gathered together a companye of roysters and cutters, and practised robberyes and spoyling of the kinges subjects, and occupied and frequented the forestes or wild countries.” See also the following note.
(9) “Little John, William Scadlock, George a Green, pinder of Wakefield, Much a miller’s son, and a certain monk or frier named Tuck.”] Of these, the pre-eminence is incontestably due to Little John, whose name is almost constantly coupled with that of his gallant leader. “Robertus Hode & littill Johanne,” are mentioned together by Fordun as early as 1341; and later instances of the connection would be almost endless. After the words, “for debt became an {xxvi} outlaw,” the Sloane MS. adds: “then joyninge to him many stout fellowes of lyke disposition, amongst whom one called Little John was principal or next to him, they haunted about Barnsdale forrest,” &c. See Notes 39, 40.
With respect to Frier Tuck, “thogh some say he was an other kynd of religious man, for that the order of freyrs was not yet sprung up” (MS. Sloan.), yet as the Dominican friers (or friers preachers) came into England in the year 1221, upward of twenty years before the death of Robin Hood, and several orders of these religious had flourished abroad for some time, there does not seem much weight in that objection: nor, in fact, can one pay much regard to the term frier, as it seems to have been the common title given by the vulgar (more especially after the Reformation) to all the regular clergy, of which the friers were at once the lowest and most numerous. If Frier Tuck be the same person who, in one of the oldest songs, is called the curtail frier of Fountains-dale, he must necessarily have been one of the monks of that abbey, which was of the Cistercian order. However this may be, Frier Tuck is frequently noticed by old writers as one of the companions of Robin Hood, and as such was an essential character in the morris-dance (see Note 34). He is thus mentioned by Skelton, laureat, in his “goodly interlude” of Magnificence, written about the year 1500, and with an evident allusion to some game or practice now totally forgotten and inexplicable:
“Another bade shave halfe my berde,And boyes to the pylery gan me plucke,And wolde have made me freer Tucke,To preche oute of the pylery hole.”
In the year 1417, as Stow relates, “one, by his counterfeite name, called Frier Tucke, with manie other malefactors, committed many robberies in the counties of Surrey & Sussex, whereupon the king sent out his writs for their apprehension” (Annales, 1592).
George a Green is George o’ the green, meaning perhaps the town-green, in which the pound or pinfold stood of which he had the care. He has been particularly celebrated, and {xxvii} “As good as George a Green” is still a common saying.17 Drayton, describing the progress of the river Calder, in the West Riding of Yorkshire, has the following lines:
“It chanc’d she in her course on ‘Kirkley’ cast her eye,Where merry Robin Hood, that honest thief, doth lie;Beholding fitly too before how Wakefield stood,She doth not only think of lusty Robin Hood,But of his merry man, the pindar of the townOf Wakefield, George a Green, whose fames so far are blownFor their so valiant fight, that every freeman’s songCan tell you of the same; quoth she, be talk’d on long,For ye were merry lads, and those were merry days.”
Thus, too, Richard Brathwayte, in his poetical epistle “to all true-bred northerne sparks of the generous society of the Cottoneers” (Strappado for the Divell, 1615):
“But haste, my muse, in colours to displaySome auncient customes in their high-roade way,At least such places labour to make knowneAs former times have honour’d with renowne.The first whereof that I intend to showIs merry Wakefield, and her pindar too,Which fame hath blaz’d with all that did belong,Unto that towne in many gladsome song,The pindar’s valour, and how firme he stoodIn th’ townes defence ’gainst th’ rebel Robin Hood,How stoutly he behav’d himselfe, and would,In spite of Robin, bring his horse to th’ fold,His many May-games which were to be seeneYearly presented upon Wakefield greene,Where lovely Jugge and lustie Tib would go,To see Tom-lively turne upon the toe;Hob, Lob, and Crowde the fidler would be there,And many more I will not speake of here.Good God! how glad hath been this hart of mine,To see that towne, which hath, in former time,So flourish’d and so gloried in her name,Famous by th’ pindar who first rais’d the same!Yea, I have paced ore that greene and oreAnd th’ more I saw’t I tooke delight the more, {xxviii}For where we take contentment in a place,A whole daies walke seemes as a cinquepace.Yet as there is no solace upon earthWhich is attended evermore with mirth,But when we are transported most with gladnesse,Then suddenly our joy’s reduc’d to sadnesse;So far’d with me to see the pindar gone,And of those jolly laddes that were not oneLeft to survive: I griev’d more then Ile say:(But now for Bradford I must hast away).Unto thy task, my muse, and now make knowneThe jolly shoo-maker of Bradford towne,His gentle craft so rais’d in former timeBy princely journey-men his discipline,Where he was wont with passengers to quaffe,But suffer none to carry up their staffeUpon their shoulders, whilst they past through town,For if they did he soon would beat them downe;(So valiant was the souter) and from henceTwixt Robin Hood and him grew th’ difference;Which, cause it is by most stage-poets writ,For brevity I thought good to omit.”
In the latter part of this extract, honest Richard evidently alludes to “A pleasant conceyted comedie of George a Greene, the pinner of Wakefield; as it was sundry times acted by the servants of the right honourable the earle of Sussex,” 1599, 4to, which has been erroneously ascribed to Heywood the epigrammatist, and is reprinted, with other trash, in the late edition of Dodsley’s Old Plays; only it unluckily happens that Robin Hood is almost the only person who has no difference with the souter (or shoemaker) of Bradford. The play, in short (or at least that part of it which we have any concern with), is founded on the ballad of Robin Hood and the Pinder of Wakefield (see part ii. song 3), which it directly quotes, and is, in fact, a most despicable performance.18 King Edward (the Fourth) having taken King James of Scotland prisoner, after a most bloody battle near Middleham Castle, from which of 30,000 Scots not 5000 had escaped, comes with his royal captive in disguise to Bradford, where they {xxix} meet Robin Hood and George a Green, who have just had a stout affray: and after having read this, and a great deal more such nonsensical stuff, Captain Grose sagaciously “supposes that this play has little or no foundation in history;” and very gravely sits down and debates his opinion in form.
“The history of George a Green, pindar of the town of Wakefield,” 4to, no date,19 is a modern production, chiefly founded on the old play just mentioned, of neither authority nor merit.
Our gallant pinder is thus facetiously commemorated by Drunken Barnaby:
“Hinc diverso cursu, seroQuod audissem de pinderoWakefeeldensi; gloria mundi,Ubi socii sunt jucundi,Mecum statui peragrareGeorgii fustem visitare.”“Turning thence, none could me hinderTo salute the Wakefield pindar;Who indeed is the world’s glory,With his comrades never sorry.This was the cause, lest you should miss it,George’s club I meant to visit.”“Veni Wakefield peramænum,Ubi quærens Georgium Greenum,Non inveni, sed in lignumFixum reperi Georgii signum,Ubi allam bibi feramDonec Georgio fortior eram.”“Strait at Wakefield I was seen a,Where I sought for George a Green a;But could find not such a creature,Yet on a sign I saw his feature,Where strength of ale had so much stir’d me,That I grew stouter far than Jordie.”
Besides the companions of our hero enumerated in the text, and whose names are most celebrated and familiar, we find those of William of Goldsbrough (mentioned by Grafton), Right-hitting Brand (by Mundy), and Gilbert with the white {xxx}
hand, who is thrice named in the Lyttell Geste of Robyn Hode (i. 52, 71), and is likewise noticed by Bishop Gawin Douglas in his Palice of Honour, printed at Edinburgh in 1579, but written before 1518:
“Thair saw I Maitlaind upon auld Beird Gray,Robene Hude, and Gilbert with the quhite hand,How Hay of Nauchton slew, in Madin land.” 20
As no mention is made of Adam Bell, Clim of the Clough, and William of Cloudeslie, either in the ancient legend or in more than one of the numerous songs of Robin Hood, nor does the name of the latter once occur in the old metrical history of those famous archers reprinted in Percy’s Reliques, and among pieces of ancient popular poetry, it is to be concluded that they flourished at different periods, or at least had no connection with each other. In a poem, however, intitled, “Adam Bell, Clim of the Clough, and young William of Cloudesley, the second part,” 1616, 4to, b. l. (Bib. Bod. Art. L. 71, being a more modern copy than that in Selden C. 39, which wants the title, but was probably printed with the first part, which it there accompanies, in 1605; differing considerably therefrom in several places, and containing many additional verses), are the following lines (not in the former copy):
“Now beare thy father’s heart, my boy,Said William of Cloudesley then,When i was young i car’d not forThe brags of sturdiest men.The pinder of Wakefield, George a Green,I try’d a sommer’s day,Yet he nor i were victors madeNor victor’d went away.Old Robin Hood, nor Little John,Amongst their merry men all,Nor fryer Tuck, so stout and young,My courage could appall.”
(10) “Marian.”] Who or whatever this lady was, it is observable that no mention of her occurs either in the Lytell Geste of Robyn Hode, or in any other poem or song {xxxi} concerning him, except the not very old ballad of Robin Hood’s Golden Prize, where she is barely named, and a still more modern one of no merit (see part ii. song 24).21 She is an important character, however, in the two old plays of The death and downfall of Robert earl of Huntington, written before 1600, and is frequently mentioned by dramatic or other writers about that period. Her presence, likewise, was considered as essential to the morris-dance. See Note 34.
In the First Part of King Henry IV. Falstaff says to the hostess, “There’s no more faith in thee than in a stew’d prune; nor no more truth in thee than in a drawn fox; and for womanhood, Maid Marian may be the deputy’s wife of the ward to thee;” upon which Dr. Johnson observes, that “Maid Marian is a man dressed like a woman, who attends the dancers of the morris.” “In the ancient songs of Robin Hood,” says Percy, “frequent mention is made of Maid Marian, who appears to have been his concubine. I could quote,” adds he, “many passages in my old MS. to this purpose, but shall produce only one:22
‘Good Robin Hood was living then,Which now is quite forgot,And so was fayre Maid Marian,’ &c.”
Mr. Steevens, too, after citing the old play of “The downfall of Robert earl of Huntington,” 1601, to prove “that Maid Marian was originally a name assumed by Matilda, the daughter of Robert, Lord Fitzwater, while Robin Hood remained in a state of outlawry,” observes, that “Shakespeare speaks of Maid Marian in her degraded state, when she was {xxxii} represented by a strumpet or a clown;” and refers to figure 2 in the plate at the end of the play, with Mr. Tollet’s observations on it. The widow, in Sir W. Davenant’s “Love and Honour,” says, “I have been Mistress Marian in a maurice ere now;” and Mr. Warton23 quotes an old piece, entitled “Old Meg of Herefordshire for a Maid Marian, and Hereford town for a morris-dance: or 12 morris-dancers in Herefordshire of 1200 years old,” London, 1609, 4to, which is dedicated, he says, to one Hall, a celebrated tabourer in that country.24 See Note 34.
(11) “His company,” &c.] See the entire passage quoted from Major in a subsequent note. “By such bootyes as he could get,” says the writer of the Sloane MS., “his company encreast to an hundred and a halfe.”
(12) —“the words of an old writer.”] The author of the Sloane manuscript; which adds: “after such maner he procured the pynner of Wakefeyld to become one of his company, and a freyr called Muchel [r. Tuck] . . . Scarlock he induced upon this occasion: one day meeting him as he walket solitary & like to a man forlorne, because a mayd to whom he was affyanced was taken from [him] by the violence of her frends, & given to another that was old & welthy, whereupon Robin, understanding when the maryage-day should be, came to the church as a begger, & having his own company not far of, which came in so soone as they hard {xxxiii} the sound of his horne, he tooke the bryde perforce from him that [bare] in hand to have marryed her, & caused the preist to wed her & Scarlocke togeyther.” (See part ii. song 8.) This MS., of which great part is merely the old legend or Lytell Geste of Robyn Hode turned into prose, appears to have been written before the year 1600.
(13) “In shooting,” &c.] MS. Sloan. Grafton also speaks of our hero’s “excellyng principally in archery or shooting, his manly courage agreeyng thereunto.”
Their archery, indeed, was unparalleled, as both Robin Hood and Little John have frequently shot an arrow a measured mile, or 1760 yards, which it is supposed no one, either before or since, was ever able to do. “Tradition,” says Master Charlton, “informs us that in one of ‘Robin Hood’s’ peregrinations, he, attended by his trusty mate Little John, went to dine [at Whitby Abbey] with the abbot Richard, who, having heard them often famed for their great dexterity in shooting with the long bow, begged them after dinner to shew him a specimen thereof; when, to oblige the abbot, they went up to the top of the abbey, whence each of them shot an arrow, which fell not far from Whitby-laths, but on the contrary side of the lane; and in memorial thereof, a pillar was set up by the abbot in the place where each of the arrows was found, which are yet standing in these our days; that field where the pillar for Robin Hood’s arrow stands being still called Robin Hood’s field, and the other where the pillar for Little John’s arrow is placed, still preserving the name of John’s field. Their distance from Whitby Abbey is more than a measured mile, which seems very far for the flight of an arrow, and is a circumstance that will stagger the faith of many; but as to the credibility of the story, every reader may judge thereof as he thinks proper; only I must here beg leave to observe that these very pillars are mentioned, and the fields called by the aforesaid names, in the old deeds for that ground, now in the possession of Mr. Thomas Watson” (History of Whitby, York, 1779, p. 146).25 {xxxiv}
Dr. Meredith Hanmer, in his Chronicle of Ireland (p. 179), speaking of Little John, says, “There are memorable acts reported of him, which I hold not for truth, that he would shoot an arrow a mile off and a great deale more; but them,” adds he, “I leave among the lyes of the land.” 26 See Note 39. {xxxv}
(14) “An outlaw, in those times, being deprived of protection, owed no allegiance,” &c.] Such a character was, doubtless, at the period treated of, in a very critical situation; it being equally as legal and meritorious to hunt down and dispatch him as it was to kill a wolf, the head of which animal he was said to bear. “Item foris facit,” says Bracton (who wrote about the time), “omnia que pacis sunt, quia a tempore quo utlagatus est caput gerit lupinum, ita ut impune ab omnibus interfici possit” (l. 2, c. 35). In the great roll of the exchequer, in the 7th year of King Richard I., is an allowance by writ of two marks to Thomas de Prestwude, for bringing to Westminster the head of William de Elleford, an outlaw. (See Madox’s History of the Exchequer, 136.) Those who received or consorted with a person outlawed were subject to the same punishment. Such was the humane policy of our enlightened ancestors! See Note 21.
(15)
“how
. . . . they could discourseThe freezing hours away! ”]
(Cymbeline, act iii. scene 3). The chief subjects of our hero’s conversation are supposed, by a poetical genius of the 16th {xxxvi} century, to have been the commendation of a forest-life and the ingratitude of mankind.
“I have no tales of Robin Hood, though mal-content was heIn better daies, first Richard’s daies, and liv’d in woods as weA Tymon of the world; but not devoutly was he soe,And therefore praise I not the man: but for from him did groeWords worth the note, a word or twaine of him ere hence we goe.Those daies begot some mal-contents, the principall of whomeA county was, that with a troope of yomandry did rome,Brave archers and deliver men, since nor before so good,Those took from rich to give the poore, and manned Robin Hood.He fed them well, and lodg’d them safe in pleasant caves and bowers,Oft saying to his merry men, What juster life than ours?Here use we tallents that abroad the churles abuse or hide,Their coffers’ excrements, and yeat for common wants denide.We might have sterved for their store, & they have dyc’st our bones,Whose tongues, driftes, harts, intice, meane, melt, as syrens, foxes, stones,Yea even the best that betterd them heard but aloofe our mones.And redily the churles could prie and prate of our amis,Forgetfull of their owne. . . .I did amis, not missing friends that wisht me to amend:I did amend, but missed friends when mine amis had end:My friends therefore shall finde me true, but I will trust no frend.Not one I knewe that wisht me ill, nor any workt me well,To lose, lacke, live, time, frends, in yncke, an hell, an hell, an hell!Then happie we (quoth Robin Hood) in merry Sherwood that dwell.” 27
It has been conjectured, however, that, in the winter season, our hero and his companions severally quartered themselves in villages or country-houses more or less remote, with persons of whose fidelity they were assured. It is not improbable, at the same time, that they might have tolerably comfortable habitations erected in the woods.
Archery, which our hero and his companions appear to have carried to a state of perfection, continued to be cultivated for some ages after their time, down, indeed, to that of Henry VIII., or about the year 1540, when, owing to the introduction of artillery and matchlock-guns, it became neglected, and the bowmen of Cressy and Agincourt utterly extinct; though it may be still a question whether a body of expert archers would not, even at this day, be superior to an equal {xxxvii} number armed with muskets.28 The loss sustained from this change by the people at large seems irreparable. Anciently, the use of the bow or bill qualified every man for a soldier; and a body of peasants, led on by a Tyler or a Cade, was not less formidable than any military force that could be raised to oppose them: by which means the people from time to time preserved the very little liberty they had, and which their tyrants were constantly endeavouring to wrest from them. See how the case stands at present: the sovereign, let him be who or what he will (kings have been tyrants, and may be so again), has a standing army, well disciplined and accoutred, while the subjects or people are absolutely defenceless: as much care having been taken, particularly since “the glorious revolution,” to deprive them of arms as was formerly bestowed to enforce their use and practice.29 The following extract from Hale’s Historia Placitorum Coronæ (i. 118) will serve to show how familiar the bow and arrow was in the 14th century:—“M. 22. E. 3. Rot. 117. coram rege Ebor. This was the case of Henry Vescy, who had been indicted before the sheriff in turno suo . . . of divers felonies, whereupon the sheriff mandavit commissionem suam Henrico de Clyderawe & aliis ad capiendum prædictum H. Vescy, & salvo ducendum usque castrum de Ebor.” Vescy would not submit to an arrest, but fled, and inter fugiendum shot with his bow and arrows at his pursuers, but in the end was killed by Clyderawe: to which may be added a remarkable passage in Harison’s “Description of England” (prefixed to Holinshed’s Chronicle, 1587), to prove how much it had declined in the 16th. “In times past,” says he, “the {xxxviii} cheefe force of England consisted in their long bowes. But now we have in maner generallie given over that kind of artillerie, and for long bowes in deed doo practise to shoot compasse for our pastime; which kind of shooting can never yeeld anie smart stroke, nor beat down our enemies, as our countrymen were woont to doo at everie time of need. Certes the Frenchmen and Rutters,30 deriding our new archerie in respect of their corslets, will not let, in open skirmish, if anie leisure serve, to turne up their tailes, and crie, Shoote, English; and all because our strong shooting is decaied and laid in bed. But if some of our Englishmen now lived that served King Edward the Third in his warres with France, the breech31 of such a varlet should have beene nailed to his bum with one arrow, and an other fethered in his bowels, before he should have turned about to see who shot the first” (p. 198). Bishop Latimer, in his sixth sermon before King Edward VI., gives an interesting account how the sons of yeomen were, in his infancy, trained up to the bow. “But now,” says he, “we have taken up whooring in townes, instead of shooting in the fieldes.”
(16)
“All clad in Lincoln green.”]
This species of cloth is mentioned by Spenser (Faerie Queene, VI. ii. 5):
“All in a woodman’s jacket he was cladOf Lincolne greene, belay’d with silver laceAnd on his head an hood with aglets sprad,And by his side his hunter’s horne he hanging had.”
It is likewise noticed by our poet himself, in another place:
“Swains in shepherds gray, and gyrles in Lincolne greene.” 32
See Polyolbion, song xxv., where the marginal note says, “Lincolne anciently dyed the best green in England.” Thus Coventry had formerly the reputation of dying the best blue. {xxxix} See Ray’s Proverbs, p. 178. Kendal green is equally famous, and appears to have been cloth of a similar quality. This colour was adopted by foresters to prevent their being too readily discovered by the deer. See Sir John Wynne’s History of the Guedir Family (Barrington’s Miscellanies), p. 419. Thus the Scotish Highlanders used to wear brown plaids to prevent their being distinguished among the heath. It is needless to observe that green has ever been the favourite dress of an archer, hunter, &c. See Note 34.33 We now call it a Saxon or grass green:
“His coat is of a Saxon green, his waistcoat’s of a plaid” (O. song).
Lincoln green was well known in France in or before the 13th century. Thus, in an old fabliau, transprosed by M. Le Grand (Fabliaux ou Contes, iv. 13), “Il mit donc son surcot fourré d’écureuil, et sa belle robe d’Estanfort teinte en verd.” Estanfort is Stamford, in Lincolnshire.34 This cloth is, likewise, often mentioned by the old Scotish poets under the names of Lincum licht, Lincum twyne, &c., and appears to have been in universal request: and yet, notwithstanding this cloud of evidence, Mr. Pinkerton has had the confidence to assert that “no particular cloth was ever made at Lincoln.” (See Ancient Scotish Poems, ii. 430.) But, indeed, this worthy gentleman, as Johnson said of Goldsmith, only stumbles upon truth by accident. {xl}
(17)
“From wealthy abbots’ chests,” &c.]
“But who,” exclaims Dr. Fuller, having cited this passage, “made him a judge? or gave him a commission to take where it might be best spared, and give where it was most wanted?” That same power, one may answer, which authorises kings to take where it can be worst spared, and give it where it is least wanted. Our hero, in this respect, was a knight-errant; and wanted no other commission than that of Justice, whose cause he militated. His power, compared with that of the king of England, was by no means either equally usurped or equally abused: the one reigned over subjects (or slaves) as a master (or tyrant), the other possessed no authority but what was delegated to him by the free suffrage of his adherents, for their general good: and as for the rest, it would be absurd to blame in Robin what we should praise in Richard.35 The latter, too, warred in remote parts of the world against nations from which neither he nor his subjects had sustained any injury; the former at home against those to whose wealth, avarice, or ambition he might fairly attribute not only his own misfortunes, but the misery of the oppressed and enslaved society he had quitted. In a word, every man who has the power has also the authority to pursue the ends of justice, to regulate the gifts of fortune, by transferring the superfluities of the rich to the necessities of the poor; by relieving the oppressed, and even, when necessary, destroying the oppressor. These are the objects of the social union, and every individual may, and to the utmost of his power should, endeavour to promote them. Had our Robin Hood been, like M’Donald of Barrisdale, a reader of Virgil, he, as well as that gallant chief, might have inscribed on his baldric— {xli}
“Hæ tibi erunt artes; pacis componere mores,Parcere subjectis, et debellare superbos.” 36
(18) “But it is to be remembered,” &c.] The passage from Major’s work, which has been already quoted, is here given entire (except as to a single sentence introduced in another place). “Circa hæc tempora [s. Ricardi I.] ut auguror, Robertus Hudus & Parvus Joannes latrones famatissimi, in nemoribus latuerunt, solum opulentum virorum bona diripientes. Nullum nisi eos invadentem vel resistentem pro suarum rerum tuitione occiderunt. Centum sagittarios ad pugnam aptissimos Robertus latrociniis aluit quos 400 viri fortissimi invadere non audebant. Fæminam nullum opprimi permisit, nec pauperum bona surripuit, verum eos ex abbatum bonis ablatis opipare pavit. Viri rapinam improbo sed latronum omnium humanissimus & princeps erat” (Majoris Britanniæ Historia, Edin. 1740, p. 128).
Stowe, in his Annales, 1592, p. 227, gives an almost literal version of the above passage; Richard Robinson versifies it;37 and Camden slightly refers to it. {xlii}
(19) —“has had the honour to be compared to the illustrious Wallace,” &c.] In the first volume of Peck’s intended supplement to the Monasticon, consisting of collections for the history of Præmonstratensian monasteries, now in the British Museum, is a very curious riming Latin poem with the following title: “Prioris Alnwicensis de bello Scotico apud Dumbarr, tempore rigis Edwardi I. dictamen sive rithmus Latinus, quo de Willielmo Wallace Scotico illo Robin Whood, plura sed invidiose canit;” and in the margin are the following date and reference:—“22. Julii 1304. 32. E. 1. Regist. Prem. fol. 59. a.” This, it maybe observed, is the first known instance of our hero’s name being mentioned by any writer whatever; and affords a strong and respectable proof of his early popularity.
(20) “The abbot of St. Mary’s in York.”] “In the year 1088, Alan, Earl of Richmond, founded here a stately abbey for black monks to the honour of St. Olave; but it was afterwards dedicated to the Blessed Virgin by the command of king William Rufus. Its yearly revenues at the suppression amounted to £1550, 7s. 9d. Dugd., £2850, 1s. 5d. Speed” (Willis’s Mitred Abbeys, i. 214). The abbots in our hero’s time were—
(21) —“the sheriff of Nottinghamshire.”] Ralph Murdach was sheriff of Derby and Nottinghamshires in the first year of King Richard I., and for the seven years preceding, and William Brewerre in his sixth year, between which and the first no name appears on the roll. See Fuller’s Worthies, &c.
In the year 1195, Hubert, Archbishop of Canterbury, {xliii} justiciary of all England, sent throughout the kingdom this form of oath: that all men of the realm of England would keep the peace of the lord the king to their power; and that they would neither be thieves nor robbers, nor the receivers of such, nor consent to them in anything; and that when they were able to know such-like malefactors, they would take them to the utmost of their power, and deliver them to the sheriff; who in no wise should be delivered unless by the lord the king or his chief justice; and if unable to take them, they should cause the bailiffs of the lord the king to know who they were: and, cry being raised for pursuing outlaws, robbers, thieves, or their receivers, all should fully do that suit to the utmost of their power, &c. Knights were to be assigned for these purposes, and men chosen and faithful were sent to execute them in every county, who by the oath of true men of the vicinages took many and put them in the king’s prisons; but many, being forewarned, and conscious of evil, left their houses and possessions and fled (R. de Hoveden, p. 757).
(22) —“an anecdote preserved by Fordun,” &c.] “De quo eciam quædam commendabilia recitantur, sicut patuit in hoc, quod cum ipse quondam in Barnisdale iram [f. ob iram] regis & fremitum principis, missam, ut solitus erat, devotissime audiret, nec aliqua necessitate volebat interrumpere officium, quadam die cum audiret missam, à quodam vicecomite & ministris regis, sæpius per prius ipsum infestantibus, in illo secretissimo loco nemorali, ubi missæ interfuit, exploratus, venientes ad eum qui de suis hoc perceperunt, ut omni annisu fugeret suggesserunt, qui, ob reverentiam sacramenti, quod tunc devotissime venerabatur, omnino facere recusavit. Sed ceteris suis, ob metum mortis trepidantibus, Robertus tantum confisus in eum, quem coluit reveritus, cum paucissimis, qui tunc forte ei affuerunt, inimicos congressus & eos de facili devicit, et de eorum spoliis ac redemptione ditatus, ministros ecclesiæ & missas semper in majori veneratione semper & de post habere præelegit, attendens quod wlgariter dictum est:
Hunc deus exaudit, qui missam sæpius audit.”
J. De Fordun Scotichronicon, à Hearne, Ox. 1722, p. 774. {xliv}
This passage is found in no other copy of Fordun’s Chronicle than one in the Harleian Library. Its suppression in all the rest may be fairly accounted for on the principle which is presumed to have influenced the conduct of the ancient English historians. See Note 1.
(23) —“a proclamation was published,” &c.] “The king att last,” says the Harleian MS., “sett furth a proclamation to have him apprehended,” &c. Grafton, after having told us that he “practised robberyes,” &c., adds, “The which beyng certefyed to the king, and he beyng greatly offended therewith, caused his proclamation to be made that whosoever would bryng him quicke or dead, the king would geve him a great summe of money, as by the recordes in the Exchequer is to be seene: But of this promise no man enjoyed any benefite. For the sayd Robert Hood, being afterwardes troubled with sicknesse,” &c. (p. 85.) See Note 14.
(24) “At length the infirmities of old age increasing upon him,” &c.] Thus Grafton: “The sayd Robert Hood, beyng troubled with sicknesse, came to a certain nonry in Yorkshire called Bircklies [r. Kircklies], where desiryng to be let blood, he was betrayed and bled to death.” The Sloane MS. says that “[Being] dystempered with could and age, he had great payne in his lymmes, his bloud being corrupted, therefore to be eased of his payne by letting bloud, he repayred to the priores of Kyrkesly, which some say was his aunt, a woman very skylful in physique & surgery; who, perceyving him to be Robyn Hood, & waying howe fel an enimy he was to religious persons, toke reveng of him for her owne howse and all others by letting him bleed to death. It is also sayd that one Sir Roger of Doncaster, bearing grudge to Robyn for some injury, incyted the priores, with whome he was very familiar, in such a maner to dispatch him.” See the Lytell Geste of Robyn Hode, ad finem. The Harleian MS., after mentioning the proclamation “sett furth to have him apprehended,” adds, “At which time it happened he fell sick at a nunnery in Yorkshire called Birkleys [r. Kirkleys]; & desiring there to be let blood, hee was betrayed & made bleed to death.”
Kirkleys, Kirklees, or Kirkleghes, formerly Kuthale, in the {xlv} deanery of Pontefract, and archdeaconry of the West Riding of Yorkshire, was a Cistercian, or, as some say, a Benedictine nunnery, founded, in honour of the Virgin Mary and St. James, by Reynerus Flandrensis in the reign of King Henry II. Its revenues at the dissolution were somewhat about £20, and the site was granted (36 Hen. 8.) to John Tasburgh and Henry Savill, from whom it came to one of the ancestors of Sir George Armytage, Bart., the present possessor. The remains of the building (if any) are very inconsiderable, and its register has been searched after in vain. See Tanner’s Notitia, p. 674. Thoresby’s Ducatus Leodiensis, p. 91. Hearne’s “Account of Several Antiquities in and about the University of Oxford,” at the end of Leland’s Itinerary, vol. ii. p. 128.
In 1706 was discovered, among the ruins of the nunnery, the monument of Elisabeth de Staynton, prioress; but it is not certain that this was the lady from whom our hero experienced such kind assistance. See Thoresby and Hearne ubi supra.
“One may wonder,” says Dr. Fuller, “how he escaped the hand of justice, dying in his bed, for ought is found to the contrary; but it was because he was rather a merry than a mischievous thief (complementing passengers out of their purses), never murdering any but deer, and . . . . ‘feasting’ the vicinage with his vension” (Worthies, p. 320). See the following note.
(25) “He was interred under some trees at a short distance from the house; a stone being placed over his grave with an inscription to his memory.”] “Kirkley monasterium monialium, ubi Ro: Hood nobilis ille exlex sepultus” (Leland’s Collectanea, i. 54). “Kirkleys Nunnery, in the Woods, whereof Robin Hood’s grave is, is between Halifax and Wakefield upon Calder” (Letter from Jo. Savile to W. Camden, Illus. viro epis. 1691).
“as Caldor comes along,
It chanced she in her course on ‘Kirkley’ cast her eye,Where merry Robin Hood, that honest thief, doth lie.”(Polyolbion, song 28.)
See also Camden’s Britannia, 1695, p. 709. {xlvi}
In the second volume of Dr. Stukeley’s Itinerarium Curiosum is an engraving of “the prospect of Kirkley’s abby, where Robin Hood dyed, from the footway leading to Heartishead church, at a quarter of a mile distance. A. The New Hall. B. The Gatehouse of the Nunnery. C. The trees among which Robin Hood was buryed. D. The way up the Hill were this was drawn. E. Bradley wood. F. Almondbury hill. G. Castle field. Drawn by Dr. Johnston among his Yorkshire Antiquitys, p. 54 of the drawings. E. Kirkall, sculp.” It makes plate 99 of the above work, but is unnoticed in the letterpress.
According to the Sloane MS., the prioress, after “letting him bleed to death, buryed him under a great stone by the hywayes syde;” which is agreeable to the account in Grafton’s Chronicle, where it is said that, after his death, “the prioresse of the same place caused him to be buried by the highway-side, where he had used to rob and spoyle those that passed that way. And vpon his grave the sayde prioresse did lay a very fayre stone, wherein the names of Robert Hood, William of Goldesborough, and others were graven. And the cause why she buryed him there was, for that the common passengers and travailers, knowyng and seeyng him there buryed, might more safely and without feare take their jorneys that way, which they durst not do in the life of the sayd outlawes. And at eyther ende of the sayde tombe was erected a crosse of stone, which is to be seene there at this present.”
“Near unto ‘Kirklees’ the noted Robin Hood lies buried under a grave-stone that yet remains near the park, but the inscription scarce legible” (Thoresby’s Ducatus Leodiensis, fo. 1715, p. 91). In the Appendix, p. 576, is the following note, with a reference to “page 91:”—
“Amongst the papers of the learned Dr. Gale, late dean of Yorke, was found this epitaph of Robin Hood:
![Hear
undernead dis laitl stean laiz robert earl of Huntingtun nea arcir
ver az hie sa geud an pipl kauld im robin heud sick utlawz az hi an
iz men vil england nivr si agen.
obiit 24 [r. 14] kal dekembris 1247.”](images/p-xlvi.jpg)
The genuineness of this epitaph has been questioned. Dr. Percy, in the first edition of his “Reliques of Ancient English Poetry” (1765), says “It must be confessed this epitaph is suspicious, because in the most ancient poems of Robin Hood there is no mention of this imaginary earldom.” This reason, however, is by no means conclusive, the most ancient poem now extant having no pretension to the antiquity claimed by the epitaph: and indeed the Doctor himself should seem to have afterward had less confidence in it, as, in both the subsequent editions, those words are omitted, and the learned critic merely observes that the epitaph appears to him suspicious. It will be admitted that the bare suspicion of this ingenious writer, whose knowledge and judgment of ancient poetry are so conspicuous and eminent, ought to have considerable weight. As for the present editor’s part, though he does not pretend to say that the language of this epitaph is that of Henry the Third’s time, nor indeed to determine of what age it is, he can perceive nothing in it from whence one should be led to pronounce it spurious, i.e. that it was never inscribed on the grave-stone of Robin Hood. That there actually was some inscription upon it in Thoresby’s time, though then scarce legible, is evident from his own words: and it should be remembered as well that the last century was not the era of imposition, as that Dr. Gale was both too good and too learned a man either to be capable of it himself or to be liable to it from others.
That industrious chronologist and topographer, as well as respectable artist and citizen, master Thomas Gent, of York, in his “List of religious houses,” annexed to “The ancient and modern state of” that famous city, 1730, 12mo, p. 234, informs us that he had been told “that his [Robin Hood’s] tombstone, having his effigy thereon, was order’d, not many years ago, by a certain knight to be placed as a harth-stone in his great hall. When it was laid overnight, the next morning it was ‘surprizingly’ removed [on or to] one side; and {xlviii} so three times it was laid, and as successively turned aside. The knight, thinking he had done wrong to have brought it thither, order’d it should be drawn back again; which was performed by a pair of oxen and four horses, when twice the number could scarce do it before. But as this,” adds the sagacious writer, “is a story only, it is left to the reader to judge at pleasure.” N.B.—This is the second instance of a miracle wrought in favour of our hero!
In Gough’s Sepulchral Monuments, p. cviii., is “the figure of the stone over the grave of Robin Hood [in Kirklees park, being a plain stone with a sort of cross fleuree thereon], now broken and much defaced, the inscription illegible. That printed in Thoresby, Ducat. Leod. 576, from Dr. Gale’s papers, was never on it.38 The late Sir Samuel Armitage owner of the premises, caused the ground under it to be dug a yard deep, and found it had never been disturbed; so that it was probably brought from some other place, and by vulgar tradition ascribed to Robin Hood” (refers to “Mr. Watson’s letter in Antiquary Society minutes”). This is probably the tomb-stone of Elizabeth de Staynton, mentioned in the preceding note.
The old epitaph is, by some anonymous hand, in a work entitled “Sepulchrorum inscriptiones; or a curious collection of 900 of the most remarkable epitaphs,” Westminster, 1727 (vol. ii. p. 73), thus not inelegantly paraphrased:
“Here, underneath this little stone,Thro’ Death’s assaults, now lieth one,Known by the name of Robin Hood,Who was a thief, and archer good;Full thirteen years, and something more,He robb’d the rich to feed the poor: {xlix}Therefore, his grave bedew with tears,And offer for his soul your prayers.” 39
(26) —“various dramatic exhibitions.”] The earliest of these performances now extant is “The playe of Robyn Hode, very proper to be played in Maye games,” which is inserted in the Appendix to this work, and may probably be as old as the 15th century. That a different play, however, on the same subject has formerly existed, seems pretty certain from a somewhat curious passage in “The famous chronicle of king Edward the first, sirnamed Edward Longshankes,” &c., by George Peele, printed in 1593.
“Lluellen . . . . . weele get the next daie from Brecknocke the booke of Robin Hood, the frier he shall instruct us in his cause, and weele even here . . . wander like irregulers up and down the wildernesse, ile be maister of misrule, ile be Robin Hood that once, cousin ‘Rice,’ thou shalt be little John, and hers frier David, as fit as a die for frier Tucke. Now, my sweet Nel, if you will make up the messe with a good heart for maide Marian, and doe well with Lluellen under the green-woode trees, with as good a wil as in the good townes, why plena est curia. [Exeunt.
Enter Mortimor, solus.Mortimor. . . . . . Maisters, have after gentle Robin Hood,You are not so well accompanied I hope,But if a potter come to plaie his part,Youle give him stripes or welcome good or worse.[Exit.Enter Lluellen, Meredith, frier, Elinor, and their traine. They are all clad in greene, &c. sing, &c. Blyth and bonny, the song ended, Lluellen speaketh.
Luellen. Why so, I see, my mates of olde,All were nor lies that Bedlams [beldams] told;Of Robin Hood and little John,Frier Tucke and maide Marian.”Mortimer, as a potter, afterwards fights the frier with “flailes.”
2. “The downfall of Robert earle of Huntington, afterward {l} called Robin Hood of merrie Sherwodde: with his love to chaste Matilda, the lord Fitzwater’s daughter, afterwardes his faire maide Marian. Acted by the right honourable, the earle of Notingham, lord high admirall of England, his servants. ¶ Imprinted at London, for William Leake, 1601.” 4to, b. l.
3. “The death of Robert, earle of Huntington, otherwise called Robin Hood of merrie Sherwodde: with the lamentable tragedie of chaste Matilda, his faire maid Marian, poysoned at Dunmowe, by king John. Acted, &c. ¶ Imprinted &c. [as above] 1601.” 4to, b. l.
These two plays, usually called the first and second part of Robin Hood, were always, on the authority of Kirkman, falsely ascribed to Thomas Heywood, till Mr. Malone fortunately retrieved the names of the true authors, Anthony Mundy and Henry Chettle.40 As they seem partly founded on traditions long since forgotten, and refer occasionally to documents not now to be found; at any rate, as they are much older than most of the common ballads upon the subject, and contain some curious and possibly authentic particulars not elsewhere to be met with, the reader will excuse the particularity of the account and length of the extracts here given.
The first part, or downfall of Robert earle of Huntington, is supposed to be performed at the court and command of Henry VIII., the poet Skelton being the dramatist, and {li} acting the part of chorus. The introductory scene commences thus:
“Enter Sir John Eltam, and knocke at Skelton’s doore.Sir John. Howe, maister Skelton! what, at studie hard?[Opens the doore.Skel. Welcome and wisht for, honest Sir John Eltam,—Twill trouble you after your great affairs,[i.e. the surveying of certain maps which his majesty had employed him in;To take the paine that I intended to intreate you to,About rehearsall of your promis’d play.Elt. Nay, master Skelton; for the king himselfe,As wee were parting, bid mee take great heedeWee faile not of our day: therefore I praySende for the rest, that now we may rehearse.Skel. O they are readie all, and drest to play.What part play you?Elt. Why, I play little John,And came of purpose with this greene sute.Skel. Holla, my masters, little John is come.[At every doore all the players runne out: some crying where? where? others, Welcome, Sir John: among others the boyes and clowne.Skel. Faith, little Tracy, you are somewhat forward.What, our maid Marian leaping like a lad!If you remember, Robin is your love,Sir Thomas Mantle yonder, not Sir John.Clow. But, master, Sir John is my fellowe, for I am Much themiller’s sonne. Am I not?Skel. I know yee are, sir:—And, gentlemen, since you are thus prepar’d,Goe in, and bring your dumbe scene on the stage.And I, as prologue, purpose to expresseThe ground whereon our historie is laied.[Exeunt, manet Skelton.Trumpets sounde, [1] enter first King Richard with drum and auncient, giving Ely a purse and sceptre, his mother and brother John, Chester, Lester, Lacie, others at the king’s appointment, doing reverence. The king goes in: presently Ely ascends the chaire, Chester, John, and the queene part displeasantly. [2] Enter ROBERT, EARLE OF HUNTINGTON, leading Marian; followes him Warman, and after Warman, the prior; Warman ever flattering and making curtsie, taking gifts of the prior behinde and his master before. Prince John enters, offereth to take Marian; Queen Elinor enters, offering to pull Robin from her; but they infolde each other, and sit downe within the curteines. [3] Warman with the prior, Sir Hugh Lacy, Lord Sentloe, and Sir Gilbert Broghton folde hands, and drawing the curteins, all (but the prior) enter, and are kindely received by Robin Hoode.”
During the exhibition of the second part of the dumb show, Skelton instructs the audience as follows:
“This youth that leads yon virgin by the handIs our earle Robert, or your Robin Hoode,That in those daies was earle of Huntington;The ill-fac’t miser, brib’d in either hand,Is Warman, once the steward of his house,Who, Judas like, betraies his liberall lord,Into the hands of that relentlesse prior,Calde Gilbert Hoode, uncle to Huntington.Those two that seeke to part these lovely friends,Are Elenor the queene, and John the prince,She loves earle Robert, he maide Marian,But vainely; for their deare affect is such,As only death can sunder their true loves.Long had they lov’d, and now it is agreed,This day they must be troth-plight, after wed:At Huntington’s faire house a feast is helde,But envie turnes it to a house of teares.For those false guestes, conspiring with the prior;To whom earle Robert greatly is in debt,Meane at the banquet to betray the earle,Unto a heavie writ of outlawry:The manner and escape you all shall see.Looke to your entrance, get you in, Sir John.My shift is long, for I play Frier Tucke;Wherein, if Skelton hath but any lucke,Heele thanke his hearers oft with many a ducke.For many talk of Robin Hood that never shot in his bowe,But Skelton writes of Robin Hood what he doth truly knowe.”
After some Skeltonical rimes, and a scene betwixt the prior, the sheriff, and justice Warman, concerning the outlawry, which appears to be proclaimed, and the taking of Earl Huntington at dinner, “Enter Robin Hoode, little John following him; Robin having his napkin on his shoulder, as if hee were sodainly raised from dinner.” He is in a violent rage at being outlawed, and Little John endeavours to pacify him. Marian being distressed at his apparent disorder, he dissembles with her. After she is gone, John thus addresses him:
“Now must your honour leave these mourning tunes,And thus by my areede you shall provide; {liii}Your plate and jewels ‘i wil’ straight packe up,And toward Notingham convey them hence.At Rowford, Sowtham, Wortley, Hothersfield,Of all your cattell mony shall be made,And I at Mansfield will attend your comming;Where weele determine which waie’s best to take.Rob. Well, be it so; a God’s name, let it be;And if I can, Marian shall come with mee.John. Else care will kill her; therefore if you please,At th’ utmost corner of the garden wall,Soone in the evening waite for Marian,And as I goe ile tell her of the place.Your horses at the Bell shall readie bee,I meane Belsavage,41 whence, as citizensThat ‘meane’ to ride for pleasure some small way,You shall set foorth.”
The company now enters, and Robin charges them with the conspiracy, and rates their treacherous proceedings. Little John in attempting to remove the goods is set upon by Warman and the sheriff; and during the fray “Enter Prince John, Ely and the prior, and others.” Little John tells the prince he but defends the box containing his own gettings; upon which his royal highness observes,
“You do the fellow wrong; his goods are his:You only must extend upon the earles.Prior. That was, my lord, but nowe is Robert Hood,A simple yeoman as his servants were.”
Ely gives the prior his commission, with directions to make speed, lest “in his country-house all his heards be solde;” and gives Warman a patent “for the high sheriffewick of Nottingham.” After this, “Enter Robin like a citizen; and then the queen and Marian disguised for each other. Robin takes Marian, and leaves the queen to Prince John, who is {liv} so much enraged at the deception that he breaks the head of Ely’s messenger. Sir Hugh, brother to Lord Lacy, and steward to Ely, who had been deeply concerned in Huntington’s ruin, is killed in a brawl by Prince John, whom Ely orders to be arrested; but the prince, producing letters from the king revoking Ely’s appointment, “lifts up his drawne sworde,” and “Exit, cum Lester and Lacy,” in triumph. Then “Enter Robin Hoode, Matilda at one doore, little John and Much the Miller’s sonne at another doore.” After mutual congratulations, Robin asks if it be
“possible that Warman’s spite
Should stretch so farre, that he doth hunt the livesOf bonnie Scarlet, and his brother Scathlock?Much. O, I, sir. Warman came but yesterday to take charge of the jaile at Notingham, and this daie, he saies, he will hang the two outlawes. . . .
Rob. Now, by my honour’s hope, . . .He is too blame: say, John, where must they die?John. Yonder’s their mother’s house, and here the tree,Whereon, poore men, they must forgoe their lives;And yonder comes a lazy lozell frier,That is appointed for their confessor,Who, when we brought your monie to their mother’s,Was wishing her to patience for their deaths.”
Here “Enter Frier Tucke;” some conversation passes, and the frier Skeltonizes; after which he departs, saying,
“let us goe our way,
Unto this hanging businesse; would for meeSome rescue or repreeve might set them free.Rob. Heardst thou not, little John, the frier’s speach?John. He seemes like a good fellow, my good lord.Rob. He’s a good fellowe, John, upon my word.Lend me thy horne, and get thee in to Much,And when I blowe this horne, come both and helpe mee.John. Take heed, my lord: the villane Warman knows you,And ten to one he hath a writ against you.Rob. Fear not: below the bridge a poor blind man doth dwell,With him I will change my habit, and disguise,Only be readie when I call for yee,For I will save their lives, if it may bee. . . .{lv}Enter Warman, Scarlet and Scathlock bounde, Frier Tuck as their confessor, officers with halberts.War. Master frier, be briefe, delay no time.Scarlet and Scatlock, never hope for life;Here is the place of execution,And you must answer lawe for what is done.Scar. Well, if there be no remedie, we must:Though it ill seemeth, Warman, thou shouldst bee,So bloodie to pursue our lives thus cruellie.Scat. Our mother sav’d thee from the gallows, Warman,His father did preferre thee to thy lord:One mother had wee both, and both our fathersTo thee and to thy father were kinde friends. . . .War. Ye were first outlawes, then ye proved theeves. . . .Both of your fathers were good honest men;Your mother lives their widowe in good fame:42But you are scapethrifts, unthrifts, villanes, knaves,And as ye liv’d by shifts, shall die with shame.”
To them enters Ralph, the sheriff’s man, to acquaint him that the carnifex, or executor of the law, had fallen off his “curtall” and was “cripplefied” and rendered incapable of performing his office; so that the sheriff was to become his deputy. The sheriff insists that Ralph shall serve the turn, which he refuses. In the midst of the altercation, “Enter Robin Hoode, like an old man,” who tells the sheriff that the two outlaws had murdered his young son, and undone himself; so that for revenge-sake he desires they may be delivered to him. They denying the charge, “Robin whispers with them,” and with the sheriff’s leave, and his man’s help, unbinds them: then, sounds his horn; and “Enter little John, Much . . . Fight; the frier, making as if he helpt the sheriffe, knockes down his men crying, Keepe the king’s peace. Sheriffe [perceiving that it is “the outlawed earle of Huntington”] runnes away, and his men.” (See the ballad of “Robin Hood rescuing the widow’s sons,” part ii. num. xxiii.) {lvi}
“Fri. Farewell, earle Robert, as I am true frier,I had rather be thy clarke then serve the prior.Rob. A jolly fellowe! Scarlet, knowest thou him?Scar. Hee is of Yorke, and of Saint Maries cloister;There where your greedie uncle is lord prior. . . .Rob. Here is no biding, masters; get yee in. . . .John, on a sodaine thus I am resolv’d.To keepe in Sherewoodde tille the king’s returne,And being outlawed, leade an outlawe’s life. . . .John. I like your honour’s purpose exceeding well.Rob. Nay, no more honour, I pray thee, little John;Henceforth I will be called Robin Hoode,Matilda shall be my maid Marian.”
Then follows a scene betwixt old Fitzwater and Prince John, in the course of which the prince, as a reason to induce Fitzwater to recall his daughter Matilda, tells him that she is living in an adulterous state, for that
“—Huntington is excommunicate,And till his debts be paid, by Rome’s decree,It is agreed, absolv’d he cannot be;And that can never be.—So never wife,” &c.
Fitzwater, on this, flies into a passion, and accuses the prince of being already married to “earle Chepstowe’s daughter.” They “fight; John falles.” Then enter the queen, &c., and John sentences Fitzwater to banishment: after which “Enter Scathlocke and Scarlet, winding their hornes at severall doores. To them enter Robin Hoode, Matilda, all in greene . . . Much, little John; all the men with bowes and arrowes.43
“Rob. Wind once more, jolly huntsmen, all your horns,Whose shrill sound, with the ecchoing wods assist,Shall ring a sad knell for the fearefull deere,Before our feathered shafts, death’s winged darts,Bring sodaine summons for their fatall ends. {lvii}Scar. Its ful seaven years since we were outlawed first,And wealthy Sherewood was our heritage:For all those yeares we raigned uncontrolde,From Barnsdale shrogs to Notingham’s red cliffes.At Blithe and Tickhill were we welcome guests:Good George a Greene at Bradford was our friend,And wanton Wakefield’s pinner lov’d us well.44At Barnsley dwels a potter, tough and strong,That never brookt we brethren should have wrong.The nunnes of Farnsfield (pretty nunnes they bee)Gave napkins, shirts, and bands to him and mee.Bateman of Kendall gave us Kendall greene;And Sharpe of Leedes sharpe arrows for us made.At Rotherham dwelt our bowyer, God him blisse,Jackson he hight, his bowes did never misse.This for our goode, our scathe let Scathlocke tell,In merry Mansfield how it once befell.Scath. In merry Mansfield, on a wrestling day,Prizes there were, and yeomen came to play,My brother Scarlet and myselfe were twaine;Many resisted, but it was in vaine,For of them all we wonne the mastery,And the gilt wreathes were given to him and me.There by Sir Doncaster of ‘Hothersfield,’We were bewraied, beset, and forst to yield;And so borne bound from thence to Notingham,Where we lay doom’d to death till Warman came.”
Some cordial expressions pass between Robin and Matilda. He commands all the yeomen to be cheerful; and orders Little John to read the articles.
“Joh. First, no man must presume to call our master,By name of earle, lorde, baron, knight, or squire:But simply by the name of Robin Hoode.That faire Matilda henceforth change her name,‘And’ by maid Marian’s name be only cald.Thirdly, no yeoman following Robin HoodeIn Sherewood, shall use widowe, wife, or maid,But by true labour, lustfull thoughts expell.Fourthly, no passenger with whom ye meete,Shall yee let passe till hee with Robin feaste:Except a poast, a carrier, or such folke,As use with foode to serve the market townes.Fiftly, you never shall the poore man wrong. {lviii}Nor spare a priest, a usurer, or a clarke.Lastly, you shall defend with all your powerMaids, widowes, orphants, and distressed men.All. All these we vowe to keepe, as we are men.Rob. Then wend ye to the greenewod merrily,And let the light roes bootlesse from yee runne,Marian and I, as soveraigns of your toyles,Will wait, within our bower, your bent bowes spoiles.[Exeunt winding their hornes.”
In the next scene, we find Frier Tucke feignedly entering into a conspiracy with the prior and Sir Doncaster to serve an execution on Robin in disguise. Jinny, the widow Scarlet’s daughter, coming in on her way to Sherwood, is persuaded by the frier to accompany him, “disguised in habit like a pedler’s mort.” Fitzwater enters like an old man:—sees Robin sleeping on a green bank, Marian strewing flowers on him; pretends to be blind and hungry, and is regaled by them. In answer to a question why the fair Matilda (Fitzwater’s daughter) had changed her name, Robin tells him it is
“Because she lives a spotlesse maiden life:And shall, till Robin’s outlawe life have ende,That he may lawfully take her to wife;Which, if King Richard come, will not be long.”
“Enter Frier Tucke and Jinny like pedlers singing,” and afterward “Sir Doncaster and others weaponed.” The frier discovers the plot, and a fray ensues. The scene then changes to the court, where the prior is informed of six of his barns being destroyed by fire, and of the different execrations of all ranks upon him, as the undoer of “the good lord Robert, earle of Huntington;” that the convent of St. Mary’s had elected “Olde father Jerome” prior in his place; and lastly, a herald brings his sentence of banishment, which is confirmed by the entrance of the prior. Lester brings an account of the imprisonment of his gallant sovereign, King Richard, by the Duke of Austria, and requires his ransom to be sent. He then introduces a description of his matchless valour in the Holy Land. John not only refuses the ransom-money, but usurps the style of king; upon which Lester grows furious, {lix} and rates the whole company. The following is part of the dialogue:
“Joh. (to Lester). Darest thou attempt thus proudly in our sight?Lest. What is’t a subject dares, that I dare not?Sals. Dare subjects dare, their soveraigne being by?Lest. O God, that my true soveraigne were ny!Qu. Lester, he is.Lest. Madame, by God, you ly.Chest. Unmanner’d man.Lest. A plague of reverence!”
After this, and more on the same subject, the scene returns to the forest, where Ely, being taken by Much, “like a countryman with a basket,” is examined and detected by Robin, who promises him protection and service. On their departure:
“Joh. Skelton, a worde or two beside the play.Fri. Now, Sir John Eltam, what ist you would say?John. Methinks I see no jeasts of Robin Hoode,No merry morices of Frier Tuck,No pleasant skippings up and downe the wodde,No hunting songs, no coursing of the bucke:Pray God this play of ours may have good lucke,And the king’s majestie mislike it not!Fri. And if he doe, what can we doe to that?I promis’d him a play of Robin Hoode,His honorable life, in merry Sherewod;His majestie himselfe survaid the plot,And bad me boldly write it, it was good.For merry jeasts, they have bene showne beforeAs how the frier fell into the well,For love of Jinny, that faire bonny bell:How Greeneleafe rob’d the shrieve of Notingham,And other mirthful matter, full of game.”
“Enter Warman banished.” He laments his fall, and applies to a cousin, on whom he had bestowed large possessions, for relief; but receives nothing, except reproaches for his treachery to his noble master. The jailor of Nottingham, who was indebted to him for his place, refuses him even a scrap of his dog’s meat, and reviles him in the severest terms. Good-wife Tomson, whose husband he had delivered from death, to his great joy, promises him a caudle, but {lx} fetches him a halter,45 in which he is about to hang himself, but is prevented by Fitzwater, and some of Robin Hood’s men, who crack a number of jokes upon him; Robin puts an end to their mockery, and proffers him comfort and favour. Then enters Frier Tucke, with an account of Sir Doncaster and the prior being stripped and wounded in their way to Bawtrey: Robin, out of love to his uncle, hastens to the place. After this “Enter Prince John, solus, in green, bowe and arrowes.
“John. Why this is somewhat like, now may I sing,As did the Wakefield pinder in his note;At Michaelmas commeth my covenant out,My master gives me my fee:Then Robin Ile weare thy Kendall greene,And wend to the greenewodde with thee.” 46
He assumes the name of Woodnet, and is detected by Scathlocke and Frier Tucke. The prince and Scathlocke fight, Scathelocke grows weary, and the frier takes his place. Marion enters, and perceiving the frier, parts the combatants. Robin enters, and John submits to him. Much enters, running, with information of the approach of “the king and twelve and twenty score of horses.” Robin places his people in order. The trumpets sound, the king and his train enter, a general pardon ensues, and the king confirms the love of Robin and Matilda. Thus the play concludes, Skelton promising the second part, and acquainting the audience of what it should consist.
The second part, or death of Robert earle of Huntington, is a pursuit of the same story. The scene, so far as our hero is concerned, lyes in Sherwood. A few extracts may not be unacceptable. {lxi}
“Sc. iiii. Winde hornes. Enter king, queene, &c. Frier Tuck carrying a stag’s head, dauncing.” The frier has been sent for to read the following incription upon a copper ring round the stag’s neck:
“When Harold Hare-foote raigned king,About my necke he put this ring.”
The king orders “head, ring, and all” to be sent to Nottingham Castle, to be kept for monuments. Fitzwater tells him he has heard “an olde tale,”
“That Harold, being Goodwin’s sonne of Kent,47Hunted for pleasure once within this wood,And singled out a faire and stately stagge,Which, foote to foote, the king in running caught;And sure this was the stagge.King. It was no doubt.Chester. But some, my lord, affirme,That Julius Cæsar, many years before,Tooke such a stagge, and such a poesie writ.” 48 {lxii}
Upon which his majesty very sagaciously remarks,
“It should not be in Julius Cæsar’s time:There was no English used in this landUntill the Saxons came, and this is writIn Saxon characters.”
The next quotation may be of service to Dr. Percy, who {lxiii} has been pleased to question our hero’s nobility, because “the most ancient poems make no mention of this earldom,” and the old legend expressly asserts him “to have been a yeoman.” It is very true; and we shall here not only find his title established, but also discover the secret of his not being usually distinguished or designed by it.
“Enter Roben Hoode.King. How now, earle Robert!Fri. A forfet, a forfet, my liege lord,My master’s lawes are on record,The court-roll here your grace may see.King. I pray thee, frier, read them mee.Fri. One shall suffice, and this is hee.No man that commeth in this wod,To feast or dwell with Robin Hood,Shall call him earle, lord, knight, or squire,He no such titles doth desire,But Robin Hood, plain Robin Hoode,That honest yoeman, stout and good,On paine of forfetting a marke,That must be paid to mee his clarke.My liege, my liege, this lawe you broke,Almost in the last word you spoke;That crime may not acquitted bee,Till Frier Tuck receive his fee.”
Now, the reason that “the most ancient poems make no mention of this earldom,” and the old legend expressly asserts him “to have been a yeoman,” appears, plainly enough, to be, that as, pursuant to his own injunction, he was never called, either by his followers, or in the vicinity, by any other name than Robin Hood, so particularly the minstrels, who were always, no doubt, welcome to Sherwood,49 {lxiv} and liberally entertained by him and his yeomanry, would take special care never to offend against the above law: which puts an end to the dispute.—Q. E. D.
Our hero is, at length, poisoned by a drink which Doncaster and the prior, his uncle, had prepared for him to give to the king. His departing scene and last dying speech are beautiful and pathetic.
“Rob. Inough, inough, Fitzwater, take your child.My dying frost, which no sunnes heat can thawe,Closes the powers of all my outward parts;My freezing blood runnes back into my heart,Where it assists death, which it would resist:Only my love a little hinders death,For he beholds her eyes, and cannot smite.Mat. O let mee looke for ever in thy eyes,And lay my warme breath to thy bloodlesse lips,If my sight can restraine death’s tyrannies,Or keep lives breath within thy bosome lockt.”
He desires to be buried
“At Wakefield, underneath the abbey-wall;”
directs the manner of his funeral; and bids his yeomen,
“For holy dirges, sing ‘him’ wodmen’s songs.”
The king, upon the earl’s death, expresses his sorrow for the tragical event; ratifies the will; repeats the directions for the funeral; and says,
“Fall to your wod-songs, therefore, yeomen bold,And deck his herse with flowers, that lov’d you deere.”
The whole concludes with the following solemn dirge:
“Weepe, weepe, ye wod-men waile,Your hands with sorrow wring;Your master Robin Hood lies deade,Therefore sigh as you sing. {lxv}“Here lies his primer, and his beades,His bent bowe, and his arrowes keene,His good sworde and his holy crosse:Now cast on flowers fresh and greene.“And, as they fall, shed teares and say,Well a, well a day, well a, well a day!Thus cast yee flowers and sing,And on to Wakefield take your way.”
The poet then prosecutes the legend of Matilda, who is finally poisoned, by the procurement of King John, in Dunmow Priory.
The story of this lady, whom the author of these plays is supposed to have been the first that converted into the character of Maid Marian, or connected in any shape with the history of Robin Hood, is thus related by Stow, under the year 1213: “The chronicle of Dunmow sayth, this discord arose betwixt the king and his barons, because of Mawd called the faire, daughter to Robert Fitzwalter, whome the king loved, but her father would not consent; and thereupon ensued warre throughout England. . . . . . Whilst Mawd the faire remayned at Dunmow, there came a messenger unto her from King John about his suite in love, but because she would not agree, the messenger poysoned a boyled or potched egge against she was hungrie, whereof she died” (Annales, 1592). Two of Drayton’s heroical epistles pass between King John and Matilda. He has also written her legend.
4. “Robin Hood’s penn’orths, by Wm. Haughton.” 50
5. “Metropolis coronata, the triumphs of ancient drapery: or, rich cloathing of England, in a second yeeres performance. In honour of the advancement of Sir John Jolles, knight, to the high office of lord maior of London, and taking his oath for the same authoritie, on Monday being the 30. day of October, 1615. Performed in heartie affection to him, and at the bountifull charges of his worthy brethren the truely honourable society of drapers, the first that received such dignitie, in this citie. Devised and written by A. M. {lxvi} [Anthony Mundy] citizen and draper of London.” 1615, 4to.
This is one of the pageants formerly usual on Lord Mayor’s day, and of which several are extant, written as well by our author Mundy,51 as by Middleton, Dekker, Heywood, and other hackney dramatists of that period. They were thought of such consequence that the City had for some time (though probably not till after the Restoration) a professed laureat for their composition; an office which expired with Elkanah Settle in 1723–24. They consisted chiefly of machinery, allegorical or historical personages, songs and speeches.
“After all these shewes, thus ordered in their appointed places, followeth another device of huntsmen, all clad in greene, with their bowes, arrowes and bugles, and a new slaine deere, carried among them. It savoureth of earle Robert de la Hude, sometime the noble earle of Huntington, and sonne in law (by marriage) to old Fitz-Alwine,52 raised by the muses all-commanding power, to honour this triumph with his father. During the time of his out-lawed life in the forest of merry Shirwood, and elsewhere, while the cruel oppression of a most unnatural and covetous brother hung heavy upon him, Gilbert de la Hude, lord abbot of Christall [r. Kirkstall] abbey, who had all or most of his lands in mortgage: he was commonly called Robin Hood, and had a gallant company of men (out-lawed in the like manner) that followed his downecast fortunes; as little John, Scathlocke, Much the miller’s son, Right-hitting Brand, fryar Tuck, and many more. In which condition of life we make instant use of him, and part of his brave bowmen, fitted with bowes and arrowes, of the like strength and length, as good records {lxvii} deliver testimonie, were then used by them in their killing of deere. . . . .
“Afterward, [viz. after “Fitz-Alwine’s speech to the lord maior at night,”] as occasion best presenteth itselfe, when the heate of all other employments are calmly overpast, earle Robin Hood, with fryer Tuck, and his other brave huntesmen, attending (now at last) to discharge their duty to my lord, which the busie turmoile of the whole day could not before affoord: they shewe themselves to him in this order, and earle Robin himselfe thus speaketh.
The speech spoken by Earl Robert de la Hude,
commonly called Robin Hood.Since graves may not their dead containe,Nor in their peacefull sleepes remaine,But triumphes and great showes must use them,And we unable to refuse them;It joyes me that earle Robert Hood,Fetcht from the forrest of merrie Shirwood,With these my yeomen tight and tall,Brave huntsmen and good archers all,Must in this joviall day partake,Prepared for your honour’s sake.No sooner was i raysde from rest,And of my former state possestAs while i liv’d, but being alone,And of my yeomen seeing not one,I with my bugle gave a call,Made all the woods to ring withall.Immediately came little John,And Scathlock followed him anon,With Much the honest miller’s sonne;And ere ought else could be done,The frollicke frier came tripping in,His heart upon a merrie pinne.Master (quoth he) in yonder brake,A deere is hid for Marian’s sake,Bid Scathlock, John, or honest Brand,That hath the happy hitting hand,Shoote right and have him: and see, my lord,The deed performed with the word.For Robin and his bow-men bold,Religiously did ever holde,Not emptie-handed to be seene,Were’t but at feasting on a greene; {lxviii}Much more then, when so high a dayCalls our attendance: all we mayIs all too little, tis your graceTo winke at weakenesse in this case:So, fearing to be over-long,End all with our old hunting song.
The song of Robin Hood and his huntes-men.
Now wend we together, my merry men all,Unto the forrest side a;And there to strike a buck or a doae,Let our cunning all be tried a.Then goe we merrily, merrily on,To the green-wood to take up our stand [a],Where we will lye in waite for our game,With our best bowes all in our hand [a].What life is there like to bold Robin Hood?It is so pleasant a thing a:In merry Shirwood he spends his dayes,As pleasantly as a king a.No man may compare with bold Robin Hood,With Robin Hood, Scathlocke and John [a]:Their like was never, nor never will be,If in case that they were gone [a].They will not away from merry Shirwood,In any place else to dwell [a]:For there is neither city nor towne,That likes them half so well [a].Our lives are wholly given to hunt,And haunt the merry greene-wood [a];Where our best service is daily spent,For our master Robin Hood [a].”
6. “Robin Hood and his pastoral May games.” 1624.
7. “Robin Hood and his crew of soldiers.” 1627.
These two titles are inserted among the plays mentioned by Chetwood in his British Theatre (p. 67) as written by anonymous authors in the 16th century to the Restoration. But neither Langbaine, who mentions both, nor any other person, pretends to have ever seen either of them. The former, indeed, may possibly be “The playe of Robyn {lxix} Hode,” already noticed; and the other is probably a future article. Langbaine, it is to be observed, gives no date to either piece; so that it may be fairly concluded those above specified are of Chetwood’s own invention, which appears to have been abundantly fertile in every species of forgery and imposture.
8. “The sad shepherd, or a tale of Robin Hood.”
The story of our renowned archer cannot be said to have been wholly occupied by bards without a name, since, not to mention Mundy or Drayton, the celebrated Ben Jonson intended a pastoral drama on this subject, under the above title; but dying, in the year 1637, before it was finished, little more than the two first acts have descended down to us. His last editor (Mr. Whalley), while he regrets that it is but a fragment, speaks of it in raptures, and, indeed, not without evident reason, many passages being eminently poetical and judicious.
“The persons of the play,” so far as concerns our immediate purpose, are: [1] “Robin Hood, the chief woodman [i.e. forester], master of the feast. [2] Marian, his lady, the mistress. [3] Friar Tuck, the chaplain and steward. [4] Little John, bow-bearer. [5, 6] Scarlet, Scathlocke,53 two brothers, huntsmen. [7] George a Green, huisher of the bower. [8] Much, Robin Hood’s bailiff or acater.” The rest are the guests invited, the witch of Paplewick, her daughter, the swin’ard her son, Puck Hairy or Robin Goodfellow, their hind, and lastly a devout hermit. “The scene, Sherwood, consisting of a landscape of a forest, hills, valleys, cottages, a castle, a river, pastures, herds, flocks, all full of country simplicity; Robin Hood’s bower, his well, &c.” “The argument of the first act” is as follows: “Robin Hood, having invited all the shepherds and shepherdesses of the vale of Be’voir to a feast in the forest of Sherwood, and trusting to his mistress, Maid Marian, with her woodmen, to kill him venison against the day; having left the like charge with Friar Tuck, his chaplain and steward, to command the rest of his merry men to see the bower made {lxx} ready, and all things in order for the entertainment: ‘meets’ with his guests at their entrance into the wood, and conducts them to his bower: where, by the way, he receives the relation of the sad shepherd Æglamour, who is fallen into a deep melancholy for the loss of his beloved Earine, reported to have been drowned in passing over the Trent, some few days before. . . . . In the meantime Marian is come from hunting. . . . . Robin Hood inquires if she hunted the deere at force, and what sport he made? how long he stood? and what head he bore? all which is briefly answered, with a relation of breaking him up, and the raven, and her bone. The suspect had of that raven to be Maudlin the witch of Paplewick, whom one of the huntsmen met i’ the morning at the rousing of the deer, and is confirmed by her being then in Robin Hood’s kitchen, i’ the chimney corner, broiling the same bit which was thrown to the raven at the quarry or fall of the deer. Marian, being gone in to shew the deer to some of the shepherdesses, returns discontented; sends away the venison she had killed to her they call the witch; quarrels with her love Robin Hood, abuseth him, and his guests the shepherds; and so departs, leaving them all in wonder and perplexity.”
By “the argument of the second act” it appears that the witch had “taken the shape of Marian to abuse Robin Hood and perplex his guests.” However, upon an explanation of the matter with the true Marian, the trick is found out, the venison recovered, and “Robin Hood dispatches out his woodmen to hunt and take her: which ends the act.” The third act was designed to be taken up with the chase of the witch, her various schemes to elude the pursuers, and the discovery of Earine in the swineherd’s enchanted oak. Nothing more of the author’s design appearing, we have only to regret the imperfect state of a pastoral drama, which, according to the above learned and ingenious editor, would have done honour to the nation.54 {lxxi}
9. “Robin Hood and his crew of souldiers, a comedy acted at Nottingham on the day of his saCRed majesties corronation. Vivat rex. The actors names: Robin Hood, commander; Little John, William Scadlocke, souldiers; messenger from the sheriffe. London, printed for James Davis, 1661.” 4to.
This is an interlude, of a few pages and no merit, alluding to the late rebellion, and the subject of the day. The outlaws, convinced by the reasoning of the sheriff’s messenger, become loyal subjects.
10. “Robin Hood. An opera, as it is perform’d at Lee’s and Harper’s great theatrical booth in Bartholomew-fair.” 1730. 8vo.
11. “Robin Hood.” 1751. 8vo.
This was a ballad-farce, acted at Drury-lane Theatre, in which the following favourite song was originally sung by Mr. Beard, in the character of Robin Hood:
As blithe as the linnet sings in the green wood,So blithe we’ll wake the morn;And through the wide forest of merry SherwoodWe’ll wind the bugle horn.The sheriff attempts to take bold Robin Hood,Bold Robin disdains to fly;Let him come when he will, we’ll, in merry Sherwood,Or vanquish, boys, or die.Our hearts they are stout, and our bows they are good,As well their masters know;They’re cull’d in the forest of merry Sherwood,And never will spare a foe.Our arrows shall drink of the fallow deer’s blood,We’ll hunt them all o’er the plain!And through the wide forest of merry Sherwood,No shaft shall fly in vain.Brave Scarlet, and John, who ne’er were subdu’d,Give each his hand so bold;We’ll range through the forest of merry Sherwood,What say my hearts of gold?
12. “Robin Hood; or Sherwood forest: a comic opera. As performed at the theatre-royal in Covent-garden. By Leonard Mac Nally, esq.” 1784. 8vo. {lxxii}
This otherwise insignificant performance was embellished with some fine music by Mr. Shield. It has been since reduced to, and is still frequently acted as, an after-piece.
A drama on the subject of Robin Hood, under the title of The Foresters, has been long expected from the elegant author of The School for Scandal. The first act, said to have been written many years ago, is, by those who have seen or heard it, spoken of with admiration.55
(27) —“innumerable poems, rimes, songs and ballads.”] The original and most ancient pieces of this nature have all perished in the lapse of time, during a period of between five and six hundred years’ continuance; and all we now know of them is that such things once existed. In the Vision of Pierce Plowman, an allegorical poem, thought to have been composed soon after the year 1360, and generally ascribed to Robert Langeland, the author introduces an ignorant, idle, and drunken secular priest, the representative, no doubt, of the parochial clergy of that age, in the character of Sloth, who makes the following confession:
“I cannot parfitli mi paternoster, as the preist it singeth,But I can ryms of Roben Hode, and ‘Randolf’ erl of Chester,But of our lorde or our lady I lerne nothyng at all.” 56
Fordun, the Scotish historian, who wrote about 1340, speaking of Robin Hood and Little John, and their accomplices, says, “of whom the foolish vulgar in comedies and tragedies make lewd entertainment, and are delighted to hear the jesters and minstrels sing them above all other ballads;” 57 and Mair (or Major), whose history was published by himself in 1521, observes that “The exploits of this Robert are celebrated in songs throughout all Britain.” 58 So, likewise, Maister Johne Bellendene, the translator of “that noble clerk Maister Hector Boece” (Bois or Boethius), having mentioned “that waithman Robert Hode with his fallow litil Johne,” adds, “of quhom ar mony fabillis and mery sportis soung amang the vulgar pepyll.” 59 Whatever may have been the nature of the compositions alluded to by the above writers, several of the pieces printed in the present collection are {lxxiv} unquestionably of great antiquity; not less, that is, than between three and four hundred years old. The Lytell Geste, which is first inserted, is probably the oldest thing upon the subject we now possess;60 but a legend, apparently of the same species, was once extant, of, perhaps, a still earlier date, of which it is some little satisfaction to be able to give even the following fragment, from a single leaf, fortunately preserved in one of the volumes of old printed ballads in the British Museum, in a handwriting as old as Henry the Sixth’s time. It exhibits the characters of our hero and his fidus Achates in the noblest point of view.
“He sayd Robyn Hod . . . . yne the preson,And owght off hit was gon.The porter rose a-non certeyn,As sone as he hard Johan call;Lytyll Johan was redy with a sword,And bare hym throw to the wall.Now will I be jayler, sayd lytyll Johan,And toke the keys in hond;He toke the way to Robyn Hod,And sone he hyme unbond.He gaffe hym a good swerd in his hond,His hed ther-with for to kepe;And ther as the wallis wer lowest,Anon down ther they lepe.To Robyn . . . . . sayd:I have done the a god torne for an . . .Quit me when thow may;I have done the a gode torne, sayd lytyll [Johan],Forsothe as I the saye; {lxxv}I have browghte the under the gren wod . . .Farewell & have gode daye.Nay, be my trowthe, sayd Robyn,So schall it never bee;I make the master, sayd Robyn,Off all my men & me.Nay, be my trowthe, sayd lytyll Johan,So schall it never bee.”
This, indeed, may be part of the “story of Robin Hood and Little John,” which M. Wilhelm Bedwell found in the ancient MS. lent him by his much honoured good friend M. G. Withers, whence he extracted and published “The Turnament of Tottenham,” a poem of the same age, and which seemed to him to be done (perhaps but transcribed) by Sir Gilbert Pilkington, formerly, as some had thought, parson of that parish.61
That poems and stories on the subject of our hero and his companions were extraordinarily popular and common before and during the 16th century is evident from the testimony of divers writers. Thus, Alexander Barclay, priest, in his translation of The Shyp of Folys, printed by Pynson in 1508, and by John Cawood in 1570,62 says:
“I write no jeste ne tale of Robin Hood.”
Again:
“For goodlie scripture is not worth an hawe,But tales are loved ground of ribaudry;And many are so blinded with their foly,That no scriptur thinke they so true nor gode,As is a foolish jest of Robin Hode.”
Again:
“And of all fables and jestes of Robin Hood,Or other trifles.”
The same Barclay, in the fourth of his Egloges, subjoined to the last edition of The Ship of Foles, but originally printed soon after 1500, has the following passage:
“Yet would I gladly heare some mery fitOf maide Marion, or els of Robin Hood,Or Benteleyes ale, which chafeth well the blood,Of Perte of Norwich, or Sauce of Wilberton,Or buckishe Joly63 well stuffed as a ton.”
Robert Braham, in his epistle to the reader, prefixed to Lydgate’s Troy-book, 1555, is of opinion that “Caxton’s recueil” [of Troy] is “worthye to be numbred amongest the trifelinge tales and barrayne luerdries of Robyn Hode and Bevys of Hampton.” (See Ames’s Typographical Antiquities, by Herbert, p. 849.)
“For one that is sand blynd,” says Sir Thomas Chaloner, “would take an asse for a moyle, or another prayse a rime of Robyn Hode for as excellent a making as Troylus of Chaucer, yet shoulde they not straight-waies be counted madde therefore?” (Erasmus’s Praise of Folye, sig. h.)
“If good lyfe,” observes Bishop Latimer, “do not insue and folowe upon our readinge to the example of other, we myghte as well spende that tyme in reading of prophane hystories, of Canterburye tales, or a fit of Roben Hode” (Sermons, sig. A. iiii.)
The following lines, from a poem in the Hyndford MS. compiled in 1568, afford an additional proof of our hero’s popularity in Scotland:
“Thair is no story that I of heir,Of Johne nor Robene Hude,Nor zit of Wallace wicht but weir,That me thinkes half so gude,As of thre palmaris,” &c.
That the subject was not forgotten in the succeeding age, can be testifyed by Drayton, who is elsewhere quoted, and in his sixth eclogue makes Gorbo thus address “old Winken de Word:” {lxxvii}
“Come, sit we down under this hawthorn-tree,The morrow’s light shall lend us day enough,And let us tell of Gawen, or Sir Guy,Of Robin Hood, or of old Clem a Clough.”
Richard Johnson, who wrote “The History of Tom Thumbe,” in prose (London, 1621, 12mo, b. l.), thus prefaces his work: “My merry muse begets no tales of Guy of Warwicke, &c. nor will I trouble my penne with the pleasant glee of Robin Hood, little John, the fryer, and his Marian; nor will I call to mind the lusty Pinder of Wakefield, &c.”
In “The Calidonian Forrest,” a sort of allegorical or mystic tale, by John Hepwith, gentleman, printed in 1641, 4to, the author says,
“Let us talke of Robin Hoode,And little John in mery Shirewoode,” &c.64
Of one very ancient, and undoubtedly once very popular, song this single line is all that is now known to exist: {lxxviii}
However, though but a line, it is of the highest authority in Westminster Hall, where, in order to the decision of a knotty point, it has been repeatedly cited, in the most solemn manner, by grave and learned judges.
M. 6 Jac. B. R. Witham v. Barker, Yelv. 147. Trespass,
for breaking plaintif’s close, &c. Plea. Liberum tenementum
of Sir John Tyndall, and justification as his servant and by his
command. Replication, That it is true it is his freehold,
but that long before the time when &c. he leased to plaintif
at will, who entered and was possessed until, &c. traversing,
that defendant entered, &c. by command of Sir John. Demurrer:
and adjudged against plaintif, on the ground of the
replication being bad, as not setting forth any seisin or possession
in Sir John, out of which a lease at will could be derived.
For a title made by the plea or replication should be
certain to all intents, because it is traversable. Here, therefor,
he should have stated Sir John’s seisin, as well as the lease
at will; which is not done here:
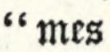
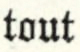
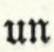

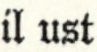
 Robin Whood in Barnwood stood, absque hoc
Robin Whood in Barnwood stood, absque hoc

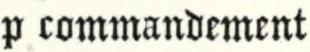
 John. Quod nota. Per Fenner, Williams et Crook
John. Quod nota. Per Fenner, Williams et Crook

 Yelv.
Yelv. 
In the case of Bush v. Leake, B. R. Trin. 23 G. 3, Buller, justice, cited the case of Coulthurst v. Coulthurst, C. B. Pasch. 12 G. 3 (an action on bond), and observed, “There a case in Yelverton was alluded to, where the court said, you might as well say, by way of inducement to a traverse, Robin Hood in Barnwood stood.”
It is almost unnecessary to observe, because it will be shortly proved, that Barnwood, in the preceding quotations, ought to be Barnsdale.65 With respect to Whood, the reader {lxxix} will see, under Note 19, a remarkable proof of the antiquity of that pronunciation, which actually prevails in the metropolis at this day. See also the word “whodes” in Note 34. So, likewise, Bale, in his Actes of English Votaries, 1560, says, “the monkes had their cowles, caprones or whodes;” and in Stow’s Survey, 1598, p. 120, have “a fooles whoode.”
This celebrated and important line occurs as the first of a foolish mock-song, inserted in an old mortality, intitled “A new interlude and a mery of the nature of the iiii elementes,” supposed to have been printed by John Rastall about 1520; where it is thus introduced:
“Hu[manyte].let us some lusty balet syng.
Yng[norance]. Nay, syr, by the hevyn kyng:For me thynkyth it servyth for no thyng,All suche pevysh prykeryd song.Hu. Pes, man, pryk-song may not be dyspysyd,For therwith God is well plesyd.Yng. Is God well pleasyd, trowest thou, therby?Nay, nay, for there is no reason why.For is it not as good to say playnlyGyf me a spade,As gyf me a spa ve va ve va ve vade?But yf thou wylt have a song that is good,I have one of Robyn Hode,The best that ever was made. {lxxx}Hu. Then a feleshyp, let us here it.Yng. But there is a bordon, thou must here it,Or ellys it wyll not be.Hu. Than begyn, and care not for . . .Downe downe downe, &c.Yng. Robyn Hode in Barnysdale stode,And lent hym tyl a mapyll thystyll;Than cam our lady & swete saynt Andrewe;Slepyst thou, wakyst thou, Geffrey Coke?66A c. wynter the water was depe,I can not tell you how brode;He toke a gose nek in his hande,And over the water he went.He start up to a thystell top,And cut hym downe a holyn clobbe;He stroke the wren betwene the hornys,That fyre sprange out of the pygges tayle.Jak boy is thy bow i-broke,Or hath any man done the wryguldy wrange?He plukkyd muskyllys out of a wyllowe,And put them in to his sachell.Wylkyn was an archer good,And well coude handell a spade;He toke his bend bowe in his hand,And set him downe by the fyre.He toke with hym lx. bowes and ten,A pese of befe, another of baken.Of all the byrdes in mery Englond,So merely pypys the mery bottel.”
“The lives, stories, and giftes of men which are contained in the bible, they [the papists] read as thinges no more pertaining unto them than a tale of Robin Hood” (Tyndale, Prologue to the prophecy of Jonas, about 1531).
Gwalter Lynne, printer, in his dedication to Ann, Duchess of Somerset, of “The true beliefe in Christ and his sacramentes,” 1550, says, “I woulde wyshe tharfore that al men, {lxxxi} women, and chyldren, would read it. Not as they haue bene here tofore accustomed to reade the fained storyes of Robin-hode, Clem of the Cloughe, wyth such lyke to passe the tyme wythal,” &c.
In 1562, John Alde had license to print “a ballad of Robyn god,” a mistake, it is probable, for Robyn Hod.
Alexander Hume, minister of Logie, about 1599, says in one of his “Hymnes or Sacred Songs,” printed in that year, that
“much to blame are those of carnal brood,
Who loath to taste of intellectual food,Yet surfeit on old tales of Robin Hood.”
Complaint of Scotland, Edin. 1801, Dissertation, p. 221.
“Exclude the scriptures, and bid them read the storyOf Robin Hood and Guy, which was both tall and stout,And Bevis of Southampton, to seek the matter out.Suffer all slander against God and his truth,And praise the old fashion in king Arthur’s days,Of abbays and monasteries how it is great ruthTo have them plucked down, and so the eldest says;And how it was merry when Robin Hood’s playsWas in every town, the morrice and the fool,The maypole and the drum, to bring the calf from school,With Midge, Madge and Marion, about the pole to dance,And Stephen, that tall stripling, to lead Volans dance,With roguing Gangweeke, a goodly remembrance,With beads in every hand, our prayers stood by tale:This was a merry work, talk among our meany,And then of good eggs ye might have twenty for a penny.”L. Ramsey’s Practice of the Divell, b. l.
All the entire poems and songs known to be extant will be found in the following collection; but many more may be traditionally preserved in different parts of the country which would have added considerably to its value.67 That {lxxxii} some of these identical pieces, or others of the like nature, were great favourites with the common people in the time of Queen Elizabeth, though not much esteemed, it would seem, by the refined critic, may, in addition to the testimonies already cited, be inferred from a passage in Webbe’s Discourse {lxxxiii} of English Poetrie, printed in 1586. “If I lette passe,” says he, “the unaccountable rabble of ryming ballet-makers and compylers of sencelesse sonets, who be most busy to stuffe every stall full of grosse devises and unlearned pamphlets, I trust I shall with the best sort be held excused. For though many such can frame an alehouse-song of five or sixe score verses, hobbling uppon some tune of a northern jygge, or Robyn Hoode, or La lubber, &c. and perhappes observe just number of sillables, eyght in one line, sixe in an other, and therewithall an A to make a jercke in the ende, yet if these might be accounted poets (as it is sayde some of them make meanes to be promoted to the lawrell), surely we shall shortly have whole swarmes of poets; and every one that can frame a booke in ryme, though, for want of matter, it be but in commendations of copper noses, or bottle ale, wyll catch at the garlande due to poets: whose potticall (poeticall, I should say) heades, I woulde wyshe, at their worshipfull comencements, might, in steede of lawrell, be gorgiously garnished with fayre greene barley, in token of their good affection to our Englishe malt.” The chief object of this satire seems to be William Elderton, the drunken {lxxxiv} ballad-maker, of whose compositions all but one or two have unfortunately perished.68
Most of the songs inserted in the second half of this volume were common broad-sheet ballads, printed in black letter, with woodcuts, between the Restoration and the Revolution; though copies of some few have been found of an earlier date. “Who was the author of the collection intitled Robin Hood’s Garland, no one,” says Sir John Hawkins, “has yet pretended to guess. As some of the songs have in them more of the spirit of poetry than others, it is probable,” he thinks, “it is the work of various hands: that it has from time to time been varied and adapted to the phrase of the times,” he says, “is certain.” None of these songs, it is believed, were collected into a garland till after the Restoration; as the earliest that has been met with, a copy of which is in the possession of Francis Douce, Esq., was printed by W. Thackeray, a noted ballad-monger, in 1670. This, however, contains no more than sixteen songs, some of which, very falsely as it seems, are said to have been “never before printed.” “The latest edition of any worth,” according to Sir John Hawkins, “is that of 1719.” None of the old editions of this garland have any sort of preface: that prefixed to the modern ones, of Bow or Aldermary churchyard, being {lxxxv} taken from the collection of old ballads, 1723, where it is placed at the head of Robin Hood’s birth and breeding. The full title of the last London edition of any note is—“Robin Hood’s Garland: being a complete history of all the notable and merry exploits performed by him and his men on many occasions: To which is added a preface [i.e. the one already mentioned] giving a more full and particular account of his birth, &c., than any hitherto published. [Cut of archers shooting at a target.]
I’ll send this arrow from my bow,And in a wager will be boundTo hit the mark aright, althoughIt were for fifteen hundred pound.Doubt not I’ll make the wager good,Or ne’er believe bold Robin Hood.
Adorned with twenty-seven neat and curious cuts adapted to the subject of each song. London, Printed and sold by R. Marshall, in Aldermary church-yard, Bow-lane.” 12mo. On the back of the title-page is the following Grub-street address:
“To all gentlemen archers.“This garland has been long out of repair,Some songs being wanting, of which we give account;For now at last, by true industrious care,The sixteen songs to twenty-seven we mount;Which large addition needs must please, I know,All the ingenious ‘yeomen’ of the bow.To read how Robin Hood and Little John,Brave Scarlet, Stutely, valiant, bold and free,Each of them bravely, fairly play’d the man,While they did reign beneath the green-wood tree;Bishops, friars, likewise many more,Parted with their gold, for to increase their store,But never would they rob or wrong the poor.”
The last seven lines are not by the author of the first six, but were added afterwards; perhaps when the twenty-four songs were increased to twenty-seven.69 {lxxxvi}
(28) —“has given rise to divers proverbs.”] Proverbs, in all countries, are, generally speaking, of very great antiquity; and therefore it will not be contended that those concerning our hero are the oldest we have. It is highly probable, however, that they originated in or near his own time, and of course have existed for upwards of 500 years, which is no modern date. They are here arranged, not, perhaps, according to their exact chronological order, but by the age of the authorities they are taken from.
1. “Good even, good Robin Hood.”
The allusion is to civility extorted by fear. It is preserved by Skelton, in that most biting satire against Cardinal Wolsey, “Why come ye not to court?” (Works, 1736, p. 147).
“He is set so hye,In his hierarchy,That in the chambre of starsAll matters there he mars;Clapping his rod on the borde,No man dare speake a word;For he hath all the saying,Without any renaying: {lxxxvii}He rolleth in his recordes,He saith, How say ye my lordes?Is not my reason good?Good even, good Robin Hood.” 70
2. “Many men talk of Robin Hood that never shot in his bow.”
“That is, many discourse (or prate rather) of matters wherein they have no skill or experience. This proverb is now extended all over England, though originally of Nottinghamshire extraction, where Robin Hood did principally reside in Sherwood forest. He was an arch-robber, and withal an excellent archer; though surely the poet71 gives a twang to the loose of his arrow, making him shoot one a cloth-yard long, at full forty score mark, for compass never higher than the breast, and within less than a foot of the mark. But herein our author hath verified the proverb, talking at large of Robin Hood, in whose bow he never shot” (Fuller’s Worthies, p. 315).
“One may justly wonder,” adds the facetious writer, “this archer did not at last hit the mark, I mean, come to the gallows for his many robberies.”
The proverb is mentioned, and given as above, by Sir Edward Coke in his 3d Institute, p. 197. See also Note 26. It is thus noticed by Jonson in “The king’s entertainment at Welbeck in Nottinghamshire, 1633:”
“This is . . . . . father Fitz-Ale, herald of Derby, &c.He can fly o’er hills and dales,And report you more odd talesOf our out law Robin Hood,That revell’d here in Sherewood,And more stories of him show,(Though he ne’er shot in his bow)Than au’ men or believe, or know.”
We likewise meet with it in Epigrams, &c., 1654:
“In Vertutem.“Vertue we praise, but practice not her good,(Athenian-like) we act not what we know;So many men doe talk of Robin Hood,Who never yet shot arrow in his bow.”
On the back of a ballad in Anthony a Wood’s collection he has written,
“There be some that prateOf Robin Hood, and of his bow,Which never shot therein, I trow.”
Ray gives it thus:
“Many talk of Robin Hood, that never shot in his bow,And many talk of little John, that never did him know:”
which Kelly has varied, but without authority.
Camden’s printer has separated the lines, as distinct proverbs (Remains, 1674):
“Many speak of Robin Hood that never shot in his bow.“Many a man talks of little John that never did him know.”
This proverb likewise occurs in The downfall of Robert earle of Huntington, 1600, and is alluded to in a scarce and curious old tract intitled “The contention betwyxte Church-yeard and Camell, upon David Dycer’s Dreame,” &c. 1560, 4to, b. l.
“Your sodain stormes and thundre claps, your boasts and braggs so loude:Hath doone no harme thogh Robin Hood spake with you in a cloud.Go learne againe of litell Jhon, to shute in Robyn Hods bowe,Or Dicars dreame shall be unhit, and all his whens, I trowe.” 72
The Italians appear to have a similar saying:
Molti parlan di OrlandoChi non viddero mai suo brando.
3. “To overshoot Robin Hood.”
“And lastly and chiefly, they cry out with open mouth as if they had overshot Robin Hood, that Plato banished them [i.e. poets] out of his commonwealth” (Sir P. Sidney’s Defence of Poesie).
4. “Tales of Robin Hood are good [enough] for fools.”
This proverb is inserted in Camden’s Remains, printed originally in 1605; but the word in brackets is supplied from Ray.
5. “To sell Robin Hood’s pennyworths.”
“It is spoken of things sold under half their value; or if you will, half sold, half given. Robin Hood came lightly by his ware, and lightly parted therewith; so that he could afford the length of his bow for a yard of velvet. Whithersoever he came, he carried a fair along with him; chapmen crowding to buy his stollen commodities. But seeing the receiver is as bad as the thief, and such buyers are as bad as receivers, the cheap pennyworths of plundered goods may in fine prove dear enough to their consciences” (Fuller’s Worthies, p. 315).
This saying is alluded to in the old North-country song of Randal a Barnaby:
“All men said, it became me well,And Robin Hood’s pennyworths I did sell.”
6. “Come, turn about, Robin Hood.”
Implying that to challenge or defy our hero must have been the ne plus ultra of courage. It occurs in “Wit and Drollery,” 1661:
“O love, whose power and might,No creature ere withstood,Thou forcest me to write,Come turn about Robin-hood.”
7. “As crook’d as Robin Hood’s bow.”
That is, we are to conceive, when bent by himself. The following stanza of a modern Irish song is the only authority for this proverb that has been met with:
“The next with whom I did engage,It was an old woman worn with age, {xc}Her teeth were like tobacco pegs,Besides she had two bandy legs,Her back more crook’d than Robin Hood’s bow,Purblind and decrepid, unable to go;Altho’ her years were sixty-three,She smil’d at the humours of Soosthe Bue.”
8. “To go round by Robin Hood’s barn.”
This saying, which now first appears in print, is used to imply the going of a short distance by a circuitous method, or the farthest way about.
(29) —“to swear by him, or some of his companions, appears to have been a usual practice.”] The earliest instance of this practice occurs in a pleasant story among “Certaine merry tales of the mad-men of Gottam,” compiled in the reign of Henry VIII. by Dr. Andrew Borde, an eminent physician of that period, which here follows verbatim, as taken from an old edition in black letter, without date (in the Bodleian Library), being the first tale in the book.
“There was two men of Gottam, and the one of them was going to the market at Nottingham to buy sheepe, and the other came from the market; and both met together upon Nottingham bridge. Well met, said the one to the other. Whither be yee going? said he that came from Nottingham. Marry, said he that was going thither, I goe to the market to buy sheepe. Buy sheepe! said the other, and which way wilt thou bring them home? Marry, said the other, I will bring them over this bridge. By Robin Hood, said he that came from Nottingham, but thou shalt not. By Maid Marrion, said he that was going thitherward, but I will. Thou shalt not, said the one. I will, said the other. Ter here! said the one. Shue there! said the other. Then they beate their staves against the ground, one against the other, as there had beene an hundred sheepe betwixt them. Hold in, said the one. Beware the leaping over the bridge of my sheepe, said the other. I care not, said the other. They shall not come this way, said the one. But they shall, said the other. Then said the other, & if that thou make much to doe, I will put my finger in thy mouth. A turd thou wilt, said the other. And as they were at that contention, another man of Gottam {xci} came from the market, with a sacke of meale upon a horse, and seeing and hearing his neighbours at strife for sheepe, and none betwixt them, said, Ah fooles, will you never learn wit? Helpe me, said he that had the meale, and lay my sack upon my shoulder. They did so; and he went to the one side of the bridge, and unloosed the mouth of the sacke, and did shake out all his meale into the river. Now, neighbours, said the man, how much meale is there in my sacke now? Marry, there is none at all, said they. Now, by my faith, said he, even as much wit is in your two heads, to strive for that thing you have not. Which was the wisest of all these three persons, judge you.” 73
“By the bare scalp of Robin Hood’s fat frier,” is an oath put by Shakespeare into the mouth of one of his outlaws in the Two Gentlemen of Verona, act iv. scene 1. “Robin Hood’s fat frier” is Frier Tuck; a circumstance of which Doctor Johnson, who set about explaining that author with a very inadequate stock of information, was perfectly ignorant.
(30) —“his songs have been preferred, not only on the most solemn occasion to the psalms of David, but in fact to the New Testament.”] [“On Friday, March 9th, 1733] was executed at Northampton William Alcock for the murder of his wife. He never own’d the fact, nor was at all concern’d at his approaching death, refusing the prayers and assistance of any persons. In the morning he drank more than was sufficient, yet sent and paid for a pint of wine, which being deny’d him, he would not enter the cart before he had his money return’d. On his way to the gallows he sung part of an old song of Robin Hood, with the chorus, Derry, derry, down,74 &c., and swore, kick’d and spurn’d at every person {xcii} that laid hold of the cart; and before he was turn’d off, took off his shoes, to avoid a well-known proverb; and being told by a person in the cart with him, it was more proper for him to read, or hear some body read to him, than so vilely to swear and sing, he struck the book out of the person’s hands, and went on damning the spectators, and calling for wine. Whilst psalms and prayers were performing at the tree, he did little but talk to one or other, desiring some to remember him, others to drink to his good journey; and to the last moment declared the injustice of his case” (Gentleman’s Magazine, vol. iii. P. 154).
To this maybe added, that at Edinburgh, in 1565, “Sandy Stevin menstrall [i.e. musician] was convinced of blasphemy, alledging, That he would give no moir credit to The new testament, then to a tale of Robin Hood, except it wer confirmed be the doctours of the church” (Knox’s Historie of the Reformation in Scotland, Edin. 1732, p. 368).
William Roy, in a bitter satire against Cardinal Wolsey, intitled, “Rede me and be nott wrothe For I saye nothynge but trothe,” printed abroad, about 1525, speaking of the bishops, says:
“Their frantyke foly is so pevisshe,That they contempne in Englisshe,To have the new testament;But as for tales of Robyn Hode,With wother jestes nether honest nor goode,They have none impediment.”
To the same effect is the following passage in another old libel upon the priests, intitled “I playne Piers which can not flatter, a plowe-man men me call,” &c. b. l. n. d. printed in the original as prose:
“No Christen booke,Maye thou on looke,Yf thou be an Englishe strunt, {xciii}Thus dothe alyens us loutte,By that ye spreade aboute,After that old sorte and wonte.You allowe they saye,Legenda aurea,Roben Hoode, Bevys, & Gower,And all bagage be syd,But God’s word ye may not abyde,These lyese are your churche ‘dower.’”
See also before, p. lxxii.75
So in Laurence Ramsey’s “Practise of the Divell” (n. d. 4to, b. l.):
“Exclude the scriptures, and byd them reade the storieOf Robin Hood, and Guye, which was both tall and stout,And Bevis of Southampton, to seeke the matter out.”
(31) “His service to the Word of God.”] “I came once myselfe,” says Bishop Latimer (in his sixth sermon before King Edward VI.), “to a place, riding on a jorney homeward from London, and I sent worde over night into the towne that I would preach there in the morning, bicause it was a holy day, and methought it was an holydayes worke. The churche stode in my way; and I tooke my horse and my company and went thither (I thought I should have found a great companye in the churche), and when I came there, the churche dore was faste locked. I taried there half an hower and more; at last the keye was founde; and one of the parishe commes to me, and sayes, Sir, this is a busie day with us, we cannot heare you; it is Robin Hoodes daye. The parishe are gone abroad to gather for Robin Hoode, I pray you let them not. I was fayne there to geve place to Robin Hoode. I thought my rochet shoulde have bene regarded, thoughe I were not; but it woulde not serve, it was fayne to geve place to Robin Hodes men. {xciv}
“It is no laughyng matter, my frendes, it is a weepyng matter, a heavy matter, under the pretence for gatherynge for Robin Hoode, a traytour76 and a theefe, to put out a preacher, to have his office lesse esteemed, to preferre Robin Hoode before the ministration of God’s worde, and all this hath come of unpreaching prelates. Thys realme hath bene ill provided for, that it hath had suche corrupte judgementes in it, to preferre Robin Hoode to God’s worde. If the bishoppes had bene preachers, there shoulde never have bene any such thing,” &c.
(32) —“may be called the patron of archery.”] The bow and arrow makers, in particular, have always held his memory in the utmost reverence. Thus, in the old ballad of London’s Ordinary:
“The hosiers will dine at the Leg,The drapers at the sign of the Brush,The fletchers to Robin Hood will go,And the spendthrift to Beggar’s-bush.” 77
The picture of our hero is yet a common sign in the country, and, before hanging-signs were abolished in London, must have been still more so in the City; there being at present no less than a dozen alleys, courts, lanes, &c., to which he or it has given a name. (See Baldwin’s New Complete Guide, 1770.) The Robin Hood Society, a club or assembly for public debate, or school for oratory, is well known. It was held at a public-house, which had once borne the sign, and still retained the name of this great man, in Butcher Row, near Temple Bar.
It is very usual in the North of England for a publican whose name fortunately happens to be John Little to have {xcv} the sign of Robin Hood and his constant attendant, with this quibbling subscription:
“You gentlemen, and yeomen good,Come in and drink with Robin Hood;If Robin Hood be not at home,Come in and drink with Little John.” 78
An honest countryman, admiring the conceit, adopted the lines, with a slight, but, as he thought, necessary alteration, viz.:
“If Robin Hood be not at home,Come in and drink with—Simon Webster.”
Drayton, describing the various ensigns or devices of the English counties at the battle of Agincourt, gives to
“Old Nottingham, an archer clad in green,Under a tree with his drawn bow that stood,Which in a chequer’d flag far off was seen;It was the picture of old Robin Hood.”
(33) —“the supernatural powers he is, in some parts, supposed to have possessed.”] “In the parish of Halifax is an immense stone or rock, supposed to be a Druidical monument, there called Robin Hood’s pennystone, which he is said to have used to pitch with at a mark for his amusement. There is likewise another of these stones, of several tons weight, which the country-people will tell you he threw off an adjoining hill with a spade as he was digging. Every thing of the marvellous kind being here attributed to Robin Hood, as it is in Cornwall to King Arthur” (Watson’s History of Halifax, p. 27).
At Birchover, six miles south of Bakewell, and four from Haddon, in Derbyshire, among several singular groups of rocks, are some stones called Robin Hood’s stride, being two {xcvi} of the highest and most remarkable. The people say Robin Hood lived here.
(34) —“having a festival allotted to him, and solemn games instituted in honour of his memory,” &c.] These games, which were of great antiquity and different kinds, appear to have been solemnised on the first and succeeding days of May, and to owe their original establishment to the cultivation and improvement of the manly exercise of archery, which was not, in former times, practised merely for the sake of amusement.
“I find,” says Stow, “that in the moneth of May, the citizens of London, of all estates, lightlie in every parish, or sometimes two or three parishes joyning together, had their severall mayinges, and did fetch in Maypoles, with divers warlike shewes, with good archers, morrice-dancers, and other devices for pastime all the day long: and towards the evening they had stage-playes and bonefires in the streetes. . . . . These greate Mayinges and Maygames, made by the governors and masters of this citie, with the triumphant setting up of the greate shafte (a principall Maypole in Cornhill, before the parish church of S. Andrew, therefore called Undershafte) by meane of an insurrection of youthes against alianes on Mayday 1517, the ninth of Henry the Eight, have not beene so freely used as afore” (Survey of London, 1598, p. 72).
The disuse of these ancient pastimes, and the consequent “neglect of archerie,” are thus pathetically lamented by Richard Niccolls, in his London’s Artillery, 1616:
“How is it that our London hath laid downeThis worthy practise, which was once the crowneOf all her pastime, when her Robin HoodHad wont each yeare, when May did clad the wood,With lustie greene, to lead his yong men out,Whose brave demeanour, oft when they did shoot,Invited royall princes from their courts,Into the wilde woods to behold their sports!A description of one drawing a bow.Who thought it then a manly sight and trim,To see a youth of cleane compacted lim,Who, with a comely grace, in his left handHolding his bow, did take his stedfast stand,Setting his left leg somewhat foorth before,His arrow with his right hand nocking sure, {xcvii}Not stooping, nor yet standing streight upright,Then, with his left hand little ’bove his sight,Stretching his arm out, with an easie strength,To draw an arrow of a yard in length.” 79
The lines,
“Invited royall princes from their courtsInto the wild woods to behold their sports,”
may be reasonably supposed to allude to Henry VIII., who appears to have been particularly attached, as well to the exercise of archery as to the observance of May. Some short time after his coronation, says Hall, he “came to Westminster with the quene, and all their traine: and on a tyme being there, his grace therles of Essex, Wilshire, and other noble menne, to the numbre of twelve, came sodainly in a mornyng into the quenes chambre, all appareled in short cotes of Kentish Kendal, with hodes on their heddes, and hosen of the same, every one of them his bowe and arrowes, and a sworde and a bucklar, like outlawes, or ‘Robyn’ Hodes men; whereof the quene, the ladies, and al other there were abashed, aswell for the straunge sight, as also for their sodain commyng: and after certayn daunces and pastime made thei departed” (Hen. VIII. fo. 6, b). The same author gives the following curious account of “A maiynge” in the 7th year of this monarch (1516): “The kyng & the quene, accompanied with many lordes & ladies, roade to the high grounde on Shoters hil to take the open ayre, and as they passed by the way they espied a company of tall yomen, clothed all in grene, with grene whodes & bowes and arrowes, to the number of ii. C. Then one of them whiche called hymselfe Robyn Hood, came to the kyng, desyring hym to se his men shote, & the kyng was content. Then he whisteled, and all the ii. C. archers shot & losed at once; and then he whisteled again, and they likewyse shot agayne; their arrowes whisteled by craft of the {xcviii} head, so that the noyes was straunge and great, and muche pleased the kyng, the quene, and all the company. All these archers were of the kynges garde, and had thus appareled themselves to make solace to the kynge. Then Robyn Hood desyred the kyng and quene to come into the grene wood, and to se how the outlawes lyve. The kyng demaunded of the quene and her ladyes, if they durst adventure to go into the wood with so many outlawes. Then the quene said, if it pleased hym, she was content. Then the hornes blewe tyll they came to the wood under Shoters-hill, and there was an arber made of bowes, with a hal, and a great chamber, and an inner chamber, very well made and covered with floures and swete herbes, which the kyng muche praised. Then sayd Robyn Hood, Sir, outlawes brekefastes is venyson, and therefore you must be content with such fare as we use. Then the kyng and quene sate doune, and were served with venyson and vyne by Robyn Hood and his men, to their great contentacion. Then the kyng departed and his company, and Robyn Hood and his men them conduicted: and as they were returnyng, there met with them two ladyes in a ryche chariot drawen with v. horses, and every horse had his name on his head, and on every horse sat a lady with her name written . . . . and in the chayre sate the lady May, accompanied with lady Flora, richely appareled; and they saluted the kyng with diverse goodly songes, and so brought hym to Grenewyche. At this maiyng was a greate number of people to beholde, to their great solace and confort” (fo. lvi. b).
That this sort of May-games was not peculiar to London appears from a passage in Richard Robinson’s “Third assertion Englishe historicall, frendly in favour and furtherance of English archery:” 80 {xcix}
“And, heare because of archery I do by penne explane,The use, the proffet, and the praise, to England by the same,(1553)Myselfe remembreth of a childe in contreye native mine,(7. E. 6.)A May-game was of Robyn Hood, and of his traine that time,To traine up young men, stripplings, and eche other younger childe,In shooting, yearely this with solempne feast was by the guyldeOr brotherhood of townsmen don, with sport, with joy, and love,To proffet which in present tyme, and afterward did prove.”
The games of Robin Hood seem to have been occasionally of a dramatic cast. Sir John Paston, in the time of King Edward IV., complaining of the ingratitude of his servants, mentions one who had promised never to desert him, “and ther uppon,” says he, “I have kepyd hym thys iii yer to pleye seynt Jorge, and Robyn Hod and the sheryf off Notyngham,81 and now when I wolde have good horse he is goon into Bernysdale, and I withowt a keeper.”
In some old accounts of the churchwardens of St. Helen’s at Abingdon, Berks, for the year 1556, there is an entry For setting up Robin Hoodes Bower; I suppose, says {c} Warton, for a parish interlude. (See History of English Poetry, ii. 175.)82 {ci}
In some places, at least, these games were nothing more, in effect, than a morris-dance, in which Robin Hood, Little John, Maid Marian, and Frier Tuck were the principal personages; the others being a clown or fool, the hobby-horse (which appears, for some reason or other, to have been frequently forgot83), the taborer, and the dancers, who were more or less numerous. Thus Warner:
“At Paske began our morrise, and ere penticost our May,Tho Roben Hood, liell John, frier Tuck, and Marian deftly play,And lard and ladie gang till kirke with lads and lasses gay.” 84
Perhaps the clearest idea of these last-mentioned games, about the beginning of the 16th century, will be derived from some curious extracts given by Mr. Lysons in his valuable work intitled “The Environs of London” (vol. i. 1792, p. 226), from the contemporary accounts of the “churchwardens of the parish of Kingston upon Thames.”
| “23 Hen. 7. To the menstorell upon May-day | 0 | 0 | 4 |
 For paynting of the mores garments and for sarten gret leveres85 For paynting of the mores garments and for sarten gret leveres85 |
0 | 2 | 4 |
 For paynting of a bannar for Robin Hode For paynting of a bannar for Robin Hode |
0 | 0 | 3 |
 For 2 M. & ½ pynnys For 2 M. & ½ pynnys |
0 | 0 | 10 |
 For 4 plyts and ½ of laun for the mores garments For 4 plyts and ½ of laun for the mores garments |
0 | 2 | 11 |
 For orseden86 for the same For orseden86 for the same |
0 | 0 | 10 |
 For a goun for the lady For a goun for the lady |
0 | 0 | 8 |
 For bellys for the dawnsars For bellys for the dawnsars |
0 | 0 | 12 |
| 24 Hen. 7. For little John’s cote | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| 1 Hen. 8. For silver paper for the mores dawnsars | 0 | 0 | 7 |
 For Kendall for Robyn Hode’s cote For Kendall for Robyn Hode’s cote |
0 | 1 | 3 |
 For 3 yerds of white for the frere’s87 cote For 3 yerds of white for the frere’s87 cote |
0 | 3 | 0 |
 For 4 yards of kendall for mayde
Marian’s88 huke89 For 4 yards of kendall for mayde
Marian’s88 huke89 |
0 | 3 | 4 |
 For saten of sypers for the same huke For saten of sypers for the same huke |
0 | 0 | 6 |
 For 2 payre of glovys for Robin Hode and mayde Maryan For 2 payre of glovys for Robin Hode and mayde Maryan |
0 | 0 | 3 |
 For 6 brode arovys For 6 brode arovys |
0 | 0 | 6 |
 To mayde Maryan for her labour for two years To mayde Maryan for her labour for two years |
0 | 2 | 0 |
 To Fygge the taborer To Fygge the taborer |
0 | 6 | 0 |
 Recd for Robyn Hod’s gaderyng
4 marks90 Recd for Robyn Hod’s gaderyng
4 marks90 | |||
| 5 Hen. 8. Recd for Robin Hood’s gaderyng at Croydon | 0 | 9 | 4 |
| 11 Hen. 8. Paid for three broad yerds of rosett for maykng the frer’s cote | 0 | 3 | 6 |
 Shoes for the mores daunsars, the frere and mayde Maryan at 7d a payre Shoes for the mores daunsars, the frere and mayde Maryan at 7d a payre |
0 | 5 | 4 |
| 13 Hen. 8. Eight yerds of fustyan for the mores daunsars coats | 0 | 16 | 0 |
| A dosyn of gold skynnes for the morres91 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 15 Hen. 8. Hire of hats for Robynhode | 0 | 0 | 16 |
 Paid for the hat that was lost Paid for the hat that was lost |
0 | 0 | 10 |
| 16 Hen. 8. Recd at the church-ale and Robyn-hode all things deducted | 3 | 10 | 6 |
 Paid for 6 yerds ¼ of satyn for Robyn Hode’s coyts Paid for 6 yerds ¼ of satyn for Robyn Hode’s coyts |
0 | 12 | 6 |
 For makyng the same For makyng the same |
0 | 2 | 0 |
 For 3 ells of locram92 For 3 ells of locram92 |
0 | 1 | 6 |
| 21 Hen. 8. For spunging and brushing Robyn-hode’s cotys | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 28 Hen. 8. Five hats and 4 porses for the daunsars | 0 | 0 | 4½ |
 4 yerds of cloth for the fole’s cote 4 yerds of cloth for the fole’s cote |
0 | 2 | 0 |
 2 ells of worstede for mayde Maryans kyrtle 2 ells of worstede for mayde Maryans kyrtle |
0 | 6 | 8 |
 For 6 payre of double sollyd showne For 6 payre of double sollyd showne |
0 | 4 | 6 |
 To the mynstrele To the mynstrele |
0 | 10 | 8 |
 To the fryer and the piper for to go to Croydon To the fryer and the piper for to go to Croydon |
0 | 0 | 8 |
| 29 Hen. 8. Mem. Lefte in the keping of the wardens nowe beinge. |
A fryers cote of russet and a kyrtele of worstyde weltyd with red cloth, a mowrens93 cote of buckram, and 4 morres {cv} daunsars cotes of white fustian spangelyd and two gryne saten cotes and a dysardd’s94 cote of cotton and 6 payre of garters with bells.”
These games appear to have been discontinued at Kingston, as a parochial undertaking at least, after the above period, as the industrious inquirer found no further entries relating to them.
Some of the principal characters of the morris seem to have gradually disappeared, so that at length it consisted only of the dancers, the piper, and the fool. In Mr. Tollet’s window we find neither Robin Hood nor Little John, though Marian and the frier are still distinguished performers.95 But in the scene of one, introduced in the old play of Jacke Drum’s Entertainment, first printed in 1601, there is not the least symptom of any of the four.96 “The taber and pipe strike up a morrice. A shoute within: A lord, a lord, a lord, who ! 97
Ed. Oh, a morrice is come, observe our country sports,’Tis Whitson tyde,98 and we must frolick it.Enter the morrice.The song.Skip it, and trip it, nimbly, nimbly,Tickle it, tickle it lustily,Strike up the taber, for the wenches favour,Tickle it, tickle it lustily.Let us be seen, on Hygate greene,To dance for the honour of Holloway.Since we are come hither, let’s spare for no leather,To dance for the honour of Holloway.Ed. Well said, my boyes, I must have my lord’s livory: what is’t? a maypole? Troth, ’twere a good body for a courtier’s impreza, if it had but this life, Frustra florescit. Hold, cousin, hold. [He gives the fool money.
Foole. Thankes, cousin, when the lord my father’s audit comes, wee’l repay you againe. Your benevolence too, sir.
Mam. What! a lord’s sonne become a begger!
Foole. Why not? when beggers are become lord’s sons. Come, ’tis but a trifle.
Mam. Oh, sir, many a small make a great.
Foole. No, sir, a few great make a many small. Come, my lords, poore and neede hath no law.
S. Ed. Nor necessitie no right. Drum, downe with them into the celler. Rest content, rest content; one bout more, and then away.
Foole. ‘Spoke’ like a true heart: I kisse thy foote, sweet knight. The morrice sing and dance and exeunt.”
It is therefore highly probable, as hath been already suggested, that the May-game of Robin Hood and the morris-dance had originally no sort of connection; that the performers had united their forces, because their joint efforts proved more successful, lucrative, or agreeable; and that, in fine, the latter gradually shook off companions from whose association they no longer derived any advantage.99
An old writer, describing a country bridal show exhibited before Queen Elizabeth at Kenilworth Castle in 1575, {cvii} mentions “a lively moris dauns, according too the auncient manner, six daunsers, mawd Marion, and the fool.”
Stubbs’s chapter, upon “Lords of mis-rule” (Anatomie of Abuses, 1583) contains a singular description of a grand parochial morris-dance, which is worthy of perusal.
It is observable that, in the sham second part of Hudibras, published 1663, this place is said to be
“Highly famed for Hocktide games.”
(Grey’s edition of Hudibras, ii. 90.) Of what nature these were (at Kingston) we are not informed. See Plot’s Natural History of Oxfordshire; Leland’s Collectanea, v. Roas.
Hocktide or Hock-day was the Tuesday fortnight after Easter. Two falsehoods are asserted of this festival: one, that its celebration was owing to the general joy excited by the death of Hardecnute, which in fact took place on the 8th of June: the other, that it was the anniversary of the general slaughter of the Danes in 1042; which Henry of Huntingdon and others expressly fix on St. Brice’s day, being the 13th of November.
It plainly appears, by these extracts, that Robyn Hode, Little John, the frere, and mayde Maryan were fitted out at the same time with the mores daunsars, and, consequently, it would seem, united with them in one and the same exhibition.100
“Also it was said, that the ladie hir selfe, the same daie hir husband and she should be crowned, said that she feared they should prove but as a summer king and queene, such as in countrie townes the yoong folks choose for short to danse about maipoles” (Holinshed, at the year 1306).
As to the original institution of May-poles, or king and queen of May,—in a word, of the primitive purpose and celebration of a popular festival at that season,—nothing {cviii} satisfactory or consequential can be discovered. The curious reader, at the same time, may consult Spelman’s Glossary, voce MAIUMA, and Ducange, vv. MAJUMA, MAIUS.
In an old manuscript music-book given lately by Mr. Dalziel to the Advocates’ Library are the following scraps of songs about Robin Hood:
“First when Robin good bow bare,Was never bairne so bold,Doune, doune, berrie, doune, doune.”“Now will ye hear a jollie jest,How Robin Hood was pope of Rome,And Wallace king of France.”“Jolly Robin goe to the green wood to thy lemman.”“The nock is out of Johnes bow, Joly, joly,” &c.
Much curious matter on the subject of the morris-dance is to be found in “Mr. Tollet’s opinion concerning the Morris-dancers upon his Window.” (See Steevens’s Shakespeare, v. 425, edition 1778, or viii. 596, edition 1793. See also Mr. Waldron’s notes upon the Sad Shepherd, 1783, p. 255.) Morris-dancers are said to be yet annually seen in Norfolk,101 and make their constant appearance in Lancashire.102
In Scotland, “The game of Robin Hood was celebrated in the month of May. The populace assembled previous to {cvix} the celebration of this festival, and chose some respectable103 member of the corporation to officiate in the character of Robin Hood, and another in that of Little John his squire. Upon the day appointed, which was a Sunday or holyday, the people assembled in military array, and went to some adjoining field, where, either as actors or spectators, the whole inhabitants of the respective towns were convened. In this field they probably amused themselves with a representation of Robin Hood’s predatory exploits, or of his encounters with the officers of justice [rather, perhaps, in feats of archery or military exercises].
“As numerous meetings for disorderly mirth are apt to engender tumult, when the minds of the people came to be agitated with religious controversy, it was found necessary to repress the game104 of Robin Hood by public statute. The populace were by no means willing to relinquish their favourite amusement. Year after year the magistrates of Edinburgh were obliged to exert their authority105 in repressing this game; often ineffectually. In the year 1561, the mob were so enraged at being disappointed in making a Robin Hood, that they rose in mutiny, seized on the city gates, committed robberies upon strangers; and one of the {cx} ringleaders being condemned by the magistrates to be hanged, the mob forced open the jail, set at liberty the criminal and all the prisoners, and broke in pieces the gibbet erected at the cross for executing the malefactor. They next assaulted the magistrates, who were106 sitting in the council-chamber, and who fled to the Tolbooth for shelter, where the mob attacked them, battering the doors, and pouring stones through the windows. Application was made to the deacons of the corporations to appease the tumult. Remaining, however, unconcerned spectators, they made this answer: ‘They will be magistrates alone; let them rule the people alone.’ The magistrates were kept in confinement till they made proclamation be published, offering indemnity to the rioters upon laying down their arms. Still, however, so late as the year 1592, we find the General Assembly complaining of the profanation of the sabbath, by making107 of Robin Hood plays” (Arnot’s History of Edinburgh, p. 77).
Notwithstanding the above representation, it is certain that these amusements were considerably upon the decline before the year 1568. This appears from a poem by Alexander Scot, preserved in the Hyndford MS. (in the Advocates’ Library, compiled and written in that identical year), and inaccurately printed in The Evergreen:
“In May quhen men zeid everichoneWith Robene Hoid and Littill Johne,To bring in bowis and birkin bobbynis:Now all sic game is fastlingis gone,But gif it be amangis clovin Robbynis.”
(35) —“His bow, and one of his arrows, his chair, his cap, and one of his slippers were preserved till within the present century.”] “We omitted,” says Ray, “the sight of Fountain’s Abbey, where Robin Hood’s bow is kept” (Itineraries, 1760, p. 161).
“Having pleased ourselves with the antiquities of ‘Notingham,’ we took horse and went to visit the well and {cxi} ancient chair of Robin Hood, which is not far from hence, within the forest of Sherwood. Being placed in the chair, we had a cap, which they say was his, very formally put upon our heads, and having performed the usual ceremonies befitting so great a solemnity, we receiv’d the freedom of the chair, and were incorporated into the society of that renowned brotherhood” (Brome’s Travels over England, &c., 1700, p. 85).
“On one side of this forest [sci. of Sherwood] towards Nottingham,” says the author of “The Travels of Tom Thumb over England and Wales” (i.e. Robert Dodsley), “I was shewn a chair, a bow, and arrow, all said to have been his [Robin Hood’s] property” (p. 82).
“I was pleased with a slipper, belonging to the famous Robin Hood, shewn me, fifty years ago, at St. Ann’s well, near Nottingham, a place upon the borders of Sherwood forest, to which he resorted” (Journey from Birmingham to London, by W. Hutton, Bir. 1785, p. 174).
(36) —“Not only places which afforded him security or amusement, but even the well at which he quenched his thirst, still retain his name.”] Robin Hood’s Bay is both a bay and a village on the coast of Yorkshire, between Whitby and Scarborough. It is mentioned by Leland as “a fischer tounlet of 20. bootes caullid Robyn Huddes bay, a dok or bosom of a mile yn length” (Itinerary, i. 53). “When his robberies,” says Master Charlton, “became so numerous, and the outcries against him so loud, as almost to alarm the whole nation, parties of soldiers were sent down from London to apprehend him: and then it was, that fearing for his safety, he found it necessary to desert his usual haunts, and, retreating northward, to cross the moors that surrounded Whitby [one side whereof happens, a little unfortunately, to lie open to the sea], where, gaining the sea-coast, he always had in readiness near at hand some small fishing vessels, to which he could have refuge, if he found himself pursued; for in these, putting off to sea, he looked upon himself as quite secure, and held the whole power of the English nation at defiance. The chief place of his resort {cxii} at these times, where his boats were generally laid up, was about six miles from Whitby, to which he communicated his name, and which is still called Robin Hood’s Bay. There he frequently went a fishing in the summer season, even when no enemy appeared to annoy him, and not far from that place he had buts or marks set up, where he used to exercise his men in shooting with the long-bow.” 108
Near Gloucester is “a famous hill” called “Robin Hood’s hill,” concerning which there is a very foolish modern song. Another hill of the same name exists in the neighbourhood of Castleton, Derbyshire.
“Over a spring call’d Robin Hoods well (3 or 4 miles [on] this side [i.e. north] of Doncaster, and but a quarter of a mile only from 2 towns call’d Skelbrough and Bourmallis) is a very handsome stone arch, erected by the Lord Carlisle, where passengers from the coach frequently drink of the fair water, and give their charity to two people who attend there” (Gent’s History of York. York, 1730, p. 234).109 {cxiii}
Though there is no attendance at present, nor is the water altogether so fair as it might and should be, the case was otherwise in the days of honest Barnaby.
“Veni Doncaster, &c.Nescit sitis artem modi,Puteum Roberti HoodiVeni, & liquente venaVincto110 catino catena,Tollens sitim, parcum odi,Solvens obolum custodi.”“Thence to Doncaster, &c.Thirst knowes neither meane nor measure,Robin Hood’s well was my treasure;In a111 common dish enchained,I my furious thirst restrained:And because I drunk the deeper,I paid two farthings to the keeper.”
He mentions it again:
“Nunc longinquos locus odi,Vale fons Roberti Hoodi.”“Now I hate all foreign places,Robin Hood’s well, and his chaces.”
A different well, sacred either to Robin Hood or to St. Ann, has been already mentioned.
“Not far [off Bitham, in Lincolnshire] is Robyn Huddes cros, a limes of the shires” (Leland’s Itinerary, i. 25).
(37) —“conferred as a singular distinction upon the prime minister to the king of Madagascar.”] The natives of this island, who have dealings with our people, pride themselves, it seems, in English names, which are bestowed upon them at the discretion or caprice of the sailors: and thus a venerable minister of state, who should have been called Sir Robert Walpole or Cardinal Fleury, acquired the name of Robin Hood. Mr. Ives, by whom he is frequently mentioned, relates the following anecdote:—
“The reader will excuse my giving him another instance . . . . which still more strikingly displays the extreme sensibility of these islanders, in respect to their king’s dignity. Robin Hood (who seemed to act as prime minister, and negotiate most of the king’s concerns with our agent-victualler) was one day transacting business with another gentleman of the squadron, and they happened to differ so much about the value of a certain commodity, that high words arose, and at length Robin Hood in the greatest agitation started from the ground where he was sitting, and swore that he would immediately acquaint the king of Baba with what had passed. Our English gentleman, too much heated with this threat, and the violent altercation which had preceded it, unguardedly replied, ‘D―n the king of Baba.’ The eyes of Robin Hood flashed like lightning, and in the most violent wrath he retorted, ‘D―n King George.’ At the same instant he left the spot, hurrying away towards the Madagascarian cottages. Our countryman was soon struck with the impropriety of his behaviour, followed and overtook the disputant, and having {cxv} made all proper concessions, the affair was happily terminated.” 112
(38) “After his death his company was dispersed.”] They and their successors, disciples, or followers are supposed to have been afterward distinguished, from the name of their gallant leader, by the title of Roberdsmen. Lord Coke, who is somewhat singular in accusing him of living “by robbery, burning of houses, felony, waste and spoil, and principally by and with vagabonds, idle wanderers, night-walkers, and draw-latches,” says that “albeit he lived in Yorkshire, yet men of his quality took their denomination of him, and were called Roberdsmen throughout all England. Against these men,” continues he, “was the statute of Winchester made in 13 E. 1. [c. 14], for preventing of robbery, murders, burning of houses, &c. Also the statute of 5 E. 3. [c. 14], which ‘recites’ the statute of Winchester, and that there had been divers manslaughters, felonies, and robberies done in times past, by people that be called Roberdsmen, wasters and draw-latches; and remedy [is] provided by that act for the arresting of them. At the parliament holden 50 E. 3.,” he adds, “it was petitioned to the king that ribauds and sturdy beggars might be banished out of every town. The answer of the king in parliament was, touching ribauds: The statute of Winchester and the declaration of the same with other statutes of Roberdsmen, and for such as make themselves gentlemen, and men of armes, and archers, if they cannot so prove theirselves, let them be driven to their occupation or service, or to the place from whence they came.” He likewise notices the statute of 7 R. 2. [c. 5], by which it is provided “that the statutes of Roberdsmen and draw-latches be firmly holden and kept” (3 Inst. 197).
These Roberdsmen are mentioned in Pierce the Ploughman’s Crede, written about 1400:
“And right as Robartesmen raken aboute.” 113
Mr. Warton, who had once thought that the friers Robertines were here meant, observes that “the expression of Robin Hoode’s men, in Bishop Latimer’s sermon, is not without an allusion to the bad sense of Roberdsmen” (H. E. P. ii. additions, sig. d. 4). It does not, however, appear that the latter word has been ever used in a good one; nor is there, after all, sufficient ground for concluding that these people were so named after Robin Hood.
(39) —“the honour of Little John’s death and burial is contended for by rival nations.”] I. By England.—At the village of Hathersage, about six miles from Castleton, in Derbyshire, is Little John’s grave. A few years ago some curious person caused it to be opened, when there were found several bones of an uncommon size, which he preserved; but, meeting afterwards with many unlucky accidents, he carefully replaced them; partly at the intercession of the sexton, who had taken them up for him, and who had in like manner been visited with misfortunes: upon restoring the bones all these troubles ceased. Such is the tradition at Castleton. E. Hargrove, in his “Anecdotes of Archery,” York, 1792, asserts that “the grave is distinguished by a large stone placed at the head, and another at the feet, on each of which are yet some remains of the letters I. L.” (p. 26).114 II. By Scotland.—“In Murray land,” according to that most veracious historian Maister Hector Bois, “is the kirke of Pette, quhare the banis of lytill Johne remanis in gret admiratioun of pepill. He hes bene fourtene fut of hycht115 with square membris effering thairto. Vi. zeris,” continues he, “afore the cumyng of this {cxvii} werk to lycht we saw his hanche-bane, als mekill as the haill bane of ane man: for we schot our arme in the mouth thairof. Be quhilk apperis how strang and square pepill grew in our regioun afore thay were effeminat with lust and intemperance of mouth.” 116 III. By Ireland.—“There standeth,” as Stanihurst relates, “in Ostmantowne greene an hillocke, named little John his shot. The occasion,” he says, “proceeded of this.
“In the yeare one thousand one hundred foure score and nine, there ranged three robbers and outlaws in England, among which Robert Hood and Little John weere cheefeteins, of all theeves doubtlesse the most courteous. Robert Hood being betrayed at a nunrie in Scotland called Bricklies, the remnant of the crue was scattered, and everie man forced to shift for himselfe. Whereupon Little John was faine to flee the realme by sailing into Ireland, where he sojornied for a few daies at Dublin. The citizens being doone to understand the wandering outcast to be an excellent archer, requested him hartilie to trie how far he could shoot at random; who yeelding to their behest, stood on the bridge of Dublin, and shot to that mole hill, leaving behind him a monument, rather by his posteritie to be woondered, than possiblie by anie man living to be counterscored. But as the repaire of so notorious a champion to anie countrie would soone be published, so his abode could not be long concealed: and therefore to eschew the danger of [the] lawes, he fled into Scotland, where he died at a towne or village called Moravie.” 117 Thus Stanihurst, who is quoted by Dr. Hanmer in his Chronicle of Ireland, p. 179, but Mr. Walker, after observing that “poor Little John’s great practical skill in archery could not save him from an ignominious fate,” says, “it appeared, from some records in the Southwell family, that {cxviii} he was publicly executed for robbery on Arbor Hill, Dublin.” 118
(40) —“some of his descendants of the name of Nailor,” &c.] See the preface to the History of George a Green. As surnames were by no means in general use at the close of the twelfth century, Little John may have obtained that of Nailor from his original profession.
(“Ye boasted worthies of the knuckle,To Maggs and to the Nailor truckle.”)
But however this, or the fact itself may be, a bow, said to have belonged to Little John, with the name of Naylor upon it, is now, as the editor is informed, in the possession of a gentleman in the West Riding of Yorkshire.
The quotation about whetstones is from the Sloane MS. Those, indeed, who recollect the equivocal meaning of the word may think that this production has not been altogether confined to the grave of Little John.

4 See Part II. Ballad 1.
5 All three mention a Loxley in Warwickshire, and another in Staffordshire (“near Needwood forest; the manor and seat of the Kinardsleys”).
6 It is 1100 in the original, but that is clearly an error of the press.
7 King Edward, it is true, is introduced in the “Lytell Geste,” &c., but the author has unquestionably meant the first of that name.
8 Thus, likewise, in a much earlier version from the same immortal bard (Homer a la mode, 1664), we read of
 greate
Apollo, who’s as good
greate
Apollo, who’s as good9 Alias R. G., the scurrilous and malignant editor of that degraded publication.
10 The authority cited by Grafton in 1569 as then “olde and auncient” must have been at least of equal antiquity with the most ancient poems that Dr. P. is acquainted with.
11 Stukeley’s Palæographia Britannica, No. II. p. 115. In an interleaved copy of Robin Hood’s Garland formerly belonging to Dr. Stukeley, and now in the possession of Francis Douce, esquire, opposite the second page of the first song, is the following note in his own hand:
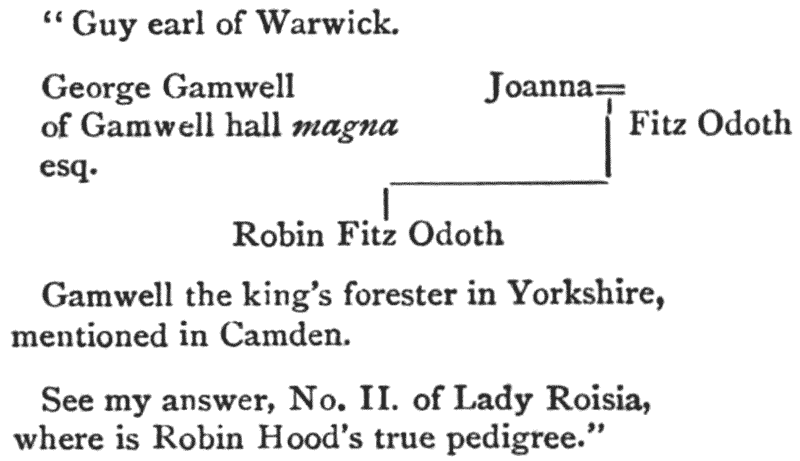
The Doctor seems, by this pedigree, to have founded our hero’s pretensions on his descent from Roisia, sister of Robert Fitzgilbert, husband of Alice, youngest daughter of Judith, Countess of Huntingdon, which, whatever it might do in those times, would scarcely be thought sufficient to support such a claim at present. Beside, though John the Scot died without issue, he left three sisters, all married to powerful barons, either in Scotland or in England, none of whom, however, assumed the title. It is, therefore, probable, after all, that Robin Hood derived his earldom by some other channel.
Dr. Stukeley, whose learned labours are sufficiently known and esteemed, was a professed antiquary, and a beneficed clergyman of the Church of England. He has not, it is true, thought it necessary to cite any ancient or other authority in support of the above representations; nor is it in the editor’s power to supply the deficiency. Perhaps, indeed, the Doctor might think himself entitled to expect that his own authority would be deemed sufficient: upon that, however, they must be content to rest. Sit fides penes auctorem! Mr. Parkin, who published “A reply to the peevish, weak, and malevolent objections brought by Dr. Stukeley in his Origines Roystonianæ, No. 2” (Norwich, 1748, 4to), terms “his pedigree of Robin Hood, quite jocose, an original indeed!” (See pp. 27, 32.)
Otho and Fitz-Otho, it must be confessed, were common names among the Anglo-Normans,* but no such name as Othes, Ooth, Fitz-Othes, or Fitz-Ooth, has been elsewhere met with. Philip de Kime, also, was certainly a considerable landholder in the county of Lincoln in the time of King Henry II., but it nowhere appears, except from Dr. Stukeley, that his surname was Fitz-Ooth.
The Doctor likewise informs us that the arms of Ralph Fitz-Ooth, and consequently of our hero, were “g. two bendlets engrailed, o.”
* “Filius Roberti filii Odonis est in custodia Domini Regis, et est vj annorum, et ipse est heres decime partis unius militis, et vix possunt inde habere victum suum ipse et mater sua.” Rotulus de vidius, &c. (31 H. 2) MSS. Har. 624.
12 Grafton’s Chronicle, p. 85.
13 Collec. i. 54.
14 See Robin Hood’s Progress to Nottingham, part ii. ballad 2.
15 Plompton Park, upon the banks of the Peterill, in Cumberland, was formerly very large, and set apart by the kings of England for the keeping of deer. It was disafforested or disparked by Henry VIII. See Camden’s Britannia, by Bishop Gibson, who seems to confound this park with Inglewood forest, a district of sixteen miles in length, reaching from Carlisle to Penrith, where the kings of England used to hunt, and Edward I. is reported to have killed 200 bucks in one day (Ibid.)
16 Anno 1194] Vicesima nona die mensis martii Richardus rex Angliæ projectus est videre Clipestone, & forrestas de Sirewode, quas ipse nunquam viderat antea: & placuerunt ei multum, & eodem die rediit ad Notingham (R. de Hoveden, Annales, p. 736).
Drayton (Polyolbion, song 26) introduces Sherwood in the character of a nymph, who, out of disdain at the preference shown by the poet to a sister-forest,
17 It occurs in “Tarlton’s Newes out of Purgatory,” 1630, 4to (entered on the Stationers’ books in 1590).
18 It likewise gives the proverb noticed in a preceding page thus:
19 There is an edition in 1706, 8vo.
20 Scotish Poems, i. 122.
21 Surely the “lady” alluded to in the old May-game cannot be our Maid Marian. The earliest notice of her occurs in Barclay’s Egloges, about 1500, where she is evidently connected with Robin Hood. See Note 26.
22 Without “the ancient songs,” to which the Doctor refers, are confined to his “old MS.,” he evidently asserts what he would probably find it difficult to prove. As for the passage he produces, it seems nothing to the purpose; as, in the first place, it is apparently not “antient,” and, in the second, it is apparently not from a “song of Robin Hood.”
23 Mr. Warton, having observed that “The play of Robin and Marian is said to have been performed by the school-boys of Angiers, according to annual custom, in the year 1392: The boys were deguisiez, says the old French record; and they had among them un fillette desguisee (Carpent. Du Cange, v. Robinet-Pentecoste),” adds, “Our old character of Mayd Marian may be hence illustrated” (His. En. po. i. 245). This, indeed, seems sufficiently plausible; but unfortunately the Robin and Marian of Angiers are not the Robin and Marian of Sherwood. The play is still extant. See Fabliaux ou Contes, Paris, 1781, ii. 144. There are, likewise, some very ancient pastoral ballads on the subject of these two lovers. See La Borde, Essai sur la Musique, ii. 163, 215. But, in fact, the names of Robin and Marion seem to have been used by the chansonniers of antiquity like those of Colin and Phœbe, &c.
24 In 1592, Richard Jones, stationer, entered on the Company’s books, “A plesant fancie, or merrie conceyt, called the passion et morrys, daunst by a crue of 8 couple of wores.
25 “The quarry from whence King Wolfere fetched stones for his royal structure [i.e. Peterborough] was undoubtedly that of Bernach near unto Stamford . . . . And I find in the charter of K. Edward the Confessor, which he granted to the abbot of Ramsey, that the abbot of Ramsey should give to the abbot and convent of Peterburgh 4000 eeles in the time of Lent, and in consideration thereof the abbot of Peterburgh should give to the abbot of Ramsey as much freestone from his pitts in Bernack, and as much ragstone from his pitts in Peterburgh as he should need. Nor did the abbot of Peterburgh from these pits furnish only that but other abbies also, as that of St. Edmunds-Bury: in memory whereof there are two long stones yet standing upon a balk in Castor-field, near unto Gunwade-ferry; which erroneous tradition hath given out to be draughts of arrows from Alwalton churchyard thither; the one of Robin Hood, and the other of Little John; but the truth is, they were set up for witnesses, that the carriages of stone from Bernack to Gunwade-ferry, to be conveyed to S. Edmunds-Bury, might pass that way without paying toll; and in some old terrars they are called S. Edmund’s stones. These stones are nicked in their tops after the manner of arrows, probably enough in memory of S. Edmund, who was shot to death with arrows by the Danes” (Gunton’s History of the Church of Peterburgh, 1686, p. 4).
26 “In this relation,” Mr. Walker observes, “the Doctor not only evinces his credulity, but displays his ignorance of archery; for the ingenious and learned Mr. Barrington, than whom no man can be better informed on the subject, thinks that eleven score and seven yards is the utmost extent that an arrow can be shot from a long bow” (Archæologia, vol. viii.) According to tradition, he adds, Little John shot an arrow from the Old-bridge, Dublin, to the present site of St. Michael’s church, a distance not exceeding, he believes, that mentioned by Mr. Barrington (Historical Essay on the Dress of the Ancient and Modern Irish, p. 129).
What Mr. Barrington “thinks” may be true enough, perhaps, of the Toxophilite Society and other modern archers; but people should not talk of Robin Hood who never shot in his bow. The above ingenious writer’s censure of Dr. Hanmer’s credulity and ignorance, seems to be misapplied, since he cannot be supposed to believe what he holds not for truth, and actually leaves among the lyes of the land.
See also the old song, printed in the Appendix, No. 3. Drayton, who wrote before archery had fallen into complete disuse, says—
That Mr. Barrington, indeed, was very ill informed on the subject is evident from a most scarce book in the editor’s possession, intitled “Aime for the archers of St. George’s fields, containing the names of all the marks in the same fields, with their true distances according to the dimensuration of the line. Formerly gathered by Richard Hannis, and now corrected by Thomas Bick and others. London, Printed by N. Howell for Robert Minehard and Benjamin Brownsmith, and are to be sold at the sign of the man in the moon in Blackman street, 1664,” 16mo, where the distance from Alpha to Bick’s memorial is 18 score 16 yards; and 11 score 7 yards (though there are inferior numbers, the lowest being 9, 12) appears to be a very moderate shot indeed. Two of these marks are Robin Hood and Little John. See also Shakespeare’s Second Part of K. Henry IV., act iii. scene 2, where it is said that Old Double “would have clapp’d i’ the clout at twelve score; and carry’d you a forehand shaft a fourteen and fourteen and a half;” and the notes upon the passage in Steevens’s edition, 1793. It is probable, after all, that the word forty in Drayton is an error, of the transcriber or pressman, for fourteen.
Whatever Robin Hood’s father might do, there can be no question that the author of the old ballad in which he is mentioned (part ii. song 1) has “shot in a lusty strong bow” when he speaks of
27 Warner’s Albion’s England, 1602, p. 132. It is part of the hermit’s speech to the Earl of Lancaster.
28 Sir Roger Williams, in his Briefe discourse of warre, 1590, has a chapter “To prooue bow-men the worst shot vsed in these daies.” Sir John Smythe, however, was of a different opinion. See his “Discourses concerning the formes and effects of divers sorts of weapons, &c. As also, of the great sufficiencie, excellencie, and wonderful effects of archers,” 1590, 4to. See also a different treatise by him upon the same subject in Num. 132 of the Harleian MSS.
29 “A prince who fills the throne with a disputed title dares not arm his subjects, the only method of securing a people fully both against domestic oppression and foreign conquest” (Hume’s Essays, “Of the Protestant Succession”).
30 Flemings.
31 Breeches.
32 Thus also in part ii. ballad 1:
33 In the sign of The green man and still, we perceive a huntsman in a green coat standing by the side of a still; in allusion, as it has been facetiously conjectured, to the partiality shown by that description of gentry to a morning dram. The genuine representation, however, should be the green-man (or man who deals in green herbs) with a bundle of peppermint or penny-royal under his arm, which he brings to have distilled.
34 There appears, however, to be a town of this name in Flanders, which may be the place here meant. The above conjecture, therefore, will be received for no more than it is worth.
35 When Bulas, or Felix, the robber, was brought before Papinian, the latter asked him why he gave himself up to robbing and spoiling: “And why, sir,” was the answer, “are you ‘a governor’?” See Dio Cassius in Severus.
“Because I do that,” said the pirate to Alexander, “with a single ship which thou dost with a great fleet, I am called a thief, and thou art called a king.”
36 See Pennant’s Tour in Scotland MDCCLXXII. part i. p. 404. The original reading, whether altered by mistake or design, is—
One might, to the same purpose, address our hero in the words of Plautus (Trinummus, act iv. scene x):
 I’ve heard before
I’ve heard before38 That this epitaph had been printed, or was well known, at least, long before the publication of Mr. Thoresby’s book, if not before either he or Dr. Gale was born, appears from the “True Tale of Robin Hood” by Martin Parker, written, if not printed, as early as 1631. (See post, p. 126.) That dates, about this period, were frequently by ides and kalends, see Madox’s Formulare Anglicanum (Dissertation), p. xxx. Even Arabic figures are produced in some of still greater antiquity; see Collectanea de rebus Hibernicis, ii. 331. Robert Grosthead, Bishop of Lincoln, makes use of these figures about the year 1240. Astle’s Origin of Writing, p. 188.
39 In “The Travels of Tom Thumb over England and Wales” [by Mr. Robert Dodsley], p. 106, is another though inferior version:
40 In “a large folio volume of accounts kept by Mr. Philip Henslowe, who appears to have been proprietor of the Rose theatre near the Bankside in Southwark,” he has entered—
In a subsequent page is the following entry: “Lent unto Robarte Shawe, the 18 of Novemb. 1598, to lend unto Mr. Cheattle, upon the mending of the first part of Robart Hoode, the sum of xs.;” and afterwards—“For mending of Robin Hood for the corte.” See Malone’s edition of “The Plays and Poems of William Shakespeare,” 1790, vol. i. part ii. (Emendations and additions.)
41 That is, the inn so called, upon Ludgate Hill. The modern sign, which, however, seems to have been the same 200 years ago, is a bell and a wild man; but the original is supposed to have been a beautiful Indian; and the inscription, La belle sauvage. Some, indeed, assert that the inn once belonged to a Lady Arabella Savage; and others, that its name, originally The bell and savage, arose (like The George and blue boar) from the junction of two inns, with those respective signs. Non nostrûm est tantas componere lites.
42 She is called the Widow Scarlet; so that Scathlocke was the elder brother. In fact, however, it was mere ignorance in the author to suppose the Scathlocke and Scarlet of the story distinct persons, the latter name being an evident corruption of the former; Scathlock, Scadlock, Scarlock, Scarlet.
43 In “The booke of the inventary of the goods of my lord admeralles men tacken the 10 of Marche in the yeare 1598,” are the following properties for Robin Hood and his retinue in this identical play:
44 George a Greene and Wakefield’s pinner were one and the same person. The shoemaker of Bradford is anonymous.
45 Which, by the way, was termed a hempen caudle. See the Second Part of K. H. VI., act iv. scene 7. Lord-Chancellor Jeffries, at the revolution, was treated much in the same manner. One day, during his confinement in the Tower, he received a barrel of oysters, upon which he observed to his keeper, “Well, you see, I have yet some friends left:” at the bottom of the barrel, however, he found a halter; which changed his countenance, and is even thought to have hastened his death.
46 See the ballad of “The Jolly Pinder of Wakefield,” part ii. num. iii.
47 Fitzwater confounds one man with another; Harold Harefoot was the son and successor of Canute the great.
48 This tradition is referred to, and the inscription given, in Ray’s Itineraries, 1760, p. 153:—“We rode through a bushet or common called Rodwell-hake, two miles from Leeds, where (according to the vulgar tradition) was once found a stag, with a ring of brass about its neck, having this inscription:
In The Midwife, or Old Woman’s Magazine (vol. i. p. 250), Mrs. Midnight, in a letter “To the venerable society of antiquarians,” containing a description of Cæsar’s camp on Windsor forest, has the following passage: “There have been many extraordinary things discovered about this camp. One thing, I particularly remember, was a deer of about sixteen hundred years old. . . . . . This deer it seems was a favourite of Cæsar’s, and on that account he bedecked her neck with a golden collar and an inscription, which I shall by and by take notice of; she had been frequently taken, but when the hunters, the peasants, and poor people saw the golden collar on her neck, they readily let her go again. However, as she continually increased in strength and in bulk, as well as in age, after the course of about fifteen or sixteen centuries, the flesh and skin were entirely grown over this collar, so that it could not be discover’d till after she was kill’d, and then to the surprise of the virtuosi it appear’d with this inscription:
“This collar, which is of pure gold, I am told weighs thirty ounces, and as the blood of the creature still appears fresh upon it, I believe it may be as valuable as any of your gimcracks; however, there will be no harm in my sending of it to you; and if I can procure it, you may depend on my taking the utmost care of it.” As no notice is announced of this wonderful piece of antiquity in the voluminous and important lucubrations of the above learned body, it most probably never came into their possession; which is very much to be lamented, as it would have been an admirable companion for Hardecnute’s chamber-pot, King Edward the first’s finger, and other similar curiosities.
Juvenal des Ursins gravely relates that in the year 1380 a hart was taken at Senlis with a chain about his neck inscribed “Cæsar hoc me donavit.”*
Upton, to be even with him, supposes a hart to have been taken at Bagshot near Windsor, with a motto on the collar in the French language, which proves the ancient Romans were familiar therewith long before it existed:
This dictator perpetuo, in fact, seems to have collared every hart he took. The family of Pompei in Italy use two harts for their supporters on whose collars were the letters N. M. T., in memory of one on whose collar were these words: “Nemo Me Tangat, Cæsaris sum.” Anstis, ii. 113.
The original of all these stories is to be found in Pliny, who says: “It is generally held and confessed that the stagge or hind live long; for an hundred yeer after Alexander the great, some were taken with golden collars about their necks, overgrowne now with haire and growne within the skin: which collars the said king had done upon them” (Naturall Historie, by Holland, 1601, B. 8, c. 32). Pausanias, moreover, speaking of one Leocydas, who fought for the Megalopolitans, in conjunction with Lydiades, against the Lacedæmonians (about the year 243 before Christ), says he was reported to be the descendant in the ninth degree of that Arcesilaus, who living in Lycosura saw that stag which is sacred to the goddess Despoine worn out with old age. This stag, he adds, had a collar on its neck with the following inscription:
By which, he concludes, it is evident that a stag lives much longer than an elephant (B. 8, c. 10).
* Histoire de Charles VI.
† Upton de re militari, p. 119.
49 Robin, in the old legend, expresses his regard for this order of men (concerning which the reader may consult an ingenious “Essay” in the Reliques of Ancient English Poetry, vol. i., and some “Observations” in a collection of ancient songs, printed in 1790):
50 This play is entered in Master Henslowe’s account-book with the date of December 1600. See Malone’s Shakespeare, vol. ii. part ii. (Emen. & ad.)
51 “The Triumphes of Reunited Britannia. A pageant in honour of Sir Leonard Holliday, lord mayor.” 1605.
52 Henry Fitz-Alwine Fitz-Liefstane, goldsmith, first mayor of London, was appointed to that office by King Richard I. in 1189, and continued therein till the 15th of King John, 1212, when he “deceased, and was buried in the priorie of the holy trinitie, neare unto Aldgate” (Stow’s Survey, 1598, p. 418). His relationship with Robin Hood is merely poetical, and invented by Mundy “for the nonce;” though it is by no means improbable that they were acquainted, and that our hero might have occasionally dined at the Mansion-house on a Lord Mayor’s day.
53 Jonson was led into this mistake by the old play of Robin Hood. See before, p. lv.
54 This play appears to have been performed upon the stage after the Restoration. The prologue and epilogue (spoken by Mr. Portlock) are to be found in num. 1009 of the Sloane MSS. It was republished, with a continuation and notes, by Mr. Waldron, of Drury-lane Theatre, in 1783.
55 A most stupid pantomime on this subject, under the title of “Merry Sherwood, or Harlequin, forester,” was performed in December 1795, at the Theatre-royal, Covent-garden.
56 1st edit. 1550, fo. xxvi. b. (Randolf is misprinted Rand of.) Subsequent editions, even of the same year, reading only “Randall of Chester.” Mr. Warton (History of English Poetry, ii. 179) makes this genius, whom he calls a frier, say “that he is well acquainted with the rimes of Randall of Chester;” and these rimes he, whimsically enough, conjectures to be the old Chester Whitsun plays; which, upon very idle and nonsensical evidence, he supposes to have been written by Randal Higden, the compiler of the Polychronicon. Of course, if this absurd idea were at all well founded, the rimes of Robin Hood must likewise allude to certain Yorkshire or Nottinghamshire plays, written by himself. The “Randolf erl of Chester” here meant is Randal Blundevile, the last earl of that name, who had been in the Holy Land, was a great warrior and patriot, and died in 1231.
The reading of the original edition is confirmed by a very old manuscript in the Cotton Library (Vespasian, B. XVI.) differing considerably from the printed copies, which gives the passage thus:
(See also Caligula, A. XI.)
The speaker himself could have told Mr. Warton he was no frier:
57 “De quibus stolidum wigus hianter in comœdiis & tragædiis prurienter festum faciunt, & super ceteras ‘romancias mimos & bardanos cantitare delectantur” (Scotichronicon, à Hearne, p. 774). Comedies and tragedies are—not dramatic compositions, but—poems of a comic or serious cast. Romance in Spanish, and romance in French, signify—not a tale of chivalry, but—a vulgar ballad, at this day.
58 “Rebus hujus Roberti gestis tota Britannia in cantibus utitur” (Majoris Britanniæ Historia, Edin. 1740, p. 128).
59 Hystory of Scotland, Edin. 1541, fo. The word “waithman” was probably suggested by Andrew of Wyntown (see before, Note 3). It seems equivalent to the English vagabond, or perhaps outlaw. Waith is waif; and it is to be remembered that, in the technical language of the English courts, a woman is said to be waived, and not outlawed. “In our auld Scottish langage,” says Skene, “ane Vothman is ane out-law, or ane fugitive fra the lawes” (De verborum significatione, Edin. 1597). It is from þæðan, venari, fugare. See Lye’s Dictionary. The passage above quoted does not occur in Boise’s original work.
60 Of this poem there have been at least five editions at London or Westminster, and one at Edinburgh. In a list of “bookes printed and . . . sold by Jane Bell, at the east end of Christ-church [1655],” in company with Frier Rush, The frier and the boy, &c., is “a book of Robin Hood and Little John.” Captain Cox of Coventry appears to have had a copy of some old edition: see Laneham’s Letter from Killingworth, 1575.
61 “Description of the Town of Tottenham-high-crosse,” &c. London (1631, 4to), 1781, 8vo. The invaluable MS. alluded to has been since discovered; and the entire poem, of which Mr. Ritson has here given a fragment, will be found in the Appendix.—ED.
62 The book, under the same title, printed by Wynken de Worde, in 1517, is a different translation in prose.
63 Mr. Warton reads Toby; and so, perhaps, it may be in former editions.
64 Honest Barnaby, i.e. Richard Brathwayte, who wrote or travelled about 1640, was well acquainted with our hero’s story.
Whitlock relates that “the [parliament] committee who carried the propositions of peace to Oxford, had the king’s answer sealed up and sent to them. They, upon advice together, thought it not fit for them to receive an answer in that manner . . . and made an address to his majesty that they might know what his answer was, and have a copy of it: to which his majesty replied, What is that to you, who are but to carry what I send, and if I will send the song of Robin Hood and Little John, you must carry it? To which the commissioners only said, that the business about which they came was of somewhat more consequence than that song” (Memorials, p. 115).
65 There is, in fact, such a place as Barnwood forest, in Buckinghamshire; but no one, except Mr. Hearne, has hitherto supposed that part of the country to have been frequented by our hero. Barnwood, in the case reported by Yelverton, has clearly arisen from a confusion of Barnsdale and green wood. “Robin Hood in the greenwood stood” was likewise the beginning of an old song now lost (see post, p. 197): and it is not a little remarkable that Jefferies, serjeant, on the trial of Pilkington and others, for a riot, in 1683, by a similar confusion, quotes the line in question thus:
A third corruption has taken place in Parker, p. 131 (King v. Cotton), though expressly cited from Yelverton, viz.
The following most vulgar and indecent rime, current among the peasantry in the North of England, may have been intended to ridicule the perpetual repetition of “Robin Hood in greenwood stood:”
66 It is possible that, amid these absurdities, there may be other lines of the old song of Robin Hood, which is the only reason for reviving them.
occurs, likewise, in a medley of a similar description, in Pammelia 1609.
67 In “Heraclitus ridens, or a discourse between Jest and Earnest,” a periodical paper against the Whigs, published in 1681, and collected and republished in 1713 (No. 34), Jest begins singing:
and says, “I hope I may sing of old Robin without offending a grand jury, or being presented for disuniting Protestants.”
In The Gentleman’s Magazine for December 1790 is the first verse of a song used by the inhabitants of Helston in Cornwall on the celebration of an annual festivity on the 8th of May, called the Furry-day, supposed Flora’s day, not, it is imagined, “as many have thought, in remembrance of some festival instituted in honour of that goddess, but rather from the garlands commonly worn on that day.” (See the same publication for June and October 1790.) This verse was the whole that Mr. Urban’s correspondent could then recollect, but he thought he might be afterwards able “to send all that is known of it, for,” he says, “it formerly was very long, but is now much forgotten.” The stanza is as follows:
“After which,” he adds, “there is something about the grey goose wing; from all which,” he concludes, “the goddess Flora has nothing to say to it.” She may have nothing to say to the song, indeed, and yet a good deal to do with the thing. But the fact is, that the first eight days of May, or the first day and the eighth, seem to have been devoted by the Celtic nations to some great religious ceremony. Certain superstitious observances of this period still exist in the Highlands of Scotland, where it is called the Bel-tein; Beltan, in that country, being a common term for the beginning of May, as “between the Beltans” is a saying significant of the first and eighth days of that month. The games of Robin Hood, as we shall elsewhere see, were, for whatever reason, always celebrated in May.—N.B. “Hel-an-tow,” in the above stanza, should be heave and how. Heave and how, and Rumbelow, was an ordinary chorus to old ballads, and is at least as ancient as the reign of Edward II., since it occurs in the stanza of a Scotish song, preserved by some of our old historians, on the battle of Bannockburn.
To lengthen this long note: Among the Harleian MSS. (num. 367) is the fragment of “a tale of Robin Hood dialouge-wise beetweene Watt and Jeffry. The morall is the overthrowe of the abbyes; the like being attempted by the Puritane, which is the wolfe, and the politician, which is the fox, agaynst the bushops. Robin Hood, bushop; Adam Bell, abbot; Little John, colleagues of the university.” This seems to have been a common mode of satirising both the old Church and the reformers. In another MS. of the same collection (N. 207), written about 1532, is a tract entitled “The banckett of John the reve, unto Peirs Ploughman, Laurens Laborer, Thomlyn Tailyor, and Hobb of the Hille, with others;” being, as Mr. Wanley says, a dispute concerning transubstantiation by a Roman Catholic. The other, indeed, is much more modern: it alludes to the indolence of the abbots, and their falling off from the original purity in which they were placed by the bishops, whom it inclines to praise. The object of its satire seems to be the Puritans; but here it is imperfect, though the lines preserved are not wholly destitute of poetical merit.—“Robin Hood and the Duke of Lancaster, a ballad, to the tune of The Abbot of Canterbury,” 1727, is a satire on Sir Robert Walpole.
68 Chatterton, in his “Memoirs of a Sad Dog,” represents “Baron Otranto” (meaning the honourable Horace Walpole, now Earl of Orford), when on a visit to “Sir Stentor,” as highly pleased with Robin Hood’s ramble, “melodiously chaunted by the knight’s groom and dairy-maid, to the excellent music of a two-stringed violin and bag-pipe,” which transported him back “to the age of his favourite hero, Richard the Third;” whereas, says he, “the songs of Robin Hood were not in being till the reign of Queen Elizabeth.” This, indeed, may be in a great measure true of those which we now have, but there is sufficient evidence of the existence and popularity of such-like songs for ages preceding; and some of these, no doubt, were occasionally modernised or new-written, though most of them must be allowed to have perished.
The late Dr. Johnson, in controverting the authenticity of Fingal, a composition in which the author, Mr. Macpherson, has made great use of some unquestionably ancient Irish ballads, said, “He would undertake to write an epick poem on the story of Robin Hood, and half England, to whom the names and places he should mention in it are familiar, would believe and declare they had heard it from their earliest years” (Boswell’s Journal, p. 486).
69 The following note is inserted in the fourth edition of the Reliques of Ancient English Poetry, published in July 1795 (vol. i. p. xcvii.):
“Of the 24 songs in what is now called ‘Robin Hood’s Garland,’ many are so modern as not to be found in Pepys’s collection, completed only in 1700. In the [editor’s] folio MS. are ancient fragments of the following, viz.—Robin Hood and the beggar.—Robin Hood and the butcher.—Robin Hood and fryer Tucke.—Robin Hood and the pindar.—Robin Hood and queen Catharine, in two parts.—Little John and the four beggars, and “Robine Hood his death.” This last, which is very curious, has no resemblance to any that have yet been published; [it is probably num. xxviii. of part ii.], and the others are extremely different from the printed copies; but they unfortunately are in the beginning of the MS. where half of every leaf hath been torn away.”
As this MS. “contains several songs relating to the civil war in the last century,” the mere circumstance of its comprising fragments of the above ballads is no proof of a higher antiquity; any more than its not containing “one that alludes to the Restoration” proves its having been compiled before that period; or than, because some of these 24 songs are not to be found in Pepys’s collection, they are more modern than 1700. If the MS. could be collated, it would probably turn out that many of its contents have been inaccurately and unfaithfully transcribed, by some illiterate persons, from printed copies still extant, and, consequently, that it is, so far, of no authority. See the advertisement prefixed.
70 Mr. Warton has mistaken and misprinted this line so as to make it absolute nonsense.
71 Drayton’s Polyolbion, song 26, p. 122 (supra, p. vii.)
72 In Churchyard’s “Replication onto Camel’s Objections” he tells the latter:
73 See the original story, in which two brothers, of whom one had wished for as many oxen as he saw stars, the other for a pasture as wide as the firmament, kill each other about the pasturage of the oxen (from Camer. oper. subscis. cent. 1, c. 92, p. 429), in Wanley’s Little World of Man, edition of 1774, p. 426. Camerarius, it seems, had the story from Scardeonius de claris civibus Patavinis, whence it is also related in the notes to Upton de studio militari; and an older, of the like kind, is in the Facetiæ of Poggius.
74 “Derry down is the burden of the old songs of the Druids sung by their Bards and Vaids, to call the people to their religious assemblys in the groves. Doire in Irish (the old Punic) is a grove: corrupted into derry. A famous Druid grove and academy at the place since called Londonderry from thence.”—MS. note by Dr. Stukeley, in his copy of Robin Hood’s Garland. “Paul, Paul, thou art beside thyself!”
75 Mr. Boyd, the famous preacher in Childsdale, finding that several of his hearers went away after the forenoon sermon, had this expression in his afternoon prayers: “Now, Lord, thou seest that many people go away from hearing thy Word; but had we told them stories of Robin Hood or Davie Lindsay, they had stayed; and yet none of these are near so good as thy Word that I preach” (Scotch Presbyterian Eloquence, 1714, p. 156).
76 The Bishop grows scurrilous. “I never heard,” says Coke, attorney-general, “that Robin Hood was a traitor, they say he was an outlaw.” (State Trials, i. 218.—Raleigh had said, “Is it not strange for me to make myself a Robin Hood, a Kett, or a Cade?”)
77 This ballad seems to have been written in imitation of a song in Heywood’s Rape of Lucrece, 1630, beginning—
78 In Arnold’s Essex Harmony (ii. 98) he gives the inscription, as a catch for three voices, of his own composition, thus:
79 This description is finely illustrated by an excellent woodcut at the head of one of Anthony a Wood’s old ballads in the Ashmoleian Museum. The frontispiece to Gervas Markham’s Archerie, 1634, is likewise a man drawing a bow.
80 See “The auncient order societie and unitie laudable of prince Arthure and his knightly armory of the round table . . . Translated and collected by R. R. London, Imprinted by John Wolfe dwelling in Distaffe-lane neere the signe of the Castle, 1583.” 4to, b. l. It appears from this publication that on the revival of London archery in Queen Elizabeth’s time, “the worshipfull socyety of archers,” instead of calling themselves after Robin Hood and his companions, took the names of “the magnificent prince Arthure and his knightly traine of the round table.” It is, probably, to one of the annual meetings of this identical society that Master Shallow alludes in the Second Part of King Henry IV. “I remember,” says he, “at Mile-end Green [their usual place of exercise],—I was then Sir Dagonet in Arthur’s shew,” &c. (See also Steevens’s Shakespeare, 1793, ix. 142.) The successors of the above “friendly and frank fellowship” assumed the ridiculous appellations of Duke of Shoreditch, Marquis of Clerkenwell, Earl of Pankridge, &c. See Wood’s Bowman’s Glory, 1682.
81 Meaning that his sole or chief employment had been in Christmas or May games, Whitsun-ales, and such like idle diversions. See Original Letters, &c., ii. 134.
In an old circular woodcut, preserved on the title of Robin Hood’s Garland, 1670, as well as on that of Adam Bell, &c., printed at Newcastle in 1772, is the apparent representation of a May-game, consisting of the following personages: 1. A bishop. 2. Robin Hood. 3. The potter (or beggar). 4. Little John. 5. Frier Tuck. 6. Maid Marian. Figures 2 and 4 are distinguished by their bows and different size. The frier holds out a cross; and Marian has flowing hair, and wears a sort of coronet. But the execution of the whole is too rude to merit a copy.
At Lord Fitzwilliams’s at Richmond there is, or lately was, a curious painting by Vinckenbooms, representing old Richmond palace, with a group of morris-dancers. It has been badly engraved by Godfrey, who reduced the figures to too small a scale. Mr. Douce has a tracing from the original picture with all the figures distinctly marked. See a poem at the end of Hall’s Downfall of May-games, 1661, 4to.
82
The precise purpose or meaning of setting up Robin Hood’s bower
has not been satisfactorily ascertained. Mr. Hearne, in an attempt to
derive the name of “The Chiltern country”
(cil![]() e
e n, Saxon) from
silex, a flint, has the following words: “Certe Silcestriam, &c. i.e.
Certainly Silchester, in Hampshire, signifies nothing but the city of
flints (that is, a city composed or built of flint-stones). And what is
more, in that very Chiltern country you may frequently see houses built
of flints, in erecting which, in ancient times, I suppose that many persons
involved themselves deeply in debt, and that, in order to extricate
themselves, they took up money at interest of I know not what great
men, which so far disturbed their minds that they would become thieves
and do many things in no wise agreeable to the English government.
Hence, the nobility ordered that large woods in the Chiltern country
should in a great measure be cut down, lest they should conceal any
considerable body of robbers, who were wont to convert the same into
lurking places. It concerns this matter to call to mind that of this sort
of robbers was that Robin or Robert Hood, of whom the vulgar dayly
sing so many wonderful things. He (being now made an outlaw)
before he retired into the north parts, frequently robbing in the Chiltern
country, lurked in the thickets thereof on purpose that he should not be
taken. Thence it was that to us boys (exhilarating, according to custom,
the mind with sports) certain countrymen, with whom we had
accidentally some conversation, shewed us that sort of den or retreat
(vulgarly called Robin Hood’s bower) in Maydenhead-thicket; which
thicket is the same that Leland in his Itinerary called Frith, by which
name the Anglo-Saxons themselves spoke of thickets. For although
n, Saxon) from
silex, a flint, has the following words: “Certe Silcestriam, &c. i.e.
Certainly Silchester, in Hampshire, signifies nothing but the city of
flints (that is, a city composed or built of flint-stones). And what is
more, in that very Chiltern country you may frequently see houses built
of flints, in erecting which, in ancient times, I suppose that many persons
involved themselves deeply in debt, and that, in order to extricate
themselves, they took up money at interest of I know not what great
men, which so far disturbed their minds that they would become thieves
and do many things in no wise agreeable to the English government.
Hence, the nobility ordered that large woods in the Chiltern country
should in a great measure be cut down, lest they should conceal any
considerable body of robbers, who were wont to convert the same into
lurking places. It concerns this matter to call to mind that of this sort
of robbers was that Robin or Robert Hood, of whom the vulgar dayly
sing so many wonderful things. He (being now made an outlaw)
before he retired into the north parts, frequently robbing in the Chiltern
country, lurked in the thickets thereof on purpose that he should not be
taken. Thence it was that to us boys (exhilarating, according to custom,
the mind with sports) certain countrymen, with whom we had
accidentally some conversation, shewed us that sort of den or retreat
(vulgarly called Robin Hood’s bower) in Maydenhead-thicket; which
thicket is the same that Leland in his Itinerary called Frith, by which
name the Anglo-Saxons themselves spoke of thickets. For although
![]()
 ið
in reality signifies peace, yet since numerous groves with them
(as well as before with the Britons) were deemed sacred, it is by no
means to be wondered at that a great wood (because manifestly an
asylum) should, in the judgment of the Anglo-Saxons, be called by no
other name than
ið
in reality signifies peace, yet since numerous groves with them
(as well as before with the Britons) were deemed sacred, it is by no
means to be wondered at that a great wood (because manifestly an
asylum) should, in the judgment of the Anglo-Saxons, be called by no
other name than
![]()
 ðe
ðe![]() :
and that Maydenhead-thicket was esteemed
among the greater woods Leland himself is a witness. Rightly therefore
did Robin Hood (as
:
and that Maydenhead-thicket was esteemed
among the greater woods Leland himself is a witness. Rightly therefore
did Robin Hood (as
![]()
 ið-bena)
reckon himself to abide there in
security” (Chronicon de Dunstaple, p. 387). What he means by all
this is, doubtless, sufficiently obscure: the mere name, however, of
Robin Hood’s bower seems a very feeble authority for concluding that
gallant outlaw to have robbed or skulked in the Chiltern hundreds.
ið-bena)
reckon himself to abide there in
security” (Chronicon de Dunstaple, p. 387). What he means by all
this is, doubtless, sufficiently obscure: the mere name, however, of
Robin Hood’s bower seems a very feeble authority for concluding that
gallant outlaw to have robbed or skulked in the Chiltern hundreds.
It may seem, perhaps, from a passage in Browne’s Britannia’s Pastorals (Song 4), that Robin Hood’s bower was prepared for the reception of himself and his Marian, as king and queen of May. The lines are these:
83 See Steevens’s Shakespeare, 1793, x. 186.
84 Albion’s England, 1602, p. 121. It is part of the “Northerne man’s speech against the friers.” He adds:
A very learned and ingenious gentleman conceives that the enumeration of characters in the passage quoted in the text belongs solely to the May, and has no relation whatever to the morrise. That the two games, however, though essentially distinct in their origin, got somehow or other blended together appears unquestionable.
“As fit as a morris for May-day” is one of the clown’s similes in All’s well that ends well (act ii. scene 2).
85 “The word livery was formerly used to signify anything delivered; see the Northumberland Household Book, p. 60. If it ever bore such an acceptation at that time, one might be induced to suppose, from the following entries, that it here meant a badge, or something of that kind:
| 15 C. of leveres for Robin Hode | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| For leveres, paper and sateyn | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| For pynnes and leveres | 0 | 6 | 5 |
| For 13 C. of leverys | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| For 24 great lyvereys | 0 | 0 | 4 |
We are told that formerly, in the celebration of May-games, the youth divided themselves into two troops, the one in winter livery, the other in the habit of the spring. See Brand’s Popular Antiquities, p. 261.” This quotation is misapplied. Liveries, in the present instance, are pieces of paper or sateyn with some device thereon, which were distributed for money among the spectators. So in a passage which will be shortly quoted from Jack Drum’s Entertainment: “Well said, my boyes, I must have my lord’s livory; what is’t? a May-pole?” See also Stubbs’s Anatomie of Abuses, 1583, sig. M. 2 b, and Skelton’s Don Quixote, part ii. chap. 22.
86 “Though it varies considerably from that word, this may be a corruption of orpiment, which was much in use for colouring the morris garments.” How orseden can be a corruption of orpiment is not very easy to conceive: it may as well be supposed to mean worsted or buckram. Mr. Steevens thinks that this orseden is the Arse-dine of old Joan Trash, in Jonson’s Bartholomew Fair, and means flame-coloured paint, used to hobby-horses. The four giants for the revived Midsummer shew at Chester, in 1668, were “to be cullered tinsille arsedine” (MSS. Har. 2150, fo. 373, b.)
87 “The friar’s coat was generally of russet, as it appears by the following extracts . . . .” The coat of this mock frier would, doubtless, be made of the same stuff as that of a real one.
88 “Marian was the assumed name of the beloved mistress of Robert, Earl of Huntingdon, whilst he was in a state of outlawry, as Robin Hood was his. See Mr. Steevens’s note to a passage in Shakespeare’s Henry IV. This character in the morris-dances was generally represented by a boy. See Strutt’s View of Customs and Manners, vol. iii. p. 150. It appears by one of the extracts, given above, that at Kingston it was performed by a woman, who was paid a shilling each year for her trouble.”
89 “Mr. Steevens suggests, with great probability, that this word may have the same meaning as howve or houve, used by Chaucer for a head-dress; Maid Marian’s head-dress was always very fine: indeed some persons have derived her name from the Italian word morione, a head-dress.” Mr. Steevens was never less happy than he is in this very probable conjecture. The word howve or houve, in Chaucer, is a mere variation of hood: and Maid Marian’s head-dress must, to be sure, have been “very fine” when made of four yards of broad cloth! A huke is a woman’s gown or habit. (Huke, palla, toga, palium Belgicis feminis usitatum.—Skin.) Skelton mentions it in his Elinour Rumming:
“All women in generall,” says Moryson, speaking of the Netherlands, “when they goe out of the house, put on a hoyke or vaile, which covers their heads, and hangs downe vpon their backs to their legges,” &c. (Itinerary, 1617, part 3, p. 169).
Sir John Cullum seems to have mistaken Rose Sparkes’ “best hook” for a “hook worn at the bottom of the stays, to regulate the sitting of the apron” (History of Hawsted, p. 25). Morione, in Italian, signifies a murrion or scull-cap; and though the derivation alluded to appears to have the sanction of Blount’s Glosographia, nothing can be more completely absurd. Marian is Mary.
90 “It appears that this, as well as other games, was made a parish concern.”
91 “Probably gilt leather, the pliability of which was particularly accommodated to the motion of the dancers.”
92 “A sort of coarse linen.”
93 “Probably a Moor’s coat; the word Morion is sometimes used to express a Moor.—The morris dance is by some supposed to have been originally derived from Moorish-dance. Black buckram appears to have been much used for the dresses of the ancient mummers. One of the figures in Mr. Tollet’s window is supposed to be a morisco.”
94 “Disard is an old word for a fool.”
95 In Ben Jonson’s Masque of the Metamorphosed Gipsies, presented to King James in 1621 (the very date, by the way, which appears on Mr. Tollet’s window), we have the following dialogue between Cockret and Clod:
“Coc. Oh the lord! what be these? . . .
Clo. They should be morris-dancers by their gingle, but they have no napkins.
Coc. No, nor a hobby-horse.
Clo. Oh, he’s often forgotten, that’s no rule; but there is no maid Marian nor friar amongst them, which is the surer mark.
Coc. Nor a fool that I see.”—(Tollet’s Memoir.)
96 Neither is any notice taken of them, where the characters of the morris-dance are mentioned, in The Two Noble Kinsmen, by Shakespeare and Fletcher.
97 This was a usual cry on occasions of mirth and jollity. Thus, in the celebration of St. Stephen’s day in the Inner-Temple hall, as we find it described in Dugdale’s Origines Juridiciales: “Supper ended, the constable-marshall ‘presenteth’ himself with drums afore him, mounted upon a scaffold, born by four men; and goeth three times round about the harthe, crying out aloud, A lord, a lord, &c. Then he descendeth and goeth to dance,” &c. (p. 156).
 “’Tis meet we all go forth,
“’Tis meet we all go forth,99 Perhaps also, Robin Hood and his party had never appeared in company with the morris-dancers but at one particular period, in the beginning of May, whereas we find that Whitsuntide was no less devoted to the latter.
100 It must be confessed that no other direct authority has been met with for constituting Robin Hood and Little John integral characters of the morris-dance. That Maid Marian, however, and the Frier, were almost constantly such, is proved beyond the possibility of a doubt; and why or how they should become so, without Robin Hood, at least, is unaccountable.
101 This county would seem to have been famous for their exertions a couple of centuries ago. Will Kemp the player was a celebrated morris-dancer; and in the Bodleian Library is the following scarce and curious tract by him: “Kemp’s nine daies wonder performed in a daunce from London to Norwich. Containing the pleasure, paines and kind entertainment of William Kemp between London and that city in his late morrice. Wherein is somewhat set downe worth note; to reproove the slaunders spred of him, many things merry, nothing hurtfull. Written by himself to satisfie his friends. London, printed by E. A. for Nicholas Ling, 1600” 4to, b. l. On the title-page is a woodcut figure of Kemp as a morrice-dancer, preceded by a fellow with a pipe and drum, whom he, in the book, calls Thomas Slye his taberer.—See, in Richard Brathwayte’s Remains after Death, 1618, some lines “upon Kempe and his morice, with his epitaph.”
102 “On Monday [July 30] the morris-dancers of Pendleton paid their annual visit in Salford. They were adorned with all the variety of colours that a profusion of ribbons could give them, and had a very showy garland.”—Star, Aug. 9, 1792.
103 “Council Register, v. 1, p. 30.”
104 “Mary, parliament 6, c. 61, A.D. 1555.” “Anentis Robert Hude, and abbot of Unreason. Item, It is statute and ordained, that in all times cumming, na maner of person be chosen Robert Hude, nor Little John, abbot of unreason, queenis of Maij, nor utherwise, nouther in burgh, nor to landwart, in onie time to cum: and gif ony provest, baillies, councell, and communitie, chuse sik ane personage as Robert Hude, Little John, abbotis of unreason, or queenis of Maij, within burgh, the chusers of sik sall tine their freedome for the space of five zeires; and utherwise salbe punished at the queenis grace will; and the acceptar of sik like office sall be banished foorth of the realme; and gif ony sik persones . . . . beis chosen out-with burgh, and uthers landward townes, the chusers sall pay to our soveraine ladie ten poundes, and their persones [be] put in waird there to remaine during the queenis grace pleasure.” Abbot of unreason is the character better known in England by the title of abbot or lord of misrule, “who,” says Percy, “in the houses of our nobility presided over the Christmas gambols, and promoted mirth and jollity at that festive season” (Northumberland Household Book, notes, p. 441).
105 “Council Register, v. 4, p. 4, 30.”
106 “Knox’s History, p. 270.”
107 “Book of Universal Kirk, p. 414.” See also Keith’s History of Scotland, p. 216.
108 History of Whitby, York, 1779, p. 146. “It was always believed,” adds the worthy pedagogue, “that these butts had been erected by him for that very purpose, till the year 1771, when this popular notion was discovered to be a mistake; they being no more than the barrows or tumuli thrown up by our pagan predecessors on interring their leaders or the other persons of distinction amongst them. However, notwithstanding this discovery, there is no doubt but Robin Hood made use of those houes or butts when he was disposed to exercise his men, and wanted to train them up in hitting a mark.” Be that as it may, there are a few hillocks of a similar nature not far from Guisbrough, which likewise bear the name of Robin Hood’s butts; and others, it is imagined, may be met with in other parts.
109 Epigram on Robin Hood’s well, “a fine spring on the road, ornamented by Sir John Vanbrugh;” by Roger Gale, Esq. (Bib. Topo. Britan. No. II. part iii. p. 427).
The same author (Gent), in his “long and pathetick prologue,” setting forth “the contingencies, vicissitudes or changes of this transitory life,” “spoken, for the most part, on Wednesday and Friday the 18th and 20th of February 1761, at the deep tragedy of beautiful, eloquent, tender-hearted, but unfortunate Jane Shore, . . . . uttered and performed at his benefit” . . . (being then ætatis 70, and far declined into the vale of sorrow,*) has very artfully contrived to introduce our hero and his famous well.
* He died in 1778, aged 87.
†
112 Voyage from England to India, 1773, p. 8. In a subsequent page this great man is employed in a commerce of a more delicate, indeed, but, according to European notions, less honourable nature, which he manages with consummate address.
113 They likewise seem alluded to in the Vision, fo. 1, b:
114 “On a loose paper, in Mr. Ashmole’s handwriting, in the museum at Oxford, is the following little anecdote:—
“The famous Little John (Robin Hood’s companion) lyes buried in Fethersedge churchyard, in the peak of Derbyshire, one stone at his head, another at his feet, and part of his bow hangs up in the chancell. Anno 1652.” H. E[llis]. European Magazine, October 1794, p. 295.
115 This seems the established size of an ancient hero. The grave of Gawin, King Arthur’s nephew, discovered in the time of William the Conqueror, was, according to Malmesbury, “quatuor decim pedes longum” (De gestis regum, l. 3). Bois, from the above circumstance, conceives our “Litil Jhon” to have been so called “per ironiam.” See his original work, fo. ix.
116 Historie of Scotland, translatit be Maister Johne Bellenden, Edin. 1541, fo. The luxury of his countrymen will appear a strange complaint in the mouth of a Scotishman of the 16th century, to such as believe, with the late Dr. Johnson, that they learned to plant kail from Cromwell’s soldiers, and that “when they had not kail they probably had nothing” (Journey to the Western Islands, p. 55).
117 Description of Ireland, in Holinshed’s Chronicle, 1587.
118 Historical Essay, &c., p. 129. This allegation demands what the lawyers call a profert in curiam. It is, however, certain that there have been persons who usurped the name of Little John. In the year 1502, “about mydsomer, was taken a felow whyche had renued many of Robyn Hodes pagentes, which named himselfe Grenelef” (Fabyan’s Chronicle, 1559). Therefore, beware of counterfeits!

This ancient legend is printed from the copy of an edition, in 4to and black letter, by Wynken de Worde, preserved in the public library at Cambridge; compared with, and, in some places, corrected by, another impression (apparently from the former), likewise in 4to and black letter, by William Copland, a copy of which is among the late Mr. Garrick’s old plays, now in the British Museum. The full title of the first edition is as follows: “Here beginneth a mery geste of Robyn Hode and his meyne, {2} and of the proude sheryfe of Notyngham;” and the printer’s colophon runs thus: “Explycit. Kynge Edwarde and Robyn hode and Lytell Johan Enprented at London in Flete strete at the sygne of the sone By Wynken de Worde.” To Copland’s edition is added “a newe playe for to be played in Maye games very plesaunte and full of pastyme;” which will be found at large in another place. No other copy of either edition is known to be extant; but, by the favour of the Reverend Dr. Farmer, the editor had in his hands and gave to Mr. Douce a few leaves of an old 4to black letter impression by the above Wynken de Worde, probably in 1489, and totally unknown to Ames and Herbert. Another edition was printed at Edinburgh by Androw Myllar and Walter Chepman in 1508, a fragment whereof is in the Advocates’ Library there. This is probably the edition noticed among the tales enumerated in Wedderburn’s Complainte of Scotland, printed at St. Andrews in 1549, under the title of “Robene Hude and litil Jhone.” Among the Doctor’s numerous literary curiosities was likewise another edition, “printed,” after Copland’s, “for Edward White” (4to, black letter, no date, but entered in the Stationers’ books 13 May 1594), which hath been collated, and every variation worthy of notice either adopted or remarked in the margin. The only deviation from all the copies (except in necessary corrections) is the division of stanzas, the indenting of the lines, the addition of points, the disuse of abbreviations, and the occasional introduction or rejection of a capital letter; liberties, if they may be so called, which have been taken with most of the other poems in this collection.







This curious, and hitherto unpublished, and even unheard of, old piece is given from a manuscript among Bishop More’s collections, in the public library of the University of Cambridge (Ee. 4. 35). The writing, which is evidently that of a vulgar and illiterate person, appears to be of the age of Henry the Seventh, that is, about the year 1500; but the composition (which he has irremediably corrupted) is probably of an earlier period, and much older, no doubt, than “The Play of Robyn Hode,” which seems allusive to the same story. At the end of the original is “Expleycyt Robyn Hode.” {82}



This poem, a North-country (or perhaps Scotish) composition of some antiquity, is given from a modern copy printed at Newcastle, where it was accidentally picked up: no other edition having been ever seen or heard of. The corruptions of the press being equally numerous and minute, some of the most trifling have been corrected without notice. But it may be proper to mention that each line of the printed copy is here thrown into two: a step which, though absolutely necessary from the narrowness of the page, is sufficiently justified by the frequent recurrence of the double rime. The division of stanzas was conceived to be a still further improvement.—The original title is, “A Pretty Dialogue betwixt Robin Hood and a Beggar.”
A similar story (“Comment un moine se débarasse des voleurs”) may be found in “Le Moyen de Parvenir,” i. 304 (edit. 1739). {98}

is reprinted from the “Reliques of Ancient English Poetry,” published by Dr. Percy (vol. i. p. 81), who there gives it from his “folio MS.” as “never before printed, and ‘carrying’ marks of much greater antiquity than any of the common popular songs on this subject.”
As for Guy of Gisborne, the only further memorial which has occurred concerning him is in an old satirical piece by William Dunbar, a celebrated Scotish poet of the 15th century, on one “Schir Thomas Nory” (MS. Maitland, p. 3; MSS. More, Ll. 5, 10), where he is named along with our hero, Adam Bell, and other worthies, it is conjectured, of a similar stamp, but whose merits have not, less fortunately, come to the knowledge of posterity. {115}
Gisborne is a market-town in the West Riding of the county of York, on the borders of Lancashire.
In the fourth edition of the publication above referred to, which appeared in July 1795, it is acknowleged that “some liberties were, by the editor, taken with this ballad, which in this edition hath been brought nearer to the folio MS.” The new readings have therefore been introduced into the present text.

A briefe touch of the life and death of that renowned outlaw Robert earl of Huntingdon, vulgarly called Robin Hood, who lived and dyed in A. D. 1198,277 being the 9th year of king Richard the first, commonly called Richard Cœur de Lyon.
Carefully collected out of the truest writers of our English Chronicles: and published for the satisfaction of those who desire truth from falshood.
This poem, given from an edition in black letter printed for I. Clarke, W. Thackeray, and T. Passinger, 1686, remaining in the curious library left by Anthony a Wood, appears to have been first entered on the hall-book of the Stationers’ Company the 29th of February 1631.
Martin Parker was a great writer of ballads, several of which, with his initials subjoined, are still extant in the Pepysian and other collections. (See “Ancient Songs,” 1829, ii. p. 263.) Dr. Percy mentions a little miscellany intitled, “The garland of withered roses, by Martin Parker, 1656.” The editor has, likewise, seen “The nightingale warbling forth her own disaster, or the rape of Philomela: newly written in English verse by Martin Parker, 1632;” and, on the 24th of November 1640, Mr. Oulton enters at Stationers’ Hall “a book called The true story of Guy earle of Warwicke, in prose, by Martyn Parker.”
At the end of this poem the author adds “The epitaph which the prioress of the monastry of Kirkslay in Yorkshire set over Robin Hood, which,” he says, “(as is before mentioned) was to be read within these hundred years, though in old broken English, much to the same sence and meaning.” He gives it thus:
“Decembris quarto die, 1198. anno regni Richardi primi 9.
“Some other superstitious words,” he adds, “were in, which I,” says he, “thought fit to leave out.” Now, under this precise gentleman’s favour, one would be glad to know what these same “superstitious words” were; there not being anything of the {128} kind in Dr. Gale’s copy, which seems to be the original, and which is shorter by two lines than the above. Thirteen should be thirty.
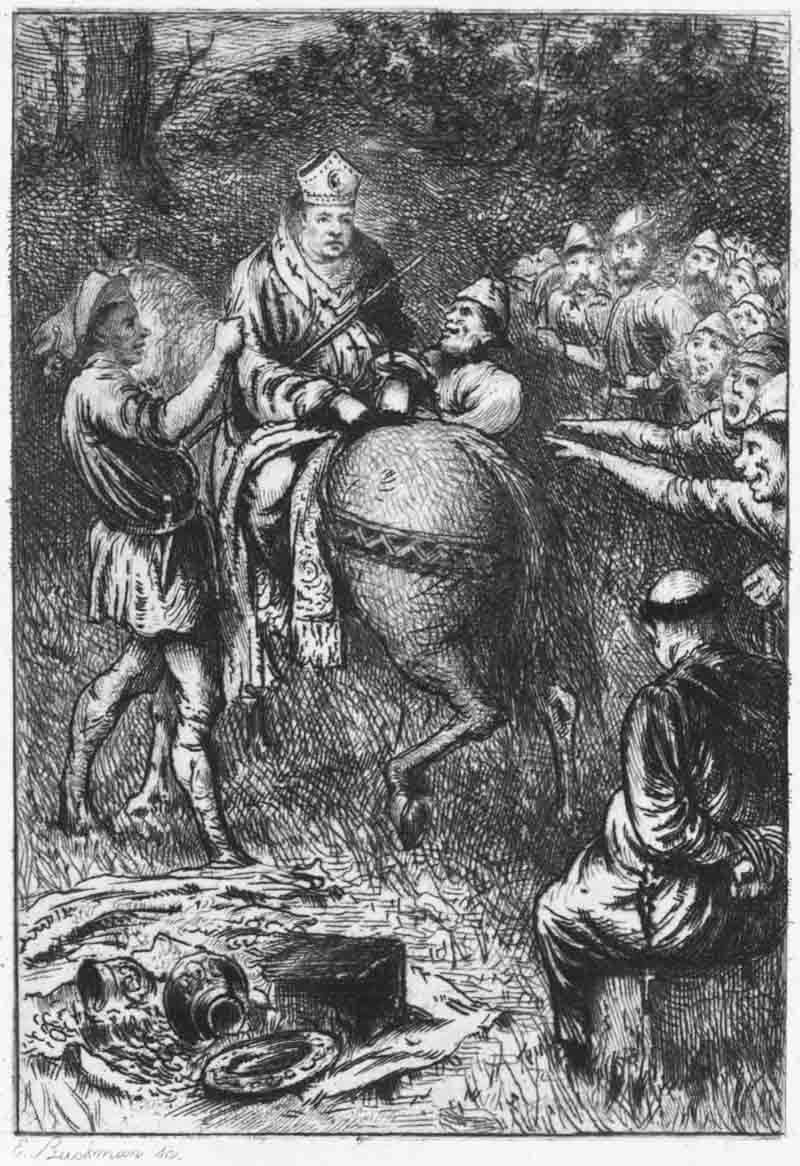



119 The irregularity or defect of the versification, in this and similar passages, is probably owing to the loss of a line.
120 This seems to have been, and, in many parts, is still, the name generally used by the vulgar for Erming Street. The course of the real Watling Street was from Dover to Chester.
The Sayles appears to be some place in the neighbourhood of Barnsdale, but no mention of it has elsewhere occurred: though, it is believed, there is a field so called not far from Doncaster.
121 All his. PCC.
122 So R. [Rastall.] all thre. W. C. [de Worde and Copland.]
123 This. R. that. W. C.
124 Ere. R.
125 To pay. R. pay. W. C.
126 Robyn. R. Robyn Hoode. W. C.
127 Two yere. R.
128 Knowe. OCC.
129 It may amende. OCC.
130 Lancasesshyre. R.
131 Not. W. C.
132 By. W. C.
133 So R. knowe me. W. C.
134 The fragment of Rastall’s edition ends here.
135 Also. PCC.
136 Wyme. PCC.
137 i.e. by so many score to the hundred, or three hundred for one. It is certainly a very hyperbolical expression: but he measures the cloth in the same way.
138 Helpe. W. wrappe. C.
139 Leue. W. lende. C.
140 The prior, in an abbey, was the officer immediately under the abbot; in priories and conventual cathedrals he was the superior.
141 This was a “S. Richard, king and confessour, sonne to Lotharius king of Kent, who, for the love of Christ, taking upon him a long peregrination, went to Rome for devotion to that sea, and in his way homward, died at Luca, about the year of Christ, seaven hundred and fifty, where his body is kept untill this day with great veneration, in the oratory and chappell of S. Frigidian, and adorned with an epitaph both in verse and prose” (English Martyrologe, 1608).
There were other saints of the same name, as Richard de la Wich, bishop of Chichester, canonised in 1262; and Richard, bishop of St. Andrews in Calabria. See Drayton’s Polyolbion, song 24.
142 Leue. W. Sende us. C.
143 Loke. W. C.
144 Grete. W. get. C.
145 Thou. PCC.
146 Uterysdale. O. CC. Wierysdale is the name of a forest in Lancashire: though it appears, in a subsequent part of this poem, that the knight’s castle was in Nottinghamshire.
147 Sute. C.
148 I up pyght. W. up ypyght. C.
149 Fere. W. in fere. C.
150 Shote. W.
151 He sleste (sliced?) W.
152 Thou wast. C. wast thou. Wh.
153 Ge. W. f. God.
154 i.e. while a man might have walked two miles and upward.
155 Hyed, C.
156 Whyle. W.
157 Syght. W. sightes. C.
158 Wo the worth. W.
159 Such. W.
160 He. Old copies.
161 You. W. Make you yonder preste. C.
162 Set. ‘shet’?
163 Yemen. C.
164 Lytell Johan, O. CC.
165 Them. O. CC.
166 To. W.
167 Nade. W. not in C.
168 Eyght pounde. W.
169 To. W.
170 Corser. W. courser. C.
171 Gayne. W.
173 I twyse. W.
174 Thi trusty. C.
175 This care. W.
176 Syt. W.
178 Al theyre. W. al of the. C.
179 They slist. W. he clefte. C.
180 Belyve. C.
181 That I after eate no bread. C.
182 Thou. W.
183 The bydde. OCC.
184 Honde and fote. W. foote and hande. C.
185 That he had Robyn Hode. W.
186 God the good Robyn. W.
187 Lady. W.
188 Late.
189 Shamly I slayne be. W.
190 For soth as I the say. W.
191 Your. W. You may them over take. C.
192 Shall he never in grene wode be Nor longer dwell with me. W.
193 It. W.
194 At. W. That. C.—good] boote. Wh.
195 Hoode. W. bande. C.
196 And yf. W.
197 Your. OCC.
198 Under the grene wode tre. W.
199 This saint is also mentioned by Chaucer in the Sompnour’s tale; by Spenser, in his 5th eclogue; in the Downfall of Robert Earl of Huntington, 1601; and in one of Ophelia’s songs in Hamlet. (See a note upon this last passage in the edition of 1793, vol. xv. p. 163.) Mr. Steevens’s assertion that “Saint Charity is a known saint among the Roman Catholics,” may be supported by infallible authority. “We read,” says Dr. Douglas, “in the Martyrology on the first of August—Romæ passio sanctarum virginum, Fidei, Spei, et Charitatis, quæ sub Hadriano principe martyris coronam adeptæ sunt” (Criterion, p. 68). Pierre Nadal, commonly called Petrus de Natalibus, in his Catalogus Sanctorum, has given the history of the saints Faith, Hope, and Charity, the daughters of St. Sophia (or Wisdom). Nothing can be too absurd for superstition.
200 I vouche it halfe on the. W.
201 Seale. C.
202 And browne. W.
203 A wys, W. For that shall be his fyne. C.
204 Good whyte. W. lilly white. C.
205 And therto sent I me. W.
206 Good. OCC.
207 Another had full sone. W.
208 Lefte never one. W.
209 Lughe. W.
210 Ferre. W.
211 Commended for. C.
212 Donkesley. W.
213 The. OCC.
214 Ye.
215 Lefe.
216 Syde.
217 Syde.
218 Hys.
219 Leffe.
220 A bad hem stond stell.
221 The potter.
222 Leppyd.
223 Felow he.
224 A.
225 Seyde hels.
226 Went yemen.
227 Thes.
228 Lytl.
229 Yemerey.
230 Grat.
231 Yede.
232 This stanza is misplaced in the MS., coming after the first verse at top of page.
233 Say.
234 Seyde sche s’ than.
235 The.
236 He.
237 Loseth.
238 To.
239 These two lines are transposed in the MS.
240 Pottys the.
241 Bolt yt.
242 Senyst.
243 Goe.
244 That Robyng gaffe me.
245 Mey they.
246 Se.
247 He.
248 Her.
249 For.
250 How haffe.
251 I leyty.
252 He had west.
253 That ye be.
254 y.
255 The MS. repeats this line after the following: Het ambellet be mey sey.
256 Bowhes.
257 Be ther.
258 Wher’e.
259 Closd. We might read: And clos’d were [baith] his een.
260 The preceding lines of this stanza are wanting in the original.
261 Gave, begack.
262 Yeen.
263 Spok.
264 Half.
265 Bound.
266 Bag.
267 Cloath.
268 Thou.
269 Speed.
270 Cloaths.
271 “It should perhaps be swards, i.e. the surface of the ground, viz. ‘when the fields are in their beauty.’”—PERCY. Rather shrobbes (shrubs). The plural of sward was never used by any writer whatever. For shaws the MS. has shales.
272 Dr. Percy, by the marks he has bestowed on this line, seems to consider it as the yeoman’s reply; but it seems rather a repetition of Robin’s complimentary address.
273 This in the three former editions of the “Reliques” is improperly altered to ‘but.’
274 So, according to Percy, reads his MS. He has altered it to ‘backward.’
275 The title of SIR, Dr. Percy says, was not formerly peculiar to knights; it was given to priests, and sometimes to very inferior personages. If the text did not seem to be in favour of the latter part of this assertion, one might reasonably question its truth. Another instance, at least, it is believed, admitting this to be one, which is by no means certain, cannot be produced.
276 Sic PC. quere the MS.
277 An absurd mistake, scarcely worth notice in this place, and which the reader will have it in his own power to correct.
278 Our.
279 There is no authority for imputing this execrable practice to our hero or his companions, in any one single instance. If, however, the lex talionis were at all justifiable, they certainly had sufficient provocation to exercise it—not, indeed, upon the clergy, in particular, but upon the king, his ministers, judges, and nobles. “The ancient punishment for killing the king’s deer,” says Dr. Percy, “was loss of eyes and castration: a punishment far worse than death!”
280 i.e. than he could otherwise have been.

From a black letter copy in the large and valuable collection of old ballads late belonging to Thomas Pearson, Esq., and now in the possession of the Duke of Roxburghe. This is the collection mentioned in the Harleian Catalogue, and would seem to be the greater part of that originally made by old Bagford (see Hearne’s Appendix to Hemingi Chartularium, p. 662), another volume or two having come, with the rest of his typographical collections, to the British Museum. The three vols. which went to Osborne were probably bought of him by Mr. West, at whose sale they {150} were purchased by Major Pearson, by whom the collection was new-arranged, ornamented, and improved.
In reading this song, we are admonished by the editor of the collection of old ballads printed in 1723 (who thinks it “the most beautiful and one of the oldest extant, written on that subject”) to observe one thing, “and that is, between some of the stanzas we must suppose a considerable time to pass. Clorinda,” he says, “might be [thought] a very forward girl, if between Robin Hood’s question and her answer we did not suppose two or three hours to have been spent in courtship; and between Robin Hood’s being entertained at Gamwell-hall and his having ninety-three bowmen in Sherwood, we must allow some years.”
With respect to its antiquity, Dr. Percy, in the new edition
of his “Reliques of Ancient English Poetry” (vol. i. p.
xcvii.), expresses a very different opinion; since, according
to him, it “seems of much later date than most of the others,
and can scarce be older than the reign of King Charles I.;
FOR,” says he, “King James I. had
no issue after his accession to the throne of England:” an
observation which, if any way to the purpose, is certainly NOT TRUE. “It may even,” he continues, “have
been written since the Restoration, and only express the wishes
of the nation for issue on the marriage of their favourite King
Charles II. on his marriage (sic) with the infanta of Portugal.”
However this may be, the writer’s having deviated from “all the old
traditions concerning this celebrated outlaw,” is no proof that
he was “ignorant” of them; and that Dr. Percy chooses to “think
it is not found in the Pepys Collection” only shows conjecture to
be easier than investigation.
 In
the second volume of
that collection, any person disposed to the search will find at
least TWO COPIES of it, both in black
letter.
In
the second volume of
that collection, any person disposed to the search will find at
least TWO COPIES of it, both in black
letter.
The full title of the original is: “A new ballad of bold Robin Hood; shewing his birth, breeding, valour, and marriage at Titbury Bull-running. Calculated for the meridian of Staffordshire, but may serve for Derbyshire or Kent.” {151}


From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood. It is there said to go “To the tune of Bold Robin Hood;” and the chorus is repeated in every stanza. To the above title are added the following doggerel lines:
 The paragraph of which the following is an extract appeared
in the evening paper intitled “The Star,” April 23, 1796:
“A few days ago as some labourers were digging in a garden
at Fox-lane, near Nottingham, they discovered six human
skeletons entire, deposited in regular order side
by side, supposed {165}
to be part of the fifteen foresters that were killed by Robin Hood.
Near the above place anciently stood a church, built in the early
ages of Christianity, dedicated to St. Michael, which was totally
demolished at the Reformation. . . . No doubt but the bones in
question were properly buried in St. Michael’s churchyard. The
proprietors of the garden humanely ordered the pit where the
bones were found to be filled up, being unwilling to disturb the
relics of humanity and the ashes of the dead.”
The paragraph of which the following is an extract appeared
in the evening paper intitled “The Star,” April 23, 1796:
“A few days ago as some labourers were digging in a garden
at Fox-lane, near Nottingham, they discovered six human
skeletons entire, deposited in regular order side
by side, supposed {165}
to be part of the fifteen foresters that were killed by Robin Hood.
Near the above place anciently stood a church, built in the early
ages of Christianity, dedicated to St. Michael, which was totally
demolished at the Reformation. . . . No doubt but the bones in
question were properly buried in St. Michael’s churchyard. The
proprietors of the garden humanely ordered the pit where the
bones were found to be filled up, being unwilling to disturb the
relics of humanity and the ashes of the dead.”


From an old black letter copy in Anthony a Wood’s collection, compared with two others in the British Museum, one in black letter. It should be sung “To an excellent tune,” which has not been recovered.
Several lines of this ballad are quoted in the two old plays of the “Downfall” and “Death of Robert, Earle of Huntington,” 1601, 4to, b. l., but acted many years before. It is also alluded to in Shakespeare’s Merry Wives of Windsor, act i. scene 1, and again in his Second Part of King Henry IV., act v. scene 3.
In 1557 certain “ballets” are entered on the books of the Stationers’ Company “to John Wallye and Mrs. Toye,” one of which is entitled “Of wakefylde and a grene:” meaning apparently the ballad here reprinted. {167}




“Shewing how Robin Hood went to an old woman’s house and changed cloaths with her to scape from the bishop; and how he robbed the bishop of all his gold, and made him sing a mass. To the tune of Robin Hood and the Stranger.” From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood.

From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony Wood. The tune is “Robin Hood and the Begger.”

“A merry and pleasant song relating the gallant and fierce combat fought between Arthur Bland, a tanner of Nottingham, and Robin Hood, the greatest and most noblest archer of England. Tune is, Robin Hood and the Stranger.” From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood.

From an old black letter copy in the library of Anthony a Wood. The full title is—

“Or a pleasant relation how a young gentleman, being in love with a young damsel, ‘she’ was taken from him to be an old knight’s bride: and how Robin Hood, pittying the young man’s case, took her from the old knight, when they were going to be marryed, and restored her to her own love again. To a pleasent northern tune, Robin Hood in the green-wood stood.
From an old black letter copy in Major Pearson’s collection.
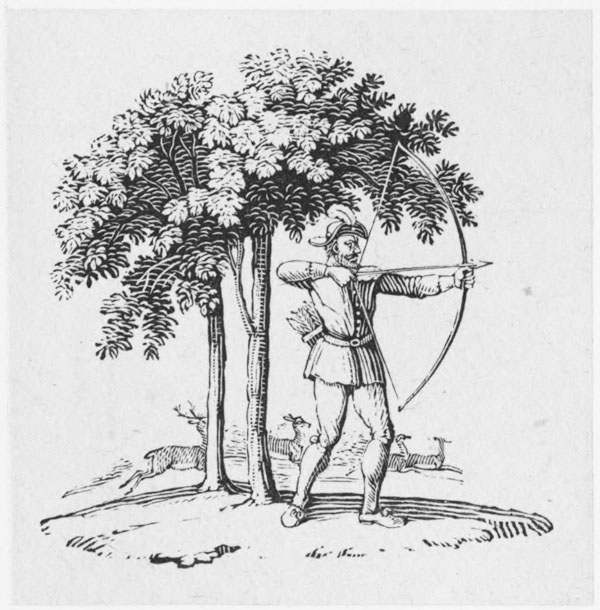


“Shewing how Robin Hood, Little John, and the Shepherd fought a sore combate.
From two old black letter copies, one of them in the collection of Anthony a Wood, the other in that of Thomas Pearson, Esq. At the head of the former is a fine cut of Robin Hood.


From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood; corrected by a much earlier one in the Pepysian Library, printed by H. Gosson, about the year 1610; compared with a later one in the same collection. The full title is: “The famous battell betweene Robin Hood and the curtall fryer. To a New Northerne tune.”
“The curtail fryer,” Dr. Stukeley says, “is a cordelier, from the cord or rope which they wore round their wast, to whip themselves with. They were,” adds he, “of the Franciscan order.” Our fryer, however, is undoubtedly so called from his “curtall dogs,” or curs, as we now say (Courtalt, F.) In fact, he is no fryer at all, but a monk of Fountains Abbey, which was of the Cistercian order. {210}

From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood. The title now given to this ballad is that which it seems to have originally borne, having been foolishly altered to “Robin Hood newly revived.” The circumstances attending the second part will be explained in a note.
The tune is already inserted, at the end of “Rood Hood and the Tanner.”


From an old black letter copy in a private collection, compared with another in that of Anthony a Wood. The full title is: “Renowned Robin Hood; Or, His famous archery truly related in the worthy exploits he acted before Queen Katherine, he being an outlaw man; and how he obtained his own and his fellows pardon. To a new tune.”
It is scarcely worth observing that there was no queen-consort named KATHERINE before Henry the Fifth’s time; but as Henry the Eighth had no less than three wives so called, the name would be sufficiently familiar to our ballad-maker.

“Or, a merry progress between Robin Hood and King Henry: Shewing how Robin Hood led the king his chase from London to London; and when he had taken his leave of the queen, he returned to merry Sherwood. To the tune of Robin Hood and the Beggar.”
From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood.

This ballad (given from an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood) was entered (amongst others) in the Stationers’ book, by Francis Coule, 13th June 1631, and by Francis Grove, 2d June 1656.
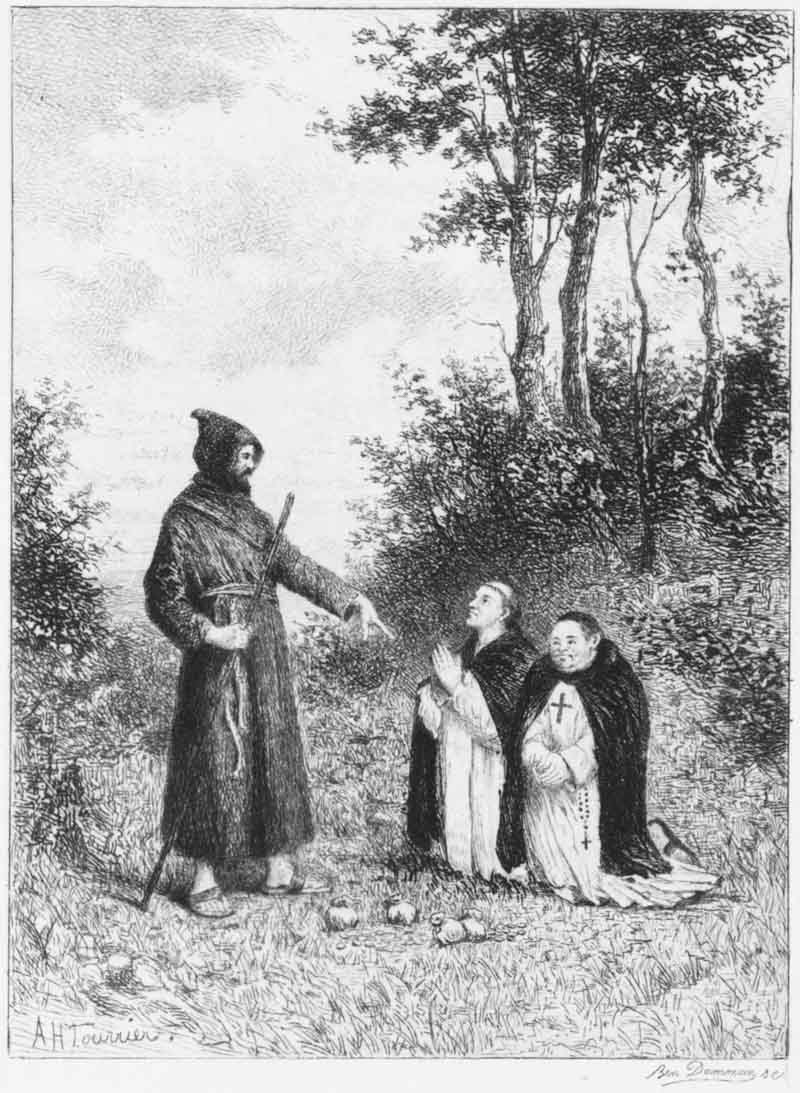
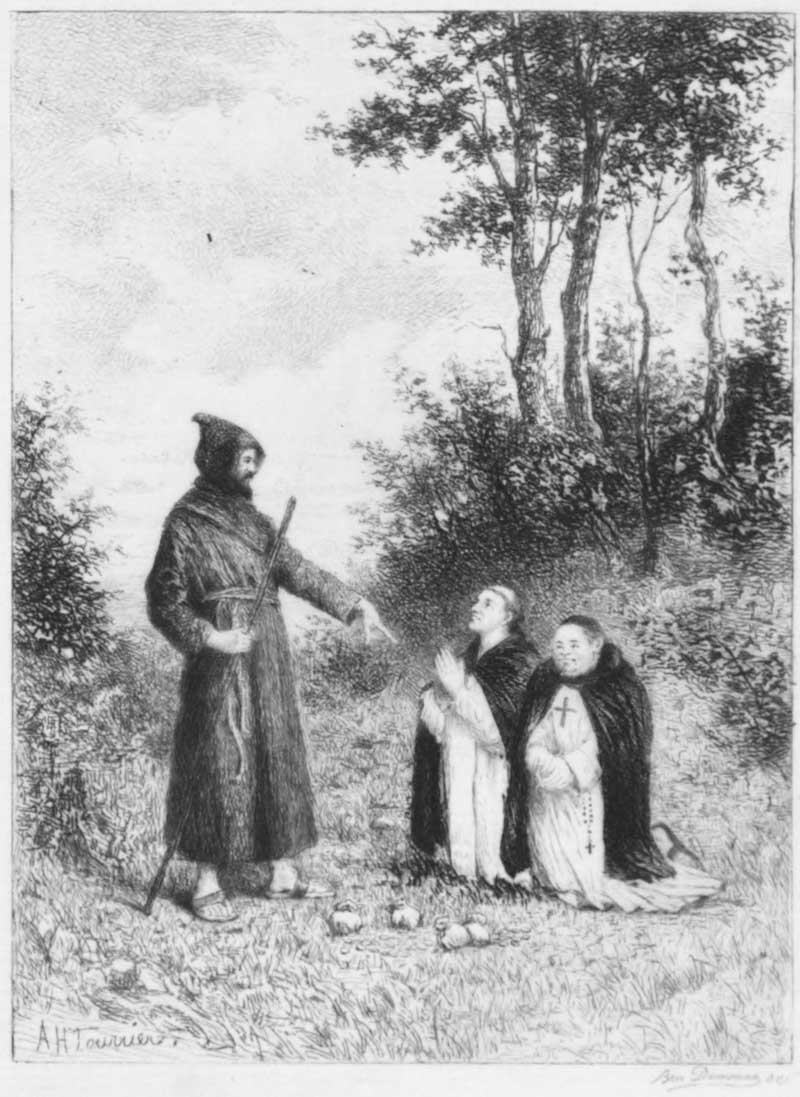
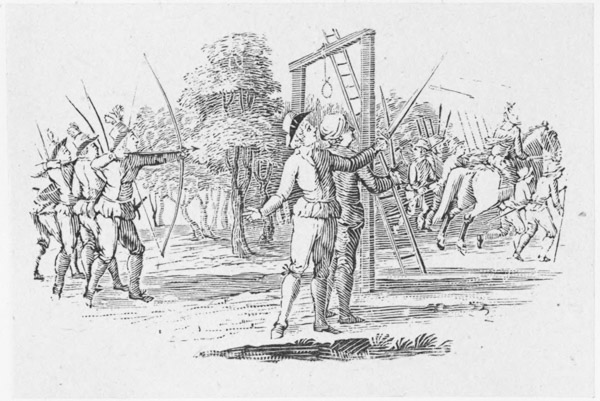



From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood. The full title is: “Robin Hood his rescuing Will Stutly from the sheriff and his men, who had taken him prisoner, and was going to hang him. To the tune of Robin Hood and Queen Katherine.” 313


“Shewing how he won a prize on the sea, and how he gave the one halfe to his dame, and the other to the building of almes-houses. The tune is, In summer time, &c.”
From three old black letter copies, one in the collection of Anthony a Wood, another in the British Museum, and the third in a private collection.

“Or, a merry combat fought between Robin Hood, Little John, and Will Scarelock, and three stout Keepers in Sheerwood Forrest.
To the tune of, Robin Hood and Queen Katherine; or, Robin Hood and the Shepheard.”
From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood. {269}


“Shewing how Robin Hood and the Beggar fought, and how he changed cloaths with the Beggar, and how he went a begging to Nottingham; and how he saved three brethren from being hang’d for stealing of deer. To the tune of Robin Hood and the Stranger.”
From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood.

From an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood: the full title being, “A new merry song of Robin Hood and Little John, shewing how Little John went a begging, and how he fought with the four beggers, and what a prize he got of the four beggers. The tune is, Robin Hood and the Begger.”

No ancient copy of this ballad having been met with, it is given from an edition of “Robin Hood’s Garland,” printed some years since at York. The tune is Arthur a Bland.

“Being an account of their first meeting, their fierce encounter, and conquest. To which is added, their friendly agreement; and how he came to be called Little John. Tune of Arthur a Bland.”
This ballad is named in a schedule of such things under an agreement between W. Thackeray and others in 1689 (Col. Pepys. vol. 5), but is here given as corrected from a copy in the “Collection of Old Ballads,” 1723.
The notion that Little John obtained this appellation, ironically, from his superior stature, though doubtless ill-founded, is of considerable antiquity. See “Notes and Illustrations to the Life,” p. cxvi.


This excellent ballad, given from the common edition of Aldermary-church-yard (compared with the York copy), is supposed to be modern; the story, however, seems alluded to in the ballad of “Renowned Robin Hood.” The full title is “The Bishop of Hereford’s entertainment by Robin Hood and Little John, &c. in merry Barnsdale.” The tune is added from an engraved sheet.
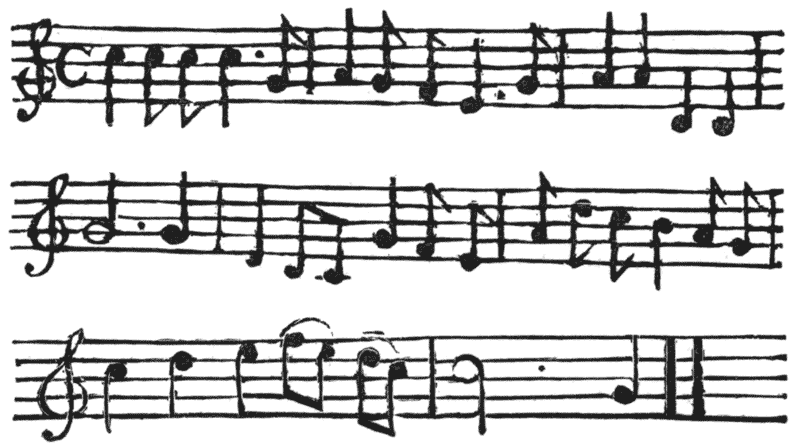 [Listen]
[Listen]

This ballad, from the York edition of “Robin Hood’s Garland,” is probably one of the oldest extant of which he is the subject. In the more common editions is a modernised copy, in which the “silly old woman” is converted into “a gay lady;” but even this is more ancient than many of the pieces here inserted, and is entitled, by its merit, to a place in the Appendix.
The circumstance of Robin’s changing clothes with the palmer is, possibly, taken from an old romance intitled “The noble hystory of the moost excellent and myghty prynce and hygh renowmed knyght kynge Ponthus of Galyce and of lytell Brytayne, Enprynted at London in Flete strete at the sygne of the sonne by Wynkyn de Worde, In the yere of our lorde god, M.CCCCC.XI.,” 4to, b. l., sig. I. 6: “And as he [Ponthus] rode he met with a poore palmer beggynge his brede the whiche had his gowne all to clouted and an olde pylled hatte, so he alyght and sayd to the palmer, frende we shall make a chaunge of all our garmentes, for {304} ye shall have my gowne and I shall have yours and your hatte. A syr sayd the palmer ye bourde you with me. In good fayth sayd Ponthus I do not, so he dyspoyled hym and cladde hym with all his rayment, and he put vpon hym the poore mannes gowne, his gyrdell, his hosyn, his shone, his hatte, and his bourden.”

This ballad, which has never been inserted in any of the publications intitled “Robin Hood’s Garland” (and, perhaps, was not worth inserting here), is given from an old black letter copy in the collection of Anthony a Wood. Its full title is, “A famous battle between Robin Hood and Maid Marian; declaring their love, life, and liberty. Tune, Robin Hood Reviv’d” (see before, p. 217).

from the common collection of Aldermary-church-yard, seems to be taken from the old legend in Part I., and to have been written by some miserable retainer to the press, merely to eke out the book; being, in fact, a most contemptible performance.
The two concluding lines (the same with those of the next ballad) refer to song xxvii., which they have once immediately preceded.


A composition of a similar nature with the preceding, and from the same authority.
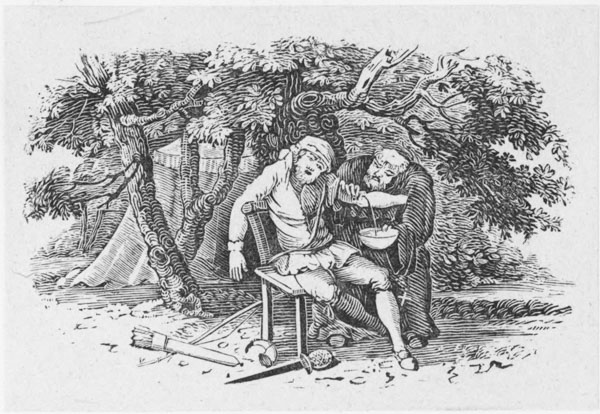


“Together with an account of his death and burial, &c. Tune of Robin Hood and the fifteen Foresters.” From the common garland of Aldermary-church-yard; corrected by the York copy.


“Shewing how he was taken ill, and how he went to his cousin at Kirkley-hall, who let him blood, which was the cause of his death. Tune of Robin Hood’s Last Farewel, &c.”
This very old and curious piece is preserved solely in the editions of “Robin Hood’s Garland” printed at York (or such as have been taken from them), where it is made to conclude with some foolish lines (adopted from the London copy of the preceding ballad), in order to introduce the epitaph. It is here given from a collation of two different copies, containing numerous variations, a few of which are retained in the margin.



281 Clowdel le. For an account of these worthies the reader may consult their old metrical legend in Percy’s “Reliques,” vol. i., or “Ancient Popular Poetry,” 1791.
282 A beseem’d.
283 Has.
284 A.
285 Lease.
286 Choose.
287 For an account of Tutbury bull-running, and the character of king of the minstrels there, see Dr. Plott’s “Natural History of Staffordshire,” chap. x. § 69; Sir J. Hawkins’s “History of Music,” vol. ii. p. 64; and Blount’s “Ancient Tenures,” by Beckwith, p. 303, 8vo edit.
288 See this old and popular ballad in the Appendix.
289 Robin Hood.
290 Robin Hood.
291 The editor thinks it his duty to retain, in some instances, even the manifest corruptions of the old copies; in hopes that earlier and better authorities may one day enable him to remove them.
292 In the bowers.
293 Did him.
294 Made then.
295 Nicke.
296 Soon from.
297 Chiefest.
298 Full froe.
299 This (from an old black letter copy in Major Pearson’s collection) is evidently the genuine second part of the present ballad, although constantly printed as an independent article, under the title of “Robin Hood, Will Scadlock, and Little John: Or, a narrative of their victories obtained against the prince of Aragon and the two giants; and how Will Scadlock married the princess. Tune of Robin Hood; or, Hey down, down, a down:” Instead of which, in all former editions, are given the following incoherent stanzas, which have all the appearance of being the fragment of a quite different ballad:—
300 Of a.
301 Forth.
302 Acaron. This termagant prince seems intended for a sort of Mahometan Pagan. Alcaron is a deity formed by metathesis from Alcoran, a book: a conversion much more ancient than the present ballad. Thus in the old metrical romance of “The Sowdon of Babyloyne,” a MS. in the possession of Dr. Farmer:
Here Alkaron is expressly the name of a BOOK (i.e. the Koran or Alcoran); in the following passage it is that of a GOD:
Wynken de Worde printed “A lytell treatyse of the Turkes law called Alcaron, &c.” See Herbert, 224.
If, however, Acaron be the true reading, we shall find an idol of that name in the Bible, 2 Regum i. 16, ed. Vulgate.
It was, at the same time, a proper name in the East: as “Accaron princeps insulæ Cypri” is mentioned by Roger de Hoveden, 786.
303 We should probably read frantick baboon!
304 Ground near Moorfields, London, famous in old times for the archery practised there. “In the year 1498,” says Stow, “all the gardens which had continued time out of minde, without Mooregate, to wit, about and beyond the lordship of Fensberry, were destroyed. And of them was made a plaine field for archers to shoote in.” Survay of London, 1598, p. 351. See also p. 77, where it is observed that “about the feast of S. Bartlemew . . . the officers of the city . . . were challengers of all men in the suburbes, . . . before the ‘lord’ maior, aldermen, and sheriffes, in FENSBERY FIELDE, to shoote the standarde, broade arrow, and flight, for games.” There is a tract intitled, “Ayme for Finsburie archers, or an alphabetical table of the names of every marke within the same fields, with the true distances, both by the map, and dimensuration with the line. Published for the ease of the skilfull, and behoofe of the yoonge beginners in the famous exercise of archerie, by J. J. and E. B. To be sold at the signe of the Swan in Grub-street, by F. Sergeant, 1594.” 16mo. Republished by R. F. 1604; and again by James Partridge, 1628, 12mo.
These famous archers are mentioned by Ben Jonson (Every Man in his Humour, act i. scene 1): “Because I dwell at Hogsden I shall keep company with none but the archers of Finsbury.”
The practice of shooting here is alluded to by Cotton in his Virgile Travestie (b. iv.), 1667:
and continued till within the memory of persons now living.
305 The situation of this chase cannot be ascertained. There is an ancient family seat in Westmoreland called Dalham-tower.
306 Either the bishop was a very bad reckoner, or there is some mistake in the copy: three hundred nobles are exactly a hundred pounds. The common editions read ninety-nine angels, which would be no more than £49, 10s. No such coin or denomination, however, as either angel or noble existed in Robin Hood’s time.
307 I see.
308 Then did.
309 He . . was.
310 Robin Hood.
311 To.
312 Robin Hood.
314 Doubtless.
315 When I came here.
316 Doth . . . arrow gain.
317 Robin Hood.
318 Robin Hood.
319 He had.
320 Robin Hood.
321 That could not.
322 Is.
323 Down a.
325 Me.
326 Wandring.
327 Till I blood letted be.
328 You blood shall letted be.
329 Get down.
330 Burnt. This stanza is omitted in one edition.
332 This line is manifestly impertinent and corrupt. We might read:

is printed by Copland at the end of his edition of the “Mery Geste,” &c., inserted in the present volume. It seems to be composed, certainly with little improvement, partly from the ballad of “Robin Hood and the Curtall Frier” (see before, p. 209), or rather, perhaps, some still older piece on the same subject, and partly from the ancient poem of “Robin Hood and the Potter” (see p. 81). The whole title runs—“Here beginnethe the playe of Robyn Hoode, very proper to be played in Maye games.” It has here received a few corrections from White’s edition, 1634.
This strange and whimsical performance is taken from a very rare and curious publication, intitled “Deuteromelia: or the second part of musicks melodie, or melodius musicke. Of pleasant roundelaies; K. H. mirth, or freemens songs. And such delightfull catches. London: printed for Thomas Adams dwelling in Paules church-yard at the signe of the white lion, 1609.” 4to. Freemen’s songs is supposed to be a corruption of Three men’s songs, from their being generally for three voices. K. H. is King Henry’s. See “Ancient Songs,” ed. 1829, vol. i. p. lxxix., and vol. ii. p. 54, &c.
In the collection of old printed ballads made by Anthony a Wood is an inaccurate copy of this ancient and singular production, in his own handwriting: “This song,” says he, “was esteemed an old song before the rebellion broke out in 1641.” It thereby appears that the first line of every stanza was “to be sung thrice.” Beside the music here given, there are three parts of “Another way,” which it was not thought necessary to insert. {354}
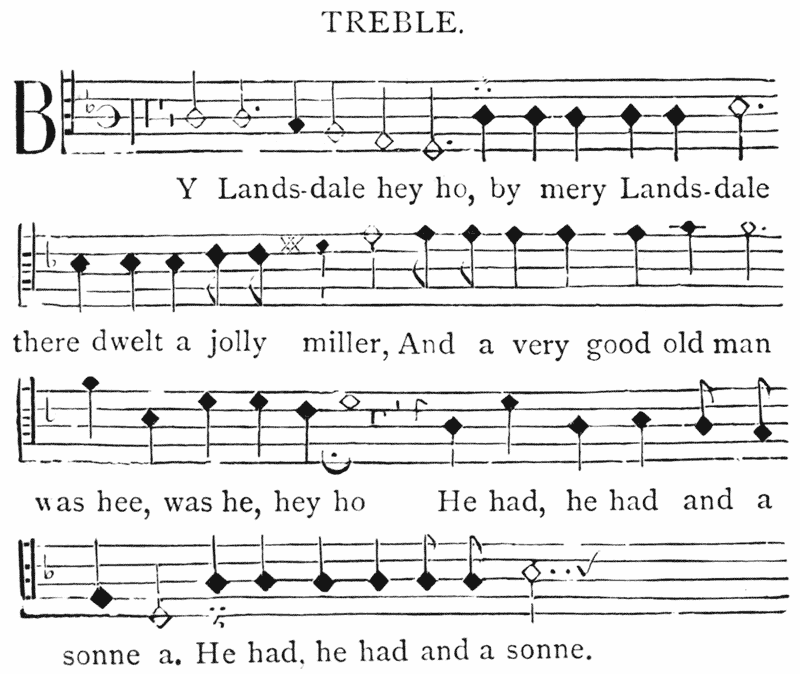
By Lands-dale hey ho, by mery Lands-dale there dwelt a jolly miller, And a very good old man was hee, was he, hey ho He had, he had and a sonne a, He had, he had and a sonne.]
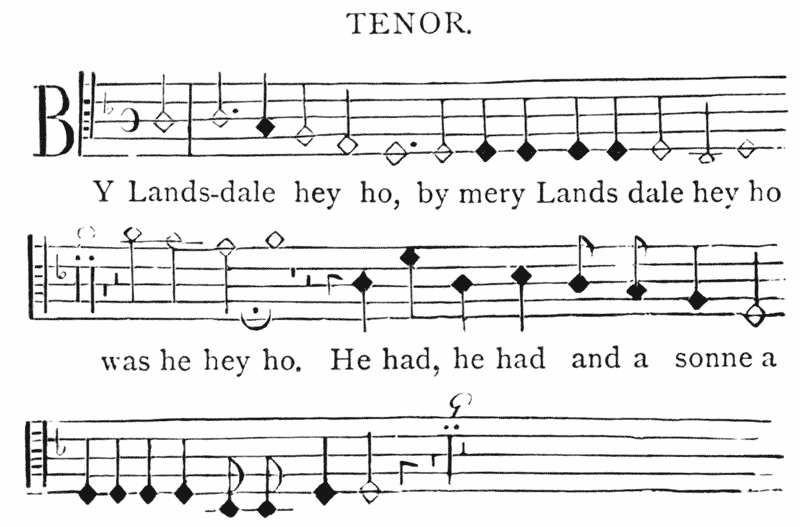
By Lands-dale hey ho, by mery Lands dale hey ho was he hey ho. He had, he had and a sonne a]
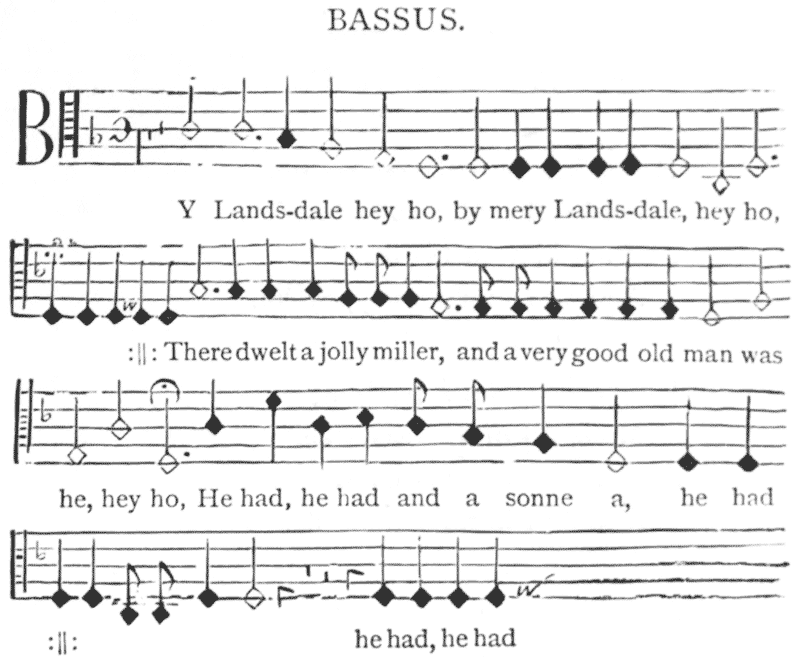
By Lands-dale hey ho, by mery Lands-dale, hey ho, There dwelt a jolly miller, and a very good old man was he, hey ho, He had, he had and a sonne a, he had he had, he had]
from “Pammelia. Musicks miscellanie. Or, mixed varietie of pleasant roundelayes, and delightfull catches, of 3. 4 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. parts in one. None so ordinarie as musicall, none so musical as not to all very pleasing and acceptable. London Printed by William Barley, for R. B. and H. W. and are to be sold at the Spread Eagle at the great north dore of Paules, 1609,” 4to, a work equally scarce and curious with that before cited. This, however, is only the tenor part; but the words of the other parts are very trifling, and relate to different subjects. It is called “A round of three country-dances in one.”

[Robin Hood, Robin Hood, said Little John, Come dance before the queene a: In a red petticote and a greene jacket, a white hose and a greene a.]
These stanzas are supplied by “A musicall dreame, or the fourth booke of ayres, &c. Composed by Robert Iones. London, Imprinted by the assignees of William Barley, and are to be solde in Powles church-yeard, at the signe of the Crowne, 1609,” fo. The music, a composition of little merit or curiosity for the present age, was not transcribed.
This old ballad, referred to in p. 158 of the present volume, is given from a black letter copy in a private collection, compared with and very much corrected by “An antidote against melancholy: made up in pills, compounded of witty ballads, jovial songs, and merry catches, 1661.” The running title of the volume is “Pills to purge melancholy,” which was afterward borrowed by Durfey. {360}
There is a different, but probably much more modern, ballad upon this popular subject, in the same measure, intitled “Arthur o’ Bradley,” and beginning,
In Jonson’s “Bartholomew Fair,” Moon-calf addresses Justice Overdo by this name: “O lord! do you not know him, mistress? ’tis mad Arthur of Bradley that makes the orations. Brave master, old Arthur of Bradley, how do you do? welcome to the fair, when shall we hear you again to handle your matters with your back against a booth, ha? I ha’ been one o’ your little disciples, i’ my days!”
In “The Honest Whore,” by Decker, 1604, Bellafront, on the Duke’s assurance that Matthio shall make her amends and marry her, replies, “Shall he? O brave Arthur of Bradley then!”
This song and its tune, as the editor is informed by his ingenious friend Edward Williams, the Welsh bard, are well known in South Wales by the name of “Marchog glas,” i.e. Green knight. Though apparently ancient, it is not known to exist in black letter, nor has any better authority been met with than the common collection of Aldermary-church-yard. See before, p. 303.
Dr. Pepusch, among other very curious articles of ancient English music, was possessed of a MS. folio (supposed to be still extant), which at p. 15 contained a tune intitled “Robin Hood.” See Ward’s “Lives of the Professors of Gresham College,” 1740 (an interleaved copy, corrected and augmented by the author, in the British Museum). “Robene Hude” is likewise the name of a dance in Wedderburn’s “Complainte of Scotland,” printed in 1549. The following tune is preserved by Oswald in his “Caledonian Pocket Companion.”
 [Listen]
[Listen]This singularly curious and excellent poem, which is probably the earliest extant on the subject, was first printed in the “Ancient Metrical Tales,” edited by the Rev. C. H. Hartshorne (8vo, 1829), from a MS. in the library of University College, Cambridge (F. F. 5. 48), with which it has been since obligingly collated by Frederic Madden, Esq. A few lines are unfortunately rendered illegible by damp.

333 Maister. C.
334 Ell. C.
335 You. you. C.
336 Donee. C.
337 Starte. C.
338 A trul of trust was a common phrase. So in the ancient morality of the iiii elements (Sig. E iij 6):
Again, in Warner’s Albion’s England, 1602:
339 Shefes. C.
340 Ballockes. C.
341 How a potter comes to be decked with so elegant and honourable a chaplet, does not seem easy to account for; unless for the reason given by Chaucer, that
The poet Gower, as represented on his monument in the church of St. Mary-Overy, hath, according to Stow, “on his head a chaplet, like a coronet of foure roses;” and it may be remembered that Copland, the printer of this identical May-game, dwelled “at the signe of the rose garlande.” We see, likewise, that “a rose garlonde” was set up (to be shot through, it is presumed) in the “Lytell Geste of Robyn Hode,” fytte 7, v. 177. Though the fashion of wearing such an ornament was formerly common in France (for which see Chaucer’s “Romaunt of the Rose,” a close translation from the French), and at a still later period in Germany, see “The Hystorye of Reynarde the Foxe,” a translation from the language of that country, and Moryson’s Itinerary, 1617 (part 1, p. 25, and part 3, p. 167), no further instance has been met with of its prevalence in this country.
342 Maryet. C.
343 The. C.
344 Not omitted in W.
345 To do. C. to or so omitted in W.
346 Wedded. C. wed. W.
347 Your. C.
348 And.
349 You shall.
350 When.
351 Come tell.
352 Th’ now. MS.
353 Wone. MS.
354 I pray to. MS.
355 So. MS.
356 Because of Robyn Hode. MS.
357 The. MS.
358 That gode was with ale. MS.
359 Mere. MS.

Abye, [to suffer].
Air, early.
Alderbest, best of all. This phrase, which occurs in Chaucer, is corrupted in De Worde’s edition to “al ther” and “al theyre,” which Coplande has changed to “al of the;” whence it may be inferred that the expression was become already obsolete, and consequently that the poem is of much greater antiquity than 1520: and yet Shakespeare, above half a century after, puts the word Alderliefest into the mouth of Queen Margaret in his Second Part of Henry the Sixth.
Angels, pieces of gold coin, value 10s.
Anker, hermit, anchorite.
Ar, ere.
Asay, Asayed, essayed, tried, proved.
A-sound, in a swoon.
Aunsetters, ancestors.
Avow, Avowe, protestation, confession. “I make myn avow to God,” profess to God: from aveu, F.
Avowe, maintain, verbum juris.
Avowè, founder, patron, protector. See Spelman’s Glossary, v. ADVOCATUS.
Awayte, Awatye me scathe, lie in wait to do me harm.
Awayted, lay in wait for.
Awet, wit, know.
Awkwarde, backward. An awkwarde stroke seems to mean an unusual or out of the way stroke, one which the receiver could not foresee, be aware of, or guard against; a sort of left or back hand stroke. “An auke stroke” is a frequent expression in La Mort d’Arthur.
Ayenst, against.
Baist, Baste, basted, belaboured.
Baith, both.
Bale, mischief, woe, sorrow, misery.
Ballup, p. 306.
Banis, bane, destruction.
Bear, moan, lamentation, outcry.
Bearing, arrow.
Bedene, behind, one after another? {388}
Bedyng, asking. Your bedyng shall be doyn, your invitation shall be complied with.
Beforen, before.
Begeck, Give them a begeck, play them a trick, make fools of them.
Behote, promised.
Benbow, [a bent bow?].
Bent, ii. 84.
Bescro, beshrew.
Bestad, Ferre and friend bestad, far
from home and without a friend. The passage, however, seems
corrupt. Perhaps, indeed, it should be fren (frend or fremd)
bestad, i.e. beset or surrounded by strangers.
(F em
em![]() ,
Saxon.) Thus, in Spenser’s 4th eclogue:
,
Saxon.) Thus, in Spenser’s 4th eclogue:
Again, in Florio’s Worlde of Wordes, 1598: “Alieno, an alien, a stranger, a forraine, a freme.”
Bestead, beset, put to it.
Beth, are, be.
Blate, sheepish or foolish, as we should now say.
Blive, belive, immediately.
Bloschems, blossoms.
Bluter, p. 105.
Blyve, fast, quickly, briskly.
Bocking, pouring, flowing.
Bode, bidden, invited.
Bolt, Bolte, Boltes, Boltys. A bolt was an arrow of a particular kind, used chiefly for shooting at birds; having a round or blunt head. Much’s object, it has been observed, was not to wound, but stun, the monk, and the bolt from its shape was peculiarly adapted to this purpose. In other passages, however, it seems to mean either an arrow in general, or one used for shooting at a mark. “I’ll make a shaft or a bolt on’t,” which Shakespeare has put into the mouth of M. Slender, appears, from Ray’s Collection, to have been a common proverb.
Boote, help.
Booting, p. 98.
Borde, table.
Borowe, Borrow, pledge, surety, bail.
Borowehode, suretyship.
Boskyd, busked, prepared, got ready.
Bottle, a small vessel, of wood or leather, in the shape of a cask, in which shepherds and others employed abroad in the fields carry or keep their drink.
Bottys, buts.
Bou, bow.
Bound, betook, went. Boldly bound away, briskly scampered off.
Bowe, bough. {389}
Bown, ready. Bowne ye, prepare ye, get ready.
Boyt, both.
Breche, breeches.
Breyde, started, stepped hastily.
Breyde, start, quick or hasty step.
Broke, brook, enjoy, use, keep.
Bronde, brand, sword.
Bushement, ambush.
Buske, I wyll me buske, i.e. go, betake myself. Buske you, address or prepare yourselves, make ready.
Bydene, one after another.
Can, did.
Carpe, [to speak].
Cankardly, peevishly, with ill-temper.
Capull hyde, horse hide. Capal or Capul in Irish or Erse is a horse or mare, as Kephyl is in Welsh.
Carel, Carril, carle, old fellow.
Caward, awkward or backward. See Awkwarde.
Cerstyn, Christian.
Chaffar, chaffer, merchandise, commodity.
Chepe, better chepe, cheaper; à meilleur marché, F. Gret chepe, very cheap; à très bon marché.
Chepe, cheapen, buy. Chepyd, cheapened, bought.
Cheys, choose.
Chiven, p. 219.
Chorle, churl, peasant, clown.
Cla’d, scratched.
Clock, cloak.
Clouted, patched.
Cole, p. 66.
Come, (pronounced com) came.
Command, warrant, authority.
Commytted, accounted.
Coresed, p. 20.
Cortessey, courteous. Q. Corteysse.
Cote a pye, upper garment, short cloke; courtepy, Chaucer. See Tyrwhitt’s note, iv. 201.
Coud, knew, understood.
Counsell, “And counsell shall it be,” and it shall be kept secret; in allusion, perhaps, to the oath of a grand juror:—“the king’s counsel, your fellows, and your own you shall keep secret.” The phrase is, however, used by Chaucer:
Covent, convent; whence our Covent Garden.
Cowed, could, knew. Cowed of curteysey, understood good manners. {390}
Crack, boast.
Craftely, skilfully, secundum artem.
Crouse, brisk.
Cun, con, owe, give.
Curn, p. 101.
Curtall, p. 210, 211.
Curteyse, courteous.
Cutters, sharking fellows; such as live by robbery or violence; bravos. So in the old play of Arden of Feversham, h. d. b. l.: “And they are cutters, and may cut your throat.”
Dame, mother.
Dead, certain; so in the common saying, “As dead as Chelsea;” i.e. as certain as a situation in that hospital.
Demed, judged.
Depart, part, separate.
Derne, privy, secret.
Deyell, devil.
Deythe, dight, dressed.
Donne, dun.
Doyt, doth, do.
Dree, hye.
Dreyffe, drive.
Dub, shallow miry pool.
Dung, beaten, overcome.
Durk, dagger.
Dyght, dressed, done.
Dyghtande, p. 69.
Dysgrate, disgraced, degraded. Hath be dysgrate, hath fallen into poverty.
Een, eyes.
Eftsones, hereafter, afterward.
Eild, age.
Elephant, p. 263.
Ender, under.
English wood. If Inglewood Forest be here intended, the Queen is a little out in her geography: she probably means Sherwood, but neither was that in the page’s way to Nottingham, and Barnsdale was still farther north. See Ancient Popular Poetry, 1791, p. 3.
Ere, before.
Eylde, yield.
Eyr, year.
Eyre, heir.
Fail, But fail, without fail, without doubt.
Failyd, wanted, missed.
Fair, fare, ado.
Fare, live.
Farley, fairly, plainly.
Fay, faith. {391}
Fayne, glad.
Fe, fee, wages.
Feardest, fearfulest, most frightened or afraid.
Feders, feathers.
Fend, Fend I godys forbode.
Fende, defend.
Fered, feared, lived.
Ferre, far. Ferre dayes, far in the day; grand jour, F. Ferre gone, long since.
Fette, fetched.
Fetteled him, made him ready, prepared himself, set about. Fettled, Them fettled, attempted, set about.
Feyffe, five.
Finikin, finical, fine, spruce.
Flee, fly.
Flinders, splinters.
Fone, foes, enemies.
Forbode, Godys forbode, ‘prohibition or curse.’ Florio, in his Italian dictionary, 1598, renders the phrase, Adio non piaceia. God forbid, Godes forbode. In A Briefe Conceipte of English Policy, 1581, it is corrupted to “God swarbote.”
Force, care.
Forgone, forego, lose.
Fors, see Force.
Forsoyt, forsooth, truly.
Foryete, forgotten.
Fostere, forester.
Fothe, foot.
Frae, from.
Frebore, free-born, gentle.
Frese, p. 39.
Furmety, [fumenty].
Frere, [friar].
Fynly, goodly.
Gae, go.
Gan, Gan they gone, are they gone, did they go.
Gang, Gange, go.
Gate, Gates, ways, passes, paths, ridings. Gate is a common word in the North for way.—P.
Geffe, given.
General, perhaps the governor, Nottingham still being a garrison town.
Ger, gear, stuff, goods, property, effects.
Gereamarsey, see Gramercy.
Gillore, plenty.
Glen, valley.
God, good, goods, property.
God-a-marsey, God-a-mercy! See Gramercy.
Godde, see God. {392}
Godys forbode. See Forbode.
Gorney, journey.
Goy, joy.
Graff, Oke graff, oak branch or sapling.
Gramercy, thanks, or many thanks; grand mercie, F.
Gree, satisfaction.
Gret, greeted, saluted.
Gripped, grasped, laid hold of.
Grome, a common man.
Hail, All hail, wholely, entirely.
Halds, holds, holding-places, supports.
Halke, perhaps haugh, low ground by the side of a river. See the glossary to Bishop Douglas’s Virgil, v. Hawchis. Halke with Chaucer signifies a corner; but seems here used in opposition to hill.
Halfendell, half.
Hals, neck.
Hambellet, ambleth.
Hansell. The vendor of any wares is said to receive hansel of his first customer; but the meaning of the text, Haffe hansell for the mar, is not understood, unless it can be thought to imply, Give me hansel, i.e. buy of my pots.
Hart of Greece means perhaps no more than a fat hart, for the sake of a quibble between Greece and grease.
Hawt, aught, anything, something.
Hayt, hath.
Held, kept preserved.
Hende, gentle, courteous.
Hent, took, caught.
Hepe, hip, haw, the fruit of the white thorn. So in Gil Morice, a Scotish ballad:—
Her, their.
Het, it.
Het, eat.
Heynd, gentle, courteous.
Heyt war howte, p. 86.
Highed, hyed, hastened.
Hight, What they hight, what they are called.
Holde, keep, held, retained of council.
Holy, wholely.
Holy dame, Our holy dame, p. 250, the Virgin Mary (so called); unless, for our “holy dame” we should read our halidome, which may mean our holiness, honesty, chastity; haligoome, sanctimonia.
Hos, Hus, us.
Hotys, oats.
Housband, Housbonde, manager, husbandman, peasant. {393}
How, hill.
Howt, out.
Hyght, vowed, promised.
Hynde, knave.
I, ay.
Ibent, bent.
Ibonde, bound.
Ichaunged, changed.
Idyght, dight, dressed, prepared, made ready.
Ifedered, feathered.
Ilke, each.
In-fere, together.
Inocked, nocked, notched.
Ipyght, Up ipyght, p. 26.
Iquyt, acquitted, set at liberty.
Iswore, sworn.
Itake, taken.
Japes, tricks.
Ken, know.
Kest, cast.
Kirtle, upper petticoat.
Knave, servant, man.
Kod, quod, quoth, said.
Kyrtell, waistcoat.
Kythe nor kin, acquaintance nor kindred.
Lappe, wrap.
Late, lake, play, game.
Launsgay, a sort of lance.
Leasynge, lying, falsehood.
Lede, train, suite.
Ledesman, guide.
Lee, plain.
Lefe, willing. Whether he were loth or lefe, whether he would or not.
Leffe, leave, left.
Leffes, leaves.
Lende, meet, encounter.
Lene, lend.
Lere, learn.
Lere, cheek.
Lese, lose.
Let, omit, hinder, hindered.
Leugh, laughed.
Lever, rather.
Lewtè, loyalty, faith, truth; leauté, F.
Leythe, light.
Ligge, lay.
Lin, stop, stay.
Lithe, attend, hear, hearken. {394}
Loffe, love.
Lore, lost.
Lough, Loughe, Low, laughed.
Lowe, “a little hill.”—P.
Lown, villain, knave, base fellow.
Lust, desire, inclination.
Lyght, light; or, perhaps, for lyte, little.
Lynde, Lyne, the lime or linden tree; or collectively lime trees, or trees in general.
Lyth, see Lithe.
Lyveray, livery, habit, delivery: the mess, portion, or quantity of provisions delivered out at a time by the butler was called a livery.
Masars, cups, vessels.
Masterye, “a trial of skill, high proof of skill.”—P.
Mair, more.
Maney, see Meyne.
May, maid.
Me, That ever yet sawe I me, a gallicism; que jamais j’ai vu moi.
Meal, oat-meal.
Meal-poke, meal-bag, bag in which oatmeal is put.
Meat-rife.
Mede, To quyte hym well his mede, to reward him to some purpose.
Medys, midst, middle.
Meede, reward.
Mesh, All to mesh, to a mash or jelly.
Met, Mete, measured.
Methe, meat.
Meyne, attendants, retinue; mesnie, F.
Meythe, might.
Mickle, much, great, very.
Mister, need. It is misters in the original.
Mo, more.
Molde, earth.
Mot, Mote, might, may.
Mote, meeting, assembly, court, audit.
Mountenaunce, amount, duration, space.
Mow, mouth.
Mowe, may.
Muckle, see Mickle.
Myrthes, mirth, merriment. A man that myrthes can, a minstrel, fiddler, juggler, or the like.
Myster, need.
Nane, none.
Nar, nor, than.
Ner, ear. So in “The Romaunt of the Rose:”
Ner, (ne wer it), were it not.
Nip, p. 100.
Nips, p. 101.
Nobellys, nobles. The noble was a gold coin, value 6s. 8d.
Nombles, Numbles, entrails; those parts
which are usually baked in a pie: now, corruptly, called humbles
or umbles: nombles, F. Thus we say, an Adder, an Apron, an
Ouche, instead of a Nadder,
(Na![]()
![]()
 e),
a Napron, a Nouche:
the n being, through ignorance, transferred to the article. The
reverse has happened in the words A newt, which should be written
An ewt: a mistake the more remarkable as we say and write An
eft; both from the same root:
e),
a Napron, a Nouche:
the n being, through ignorance, transferred to the article. The
reverse has happened in the words A newt, which should be written
An ewt: a mistake the more remarkable as we say and write An
eft; both from the same root:
![]()
![]() e
e![]() ,
Saxon.
,
Saxon.
Obeyedores, [obediener].
Okerer, usurer.
Or, [en].
Os, us.
Outdone, undone.
Owthe, out.
Paid, beat, beaten.
Palmer. A palmer was, properly, a pilgrim who had visited the Holy Land, from the palm-branch or cross which he bore as a sign of such visitation: but it is probable that the distinction between palmers and other pilgrims was never much attended to in this country. The palmer in the text seems to be no more than a common beggar; as is, likewise, the one in the romance.
Partakers, assistants, persons to take thy part.
Passe, extent, bounds, limits, district; as the Pas de Calais. Copland’s edition reads compas.
Pauage, Pavag, Pavage, Pawage, a toll or duty payable for the liberty of passing over the soil or territory of another: paagium, L.
Pay, content, satisfaction, money.
Peces, p. 32.
Pecocke, With pecocke well ydight, handsomely dressed with peacock feathers. Thus Chaucer, describing his “squire’s yeman:”
In a little treatise of “The Hors, the Shepe, and the Ghoos,” printed by Caxton, it is said—
Pinder. The pinder is the pounder or pound-keeper; the petty officer of a manor, whose duty it is to impound all strange cattle straying upon the common, &c. {396}
Plucke-buffet, p. 75.
Polle, pull.
Poke, bag.
Preke, prick, a piece of wood in the centre of the target.
Prese, company.
Prest, ready, ready to go.
Puding-pricks, skewers that fasten the pudding-bag.
Pyne, Goddes pyne, Christ’s passion or crucifixion.
Quequer, quiver:
![]() ocu
ocu ,
Saxon.
,
Saxon.
Queyt, quit, recompense.
Qod, quoth, says, said.
Raked, walked apace.
Ray, Battle ray, Battle-array. The same expression occurs in The Tragicall History of Didaco and Violenta, 1567:
Ray, array, put in order.
Raye. Cloth of ray was cloth not coloured or dyed. It is mentioned in many old statutes in contradistinction to cloth of colour. See 17 E. 3. c. 1, 7 H. 4. c. 10, 11 H. 4. c. 6, 1 R. 3. c. 8. The “reied or striped cloth” (Stow’s Survay, 1598, p. 436, 430) must have been very different.
Reachles, careless, regardless, unobservant.
Red, clear.
Reuth, pity, compassion.
Reve, taken by force.
Reves, bailiffs, receivers.
Ripe, cleanse. Riped, cleansed.
Rod, poles, perches. A rod, pole, or perch is usually sixteen feet and a half, but in Sherwood forest (according to Blount) it is 21 feet, the foot there being 18 inches.
Rode, rood, cross.
Rung, staff.
Ryall, royal.
Ryalty, royalty.
Ryghtwys, righteous, just.
Sack, a kind of Spanish wine, perhaps sherry, formerly much drank in this country; very different, at least, from the sweet (or canary) wine now so called.
Sair, sore.
Salved, (salued?) saluted. The word salewed, in this sense, occurs repeatedly in The Hystorye of Reinard the Foxe (Pinson’s edition); and (vide tamen Salvid in the Gesta Romanorum, MS. Har. 7333, No. 48) in that of “Kynge Ponthus of Galyce,” 1511. “Salue,” F. i. “Salewe,” F. ii. K. Ponthus.
Scathe, harm.
Schetyng, shooting.
Schomer, summer. {397}
Sclo, slay.
Scop, scalp, pate.
Scoper, supper.
Scouth, p. 105.
Serefe, Screffe, sheriff.
Se, vide See.
Seche, seek.
See, regard, protect. The same phrase occurs in Chaucer’s Troilus and Cresside:
Seker, sure.
Selerer. The cellarer (celerier, cellararius, or cellarius) was that officer who furnished the convent with provisions, cui potus et escæ cura est, qui cellæ vinariæ et escariæ præest, promus (DU CANGE). He appears to have been a person of considerable trust, and to have had a principal concern in the management of the society’s revenues. See Spelman’s Glossary, Fuller’s Church History, &c.
Semblaunte, semblance, appearance.
Sene, see.
Sete, p. 25.
Sets. Sets with Roben Hood such a lass! probably such a lass would suit or become him well; but the passage is either singular or corrupt.
Sette, mortgaged.
Shawe. Shaw is usually explained by little wood, but greenwood little wood would be ridiculous tautology; it may therefore mean shade, which appears its primitive signification: Scuƿa, Saxon. See p. 327, ver. 5. Shaws, “little woods.”—P.
Shende, hurt, annoy. Shente, hurt, wounded.
Shet, shut.
Shete, shoot.
Shone, [shoes].
Shope, shaped, made.
Shraddes. See the note.
Shrewde, Shrewed, unlucky.
Shrift, confession.
Shroggs, “shrubs, thorns, briars. G. Doug. scroggis.”—P.
Shyt, shut.
Skaith, hurt, harm. They feared for his skaith, i.e. for the harm it might do them.
Slack, low ground.
Slade, “a slip of greensward between plow-lands, or woods, &c.”—P.
Slawe, Slone, slain.
Sle, Sloo, slay.
Somers, sumpter-horses.
Sorowe, sorry. {398}
Sothe, sooth, truth.
Sound, see A-sound.
Soyt, sooth, truth.
Spear, ask. Speer’d, asked, inquired.
Stalward, Stalworthe, stout, well made.
Stane, stone.
Stark, stiff.
Stede, time.
Steven. At some unsett-steven, at some unlooked for time, by some odd accident, by mere chance, voice.
Stime, spark, particle or ray of light.
Stint, stop.
Sto’, store, p. 219.
Strang, strong.
Strete, lane, path, way.
Sweaven, dream.
Sweer, p. 100.
Syne, after, afterward, then.
Syth, afterward.
Takles, arrows.
Takyll, arrow.
Tarpe, p. 68.
Tene, grief, sorrow, distress, vexation.
Tene, grieve.
The, thrive, prosper.
Thes, thus, this.
Thos, thus.
Throwe, space.
To-broke, broken.
To-hande staffe, two-hand staff, quarter-staff.
Tortyll, wreathed, twined, twirled, twisted; tortillé, F.
Tray, anger.
Tree, staff.
Treyffe, thrive.
Trow, true.
Trowet, troth.
True, trow, believe.
Trystell, Trystyll.
Tynde, Tyndes, tines, antlers, the pointed branches that issue from the main beam of a stag. “In Ynglond ther ys a shepcote, the wyche schepekote hayt ix dorys, & at yeuery dor stondet ix ramys, & every ram hat ix ewys, & yevery ewe hathe ix lambys, & yevery lambe hayt ix homes, & every horne hayt ix TYNDES: what ys the somm of all thes belle?” (MSS. More, Ee. 4. 35.)
Unketh, uncouth, strange.
Unneth, scarcely.
Up-chaunce, by chance.
Venie, Brave venie, merry vein, jovial humour. {399}
Wan, Wonnynge wan, dwelling-place.
Wan, got.
Warden-pies. Wardens are a species of large pears. In Shakespeare’s Winter’s Tale, the clown, enumerating the articles he had to provide for the sheep-shearing feast, says he “must have saffron to colour the warden-pies.”
Warse, worse.
Was, wash. “And afterward the justices arise and wasse, and geffe thanks unto the new serjaunts forther gode dyner” (Origines Juridiciales, p. 116). This ceremony, which, in former times, was constantly practised as well before as after meat, seems to have fallen into disuse on the introduction of forks, about the year 1620: as before that period our ancestors supplyed the place of this necessary utensil with their fingers.
Watchman, a probable mistake for Waithman, outlaw. See Notes, &c., p. lxxiii.
Wed, Wedde, pawn, pledge, or deposit. To wedde, in mortgage. Lay my life to wedde, pawn my life.
Weele, well.
Welt, Welt them at his wyll, did as he pleased with them, used them at his pleasure.
Wed, Wende, go, hye.
Wenest, thinkest.
Wenion, Marry gep with a wenion! “He shoulde have bene at home a preaching with a waniant,” says Bishop Latimer, Sermons before King Edward VI., p. 35. This phrase, with a wannion, is common in old plays, but, though its meaning be obvious, even Mr. Steevens is unable to “explain the word at the end of it” (Shak. xiii. 440). It is now corrupted to with a vengeance.
Went, wended, gone.
Werschep, worshipped, reverenced, respected.
West, wist, known.
Wete, know.
Whang, Leathern whang, leather thong or string.
Whereas, where.
Whute, whistle.
Wigger wand, wicker wand.
Wight, Wighty, strong. N.B. The latter word seems everywhere a mistake for the former.
Wilfulle, doubtful.
Win, see Wen.
Win, get.
Wist, wis, trow, believe.
Wist, knew.
Wode, mad.
Wodys, woods.
Wolwarde, wearing a flannel shirt, by way of penance. See Steeven’s Shakespeare, 1793, v. 360. {400}
Won, dwell.
Wonest, dwellest.
Woodweele, “the golden ouzle, a bird of the thrush kind.”—P.
Worthe, Wo worthe the, woe be to thee.
Wrack, ruin, destruction.
Wroken, wreaked, revenged.
Wyght, strong, stout.
Wynne, go.
Wys, trow; there is no modern word precisely synonymous.
Wyte, Wytte, know.
Y, I.
Yede, Yeed, went.
Yeff, if.
Yeffell, evil.
Yeft, gift.
Yemenry, yeomanry. Thow seys god yemenry, thou speakest honestly, fairly, sensibly, like a good yeoman.
Yend, yon.
Yeomandree, Yeomandry, yeomanry, followers.
Yerdes, rods.
Yever, ever.
Yfere, together.
Ylke, same. Ylke same, very same.
Ynowe, enough.
Yode, went.
Yole, Christmas.
Yonder, under.
Yong men, yeomen (which is every where substituted in Copland’s edition). See Spelman’s Glossary in the wordes Juniores, Yeoman; Minshen’s Guide into Tongues, in the latter word; Tyrwhitt’s edition of the Canterbury Tales, iv. 195; Shakespeare’s Plays, 1793, xiv. 347.
Original spelling and grammar have been generally retained, with some exceptions noted below. Original printed page numbers are shown like this: {52}. Footnotes have been relabeled 1–359, and moved from within paragraphs to the ends of chapters. The transcriber produced the cover image and hereby assigns it to the public domain. Original page images are available from archive.org—search for "odcollectrobinho00ritsrich".
This ebook transcription includes five midi format audio files, which permit listening to a representation of the music printed in the original book. A midi file is not a recording of audio. It is instead a set of instructions that are interpreted by your own software, so that what you hear may be different from what the transcriber heard. Sadly, many e-reading devices that use the epub or mobi e-book format don't support links to external files, which means that readers using such devices won't be able to conveniently hear or download the mobi files. In that case, the html edition of the ebook must be consulted. Also, some html browsers don't automatically play MIDI files when the link is clicked. The user may have to adjust some browser settings, or install a plugin, or if the click downloads the file, then just go find the downloaded file and open it.
 ðe
ðe
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Robin Hood, by Joseph Ritson
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK ROBIN HOOD ***
***** This file should be named 56926-h.htm or 56926-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/6/9/2/56926/
Produced by MWS, RichardW, and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net. Music transcribed
by Linda Cantoni. (This file was produced from images
generously made available by The Internet Archive.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.